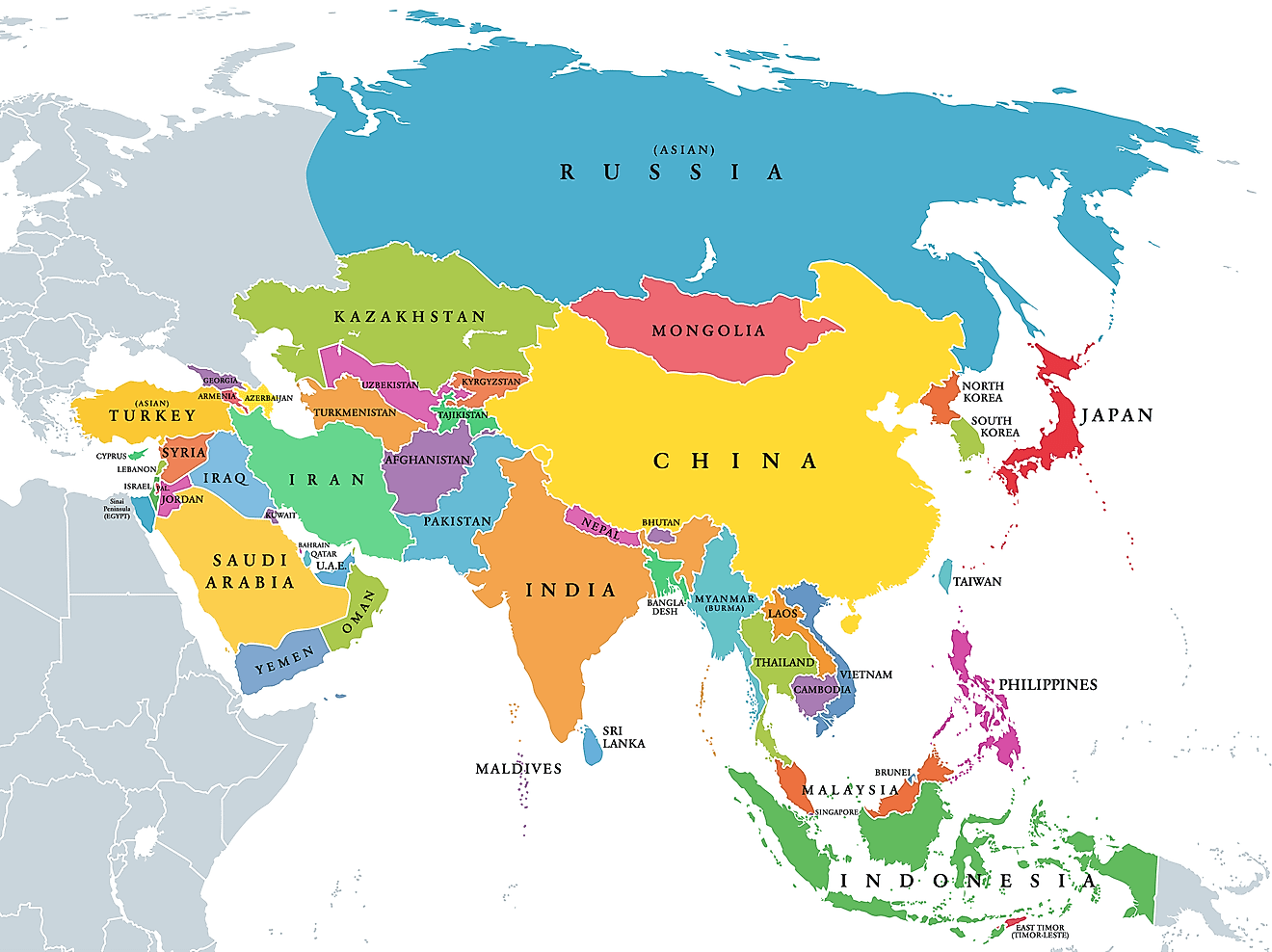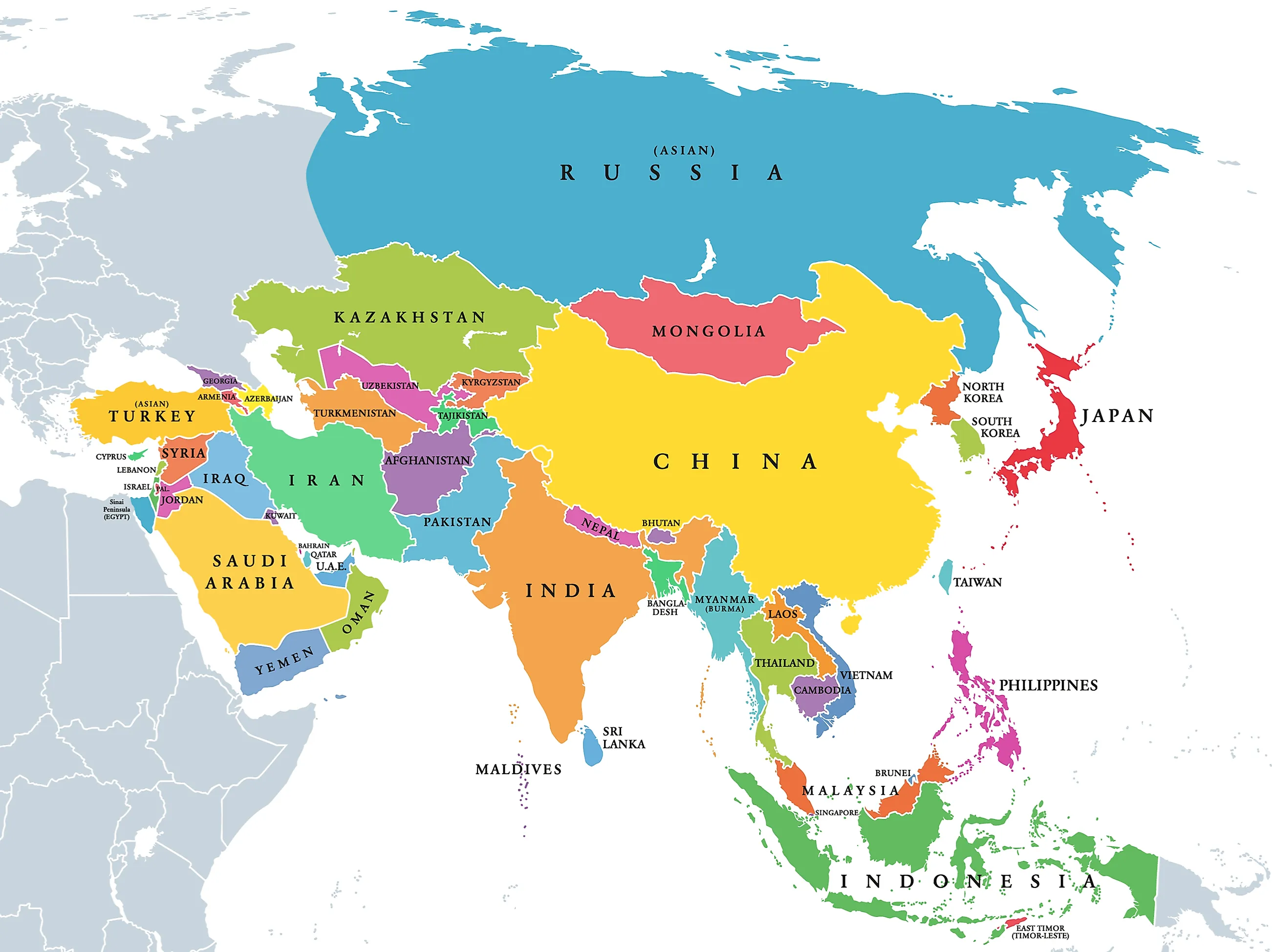
What Are The Five Regions Of Asia?
Asia is the world's largest continent in terms of land area and population. It covers around 17 million square miles and is home to over 4.5 billion people. Asia consists of 48 countries, three of which are transcontinental. Given its large size, Asia has been subdivided based on many factors, including cultural, political, and physiographical.
Physiographically, there are five major regions of Asia: Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Western Asia. Another region can be defined as North Asia, including the bulk of Siberia of Russia and the northeastern parts of Asia.
The five main divisions of Asia have been mentioned in detail below.
The Five Regions Of Asia
| Region | Population | Land Area |
|---|---|---|
| Central Asia | 77 million | 2,487,629 km2 |
| East Asia | 1.69 billion | 7,356,459 km2 |
| South Asia | 1.99 billion | 3,218,688 km2 |
| Southeast Asia | 684 million | 2,792,406 km2 |
| Western Asia | 290 million | 3,886,565 km2 |
Central Asia (Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan)
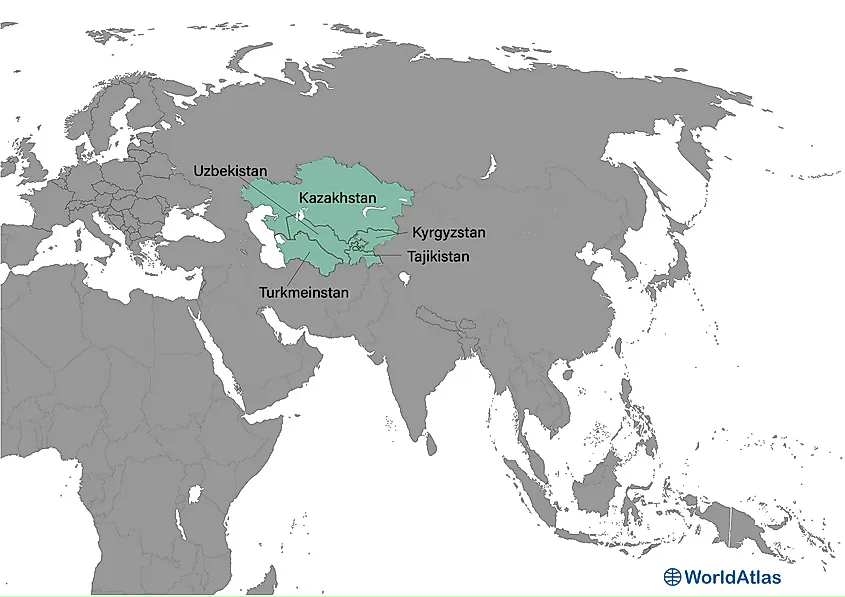
Central Asia is west of China, south of Russia, and north of Afghanistan. The western border of this region runs along the Caspian Sea.
Central Asia is politically divided into five countries: Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Kyrgyzstan. Given that the name of each of these countries ends in "-stan," Central Asia is sometimes informally referred to as "The Stans." The region covers 2,487,629 square kilometers and has a population of just over 77 million individuals.
Central Asia played an essential role in the transportation of goods between China and Europe during the Silk Road trading era.
Scientifically, it is a living laboratory of continental collision: the Indian Plate’s ongoing push against Eurasia uplifts the snow-clad Pamir, Tien Shan, and Altai ranges, generating frequent magnitude-7 earthquakes and hosting over 15,000 glaciers. Central Asia spans vast steppe plains and harsh deserts like the Karakum and Kyzylkum. The Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers carve fertile valleys before draining toward the rapidly receding Aral Sea, with the Caspian lowlands.
East Asia (China, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Japan, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Macau)
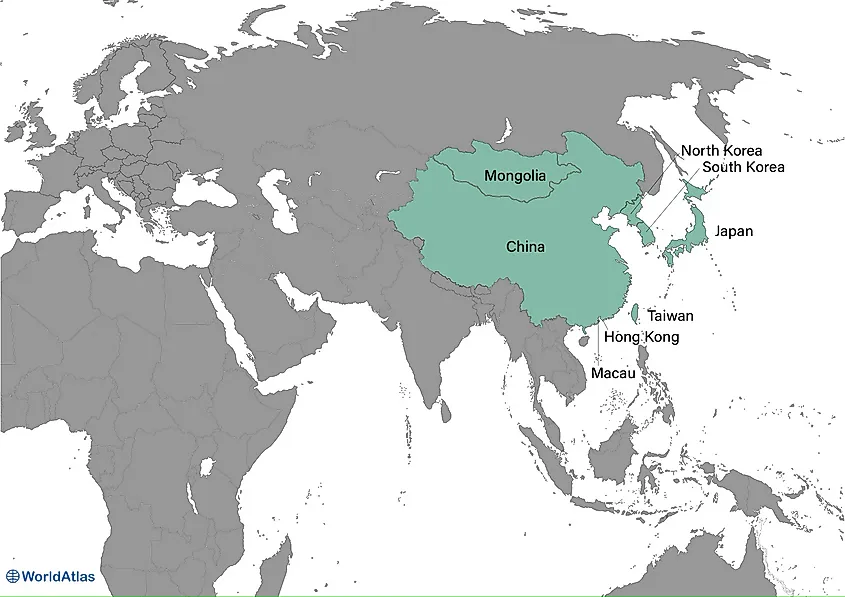
East Asia, one of the five regions of Asia, is located east of Central Asia, with its eastern border running along the East China Sea.
East Asia is politically divided into five sovereign states—China, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Japan— and three administrative regions—Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Macao. This region covers a total area of 7,356,459 square kilometers and has a population size of more than 1.69 billion, representing 22% of the global population and 38% of Asia's total population. Many residents of East Asia are concentrated in major metropolitan areas such as Beijing and Tokyo.
The geography of East Asia varies depending on the zone. The inner continental area experiences a temperate climate, while the arid Gobi desert covers Mongolia. China, the largest country in the region, is home to mountains and plateaus, while thousands of islands and coastlines characterize Japan. East Asia manufactures some of the most advanced technologies in the world, which fosters economic development.
South Asia (Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, India, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, the Maldives, Iran)
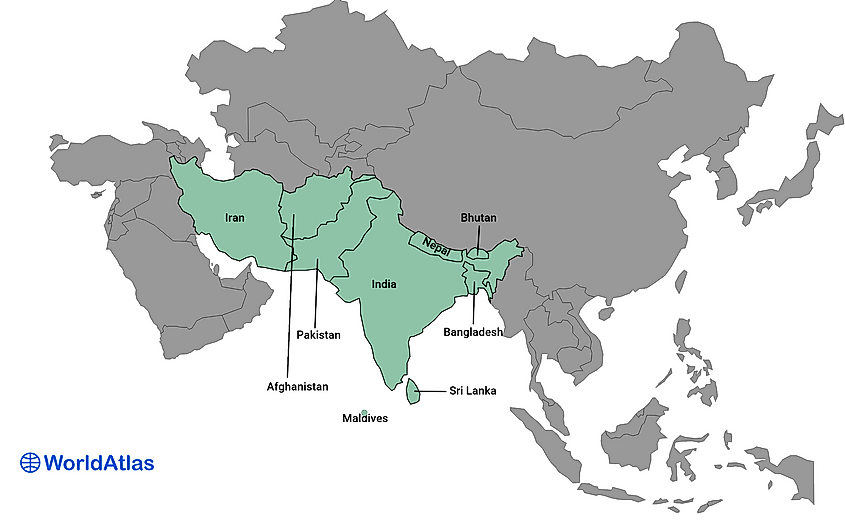
South Asia has a peninsula-like shape bordered by three bodies of water: the Indian Ocean to the south, the Bay of Bengal to the east, and the Arabian Sea to the west.
The region includes the Indian subcontinent and surrounding countries. South Asia is politically divided into nine autonomous countries: Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, India, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Bhutan, Nepal, Iran, and the Maldives. The region covers roughly 3,218,688 square kilometers and has a population of more than 1.99 billion, nearly a quarter of the global population. Additionally, South Asia is the most densely populated area in the world.
South Asia stretches from the snow-clad Himalaya, Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges across the fertile Indo-Gangetic plain to tropical peninsulas and island archipelagos in the Indian Ocean. The region encompasses the arid Thar Desert, lush monsoon-fed Western Ghats and deltaic lowlands like the Sundarbans.
Southeast Asia (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor Leste, Vietnam)
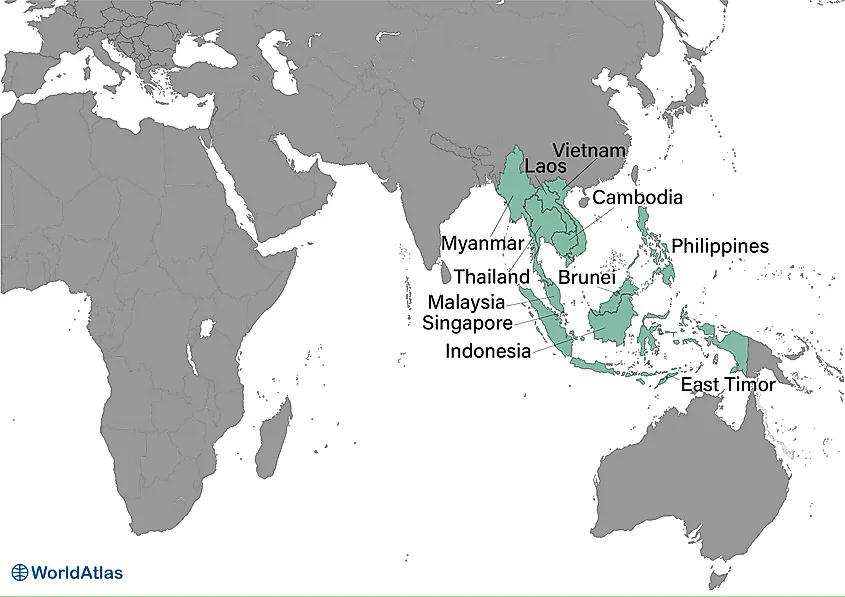
Southeast Asia is located north of Australia, south of East Asia, west of the Pacific Ocean, and east of the Bay of Bengal. It encompasses several island and archipelago nations that stretch between the northern and southern hemispheres, making it the only Asian region located on both sides of the equator.
Southeast Asia is politically divided into 15 countries and territories: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor Leste, and Vietnam.
Southeast Asia covers a total area of 2,792,406 square kilometers and has a population size of more than 684 million. A large number of archipelagos characterize the geography of Southeast Asia. The Indonesian Archipelago is the largest in the world and is home to the largest number of active volcanoes in the world. The region's importance in global trade began during the spice trade, which started before European exploration. Today, the economy of Southeast Asia is rapidly developing. Indonesia is considered the largest economy in the region and is East Asia's only member of the G20.
Western Asia (Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkey, Cyprus, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Iraq, Oman, Yemen, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, Saudi Arabia)
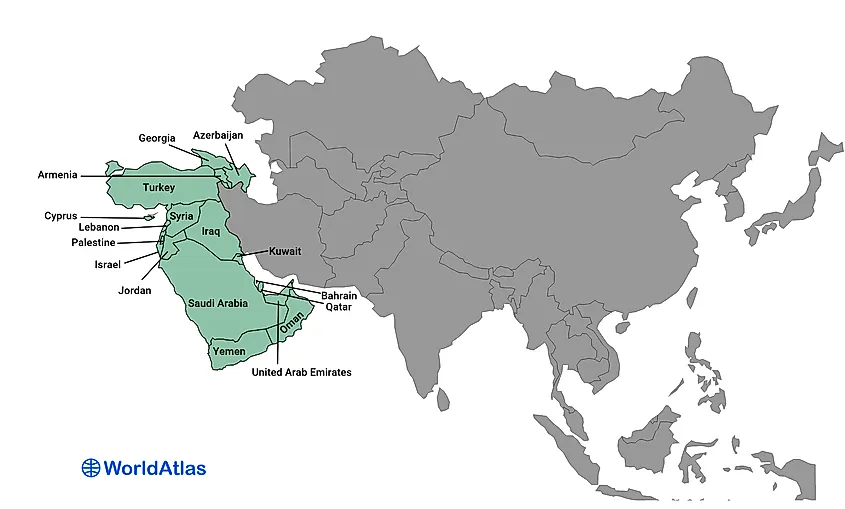
West Asia is located between Central Asia and Africa, south of Eastern Europe. The majority of the region is often referred to as the Middle East, although it geographically excludes the mainland of Egypt (which is culturally considered a Middle Eastern country). West Asia is politically divided into 18 states: Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkey, Cyprus, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Oman, and Yemen. It also includes the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. The region covers around 3,886,565 square kilometers and has a population of 290 million.
An arid desert environment covers a large area of the region. However, West Asia does have several points of access to large bodies of water, including the Black Sea, Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea, Red Sea, Caspian Sea, Mediterranean Sea, and the Aegean Sea.
Asia defies one-size-fits-all descriptions. From ultracontinental steppes to equatorial archipelagos, its five (sometimes six) regions knit 4.5 billion lives into a single, restless tapestry. Understanding their contrasts, population density versus empty desert, monsoon deluge versus water scarcity, illuminates trade, climate policy and cultural exchange far beyond the continent. As Asia’s cities swell and its resources are tapped, the map you’ve explored becomes not a boundary chart but a preview of humanity’s shared future.