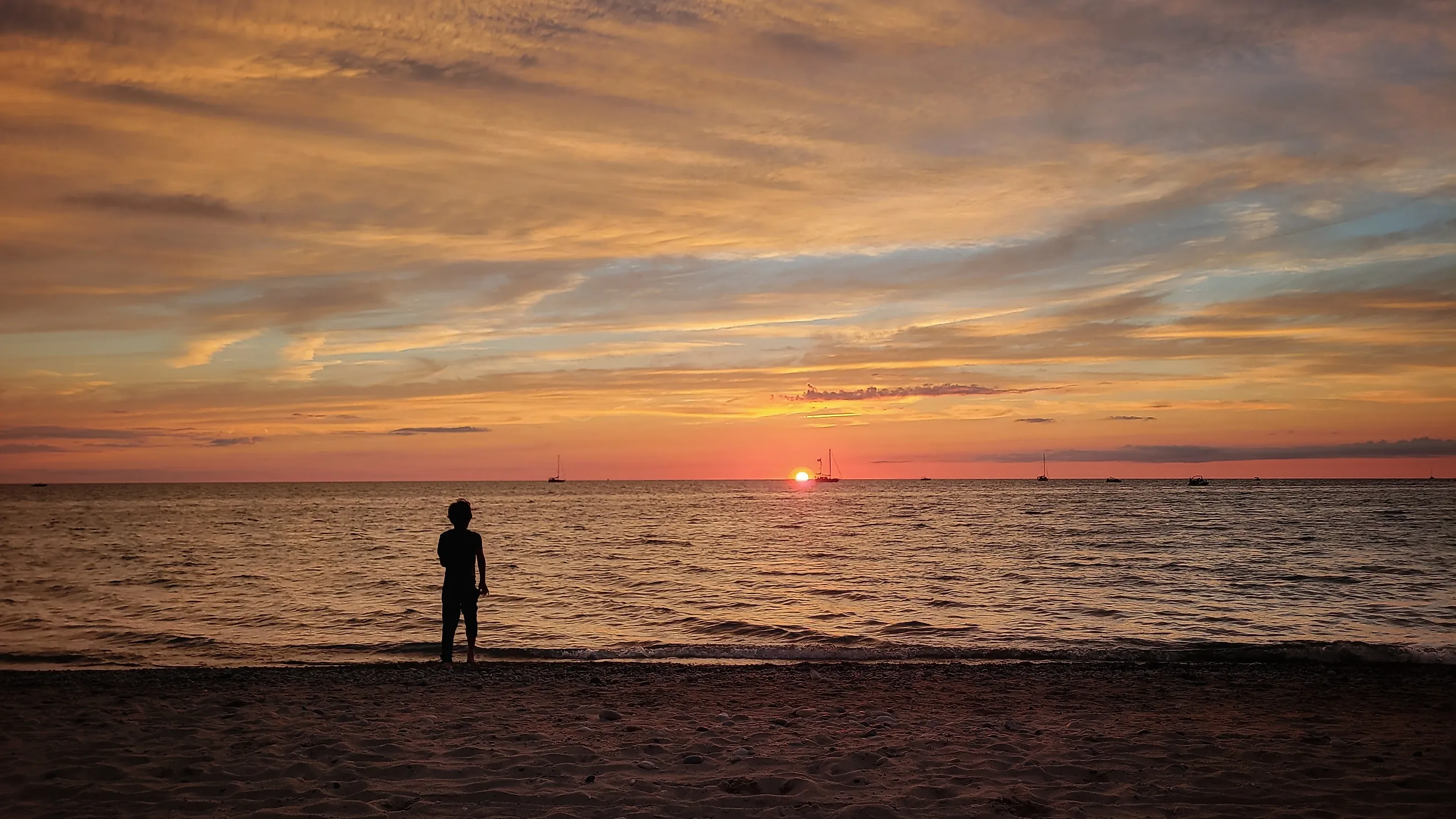
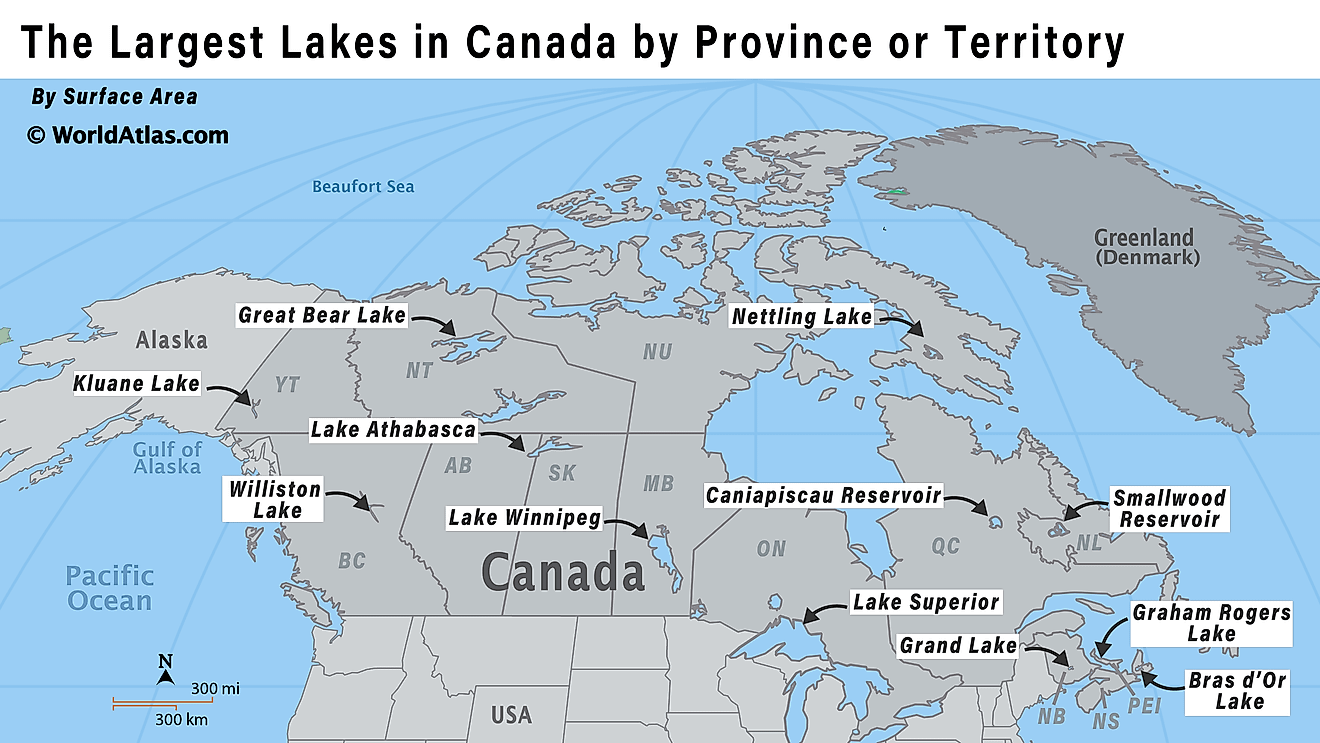
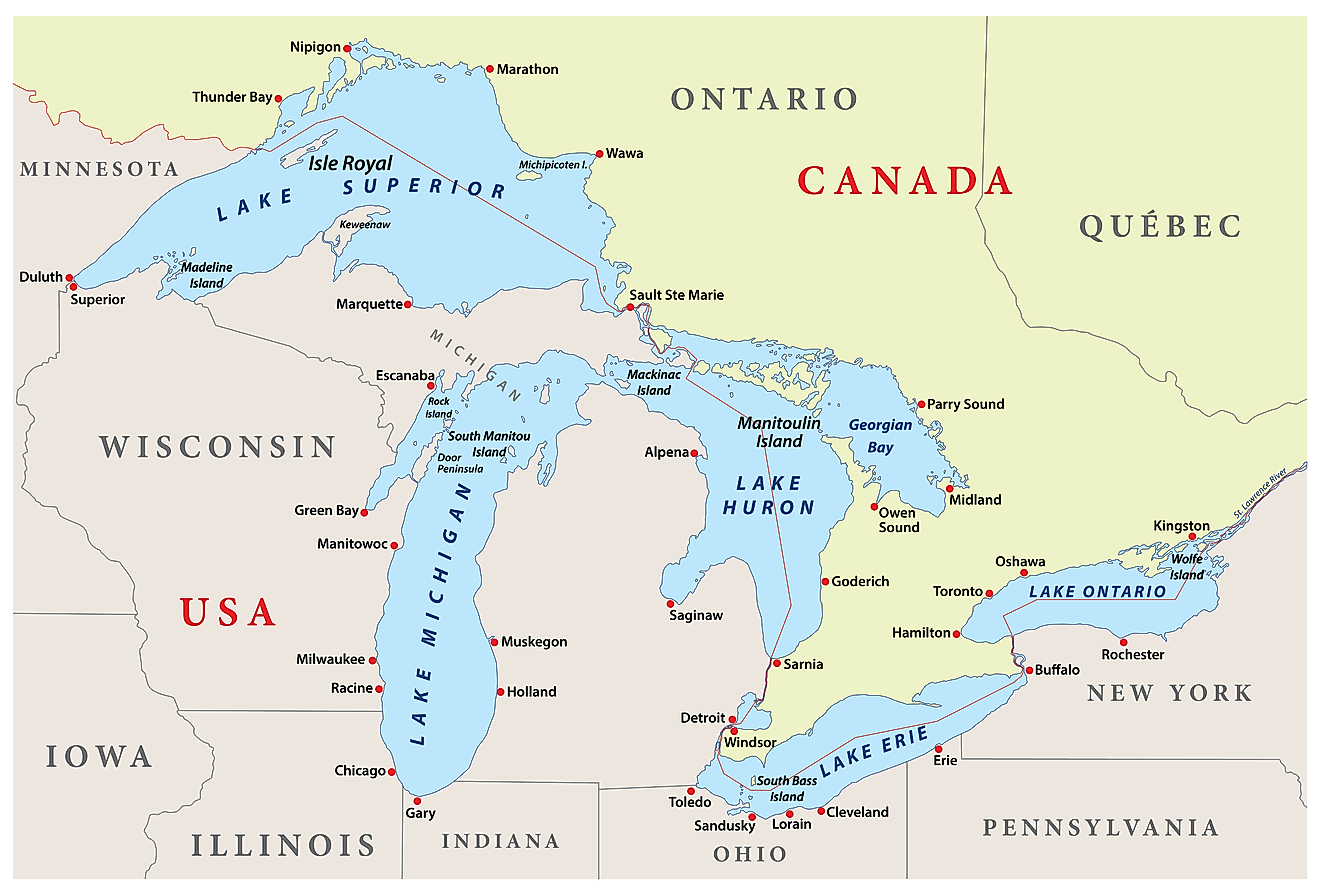
The Great Lakes Ranked by Coastline Length
The Great Lakes — Superior, Huron, Michigan, Erie, and Ontario — form the largest chain of freshwater lakes in the world, spanning eight US states and the Canadian province of Ontario in east-central North America. Together, they contain nearly 10,000 miles (16,000 kilometers) of shoreline and support diverse ecosystems, recreational opportunities, and water resources for millions of people.
Lake Huron has the longest coastline, including islands, followed by Superior, Michigan, Erie, and Ontario. This ranking lists all five lakes by total coastline and highlights their unique geography — from rocky headlands and sandy beaches to wetlands and dunes that support thousands of plant and animal species — as well as other notable features.
1. Lake Huron: 3,830 miles (6,164 kilometers)
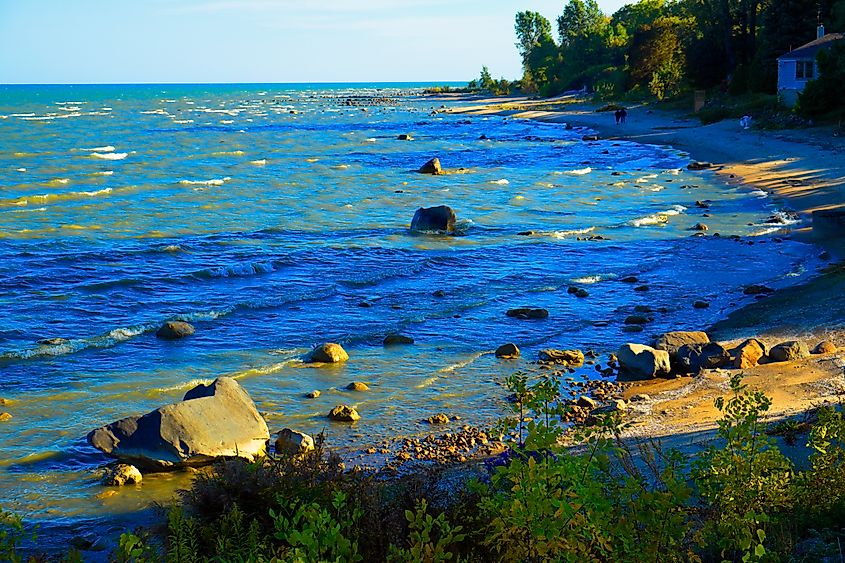

Lake Huron is the second-largest of the Great Lakes and the fourth-largest lake in the world by surface area. However, at 3,830 miles (6,164 kilometers), it has the longest shoreline of the Great Lakes, with coastlines touching Michigan to the west and Ontario to the north and east.
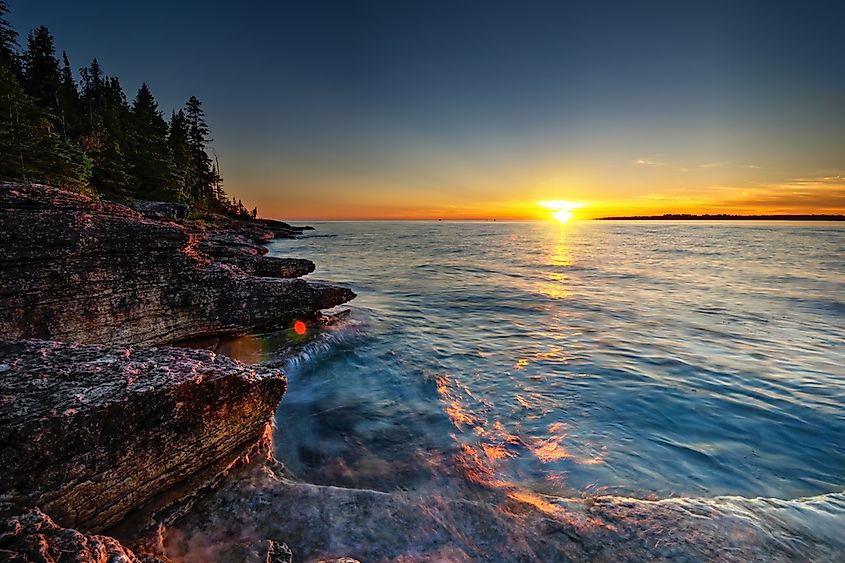

Its large shoreline is attributed to its many islands, of which it has the most of any of the lakes. This includes Manitoulin Island, which is the world’s largest freshwater island and has over 100 lakes of its own. Lake Huron’s coastline is characterized by rocky shores made up of the Canadian Shield on the north and east coast. On Huron’s southern shore, glacial deposits of sand and gravel have created rare sand dune systems. These dunes are a habitat for rare and endangered plant species.
2. Lake Superior: 2,726 miles (4,385 kilometers)
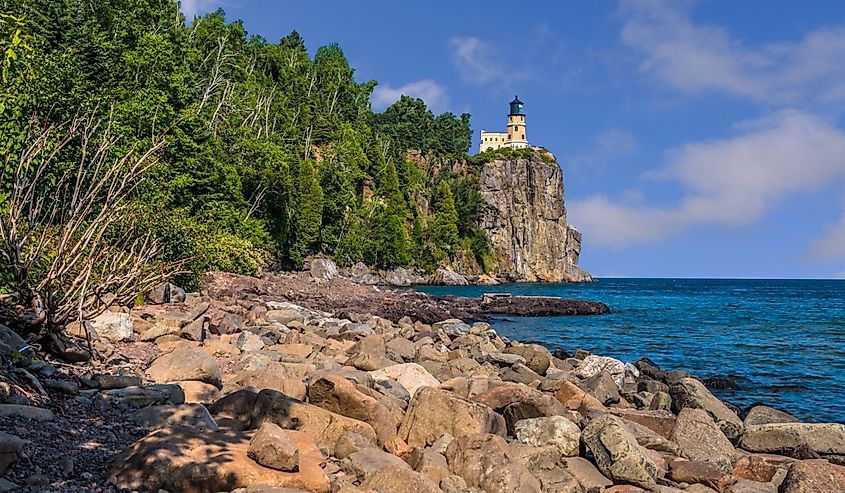

Lake Superior is the largest of the Great Lakes by both surface area and water volume; it's also the most northwesterly of the Great Lakes. It has a coastline on Ontario to the north and east, Wisconsin and Michigan to the south, and Minnesota to the west. Lake Superior’s 2,726 miles (4,385 kilometers) of coastline is the longest undeveloped coastline of the Great Lakes, with less than 5% of developed shoreline.
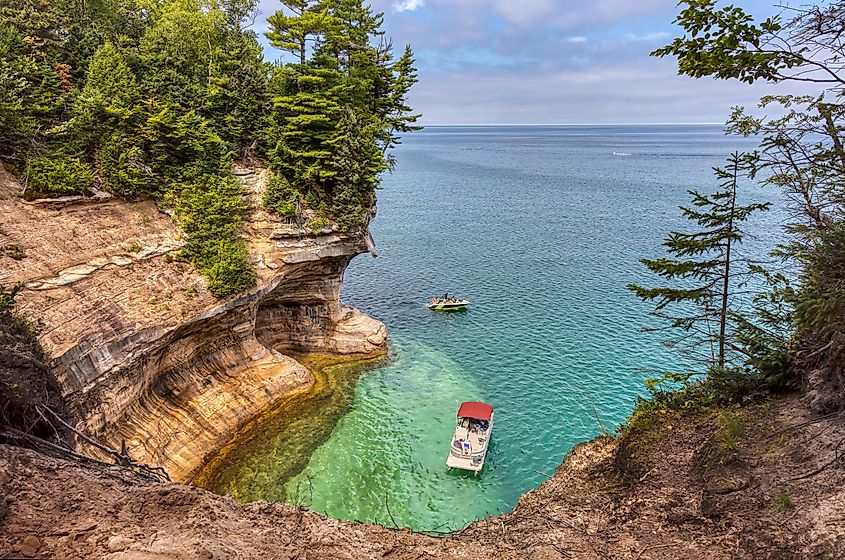

Lake Superior’s shores include the Kakagon Sloughs on Wisconsin’s Bad River Reservation, one of the last remaining extensive coastal wild rice marshes in the Great Lakes region, an ecologically and culturally significant habitat. The coast is covered by some of the world’s oldest rocks, which date back over 2.7 billion years, and colorful sandstone cliffs up to 656 ft (200 m) in height. Other features include sea caves, large islands, white sandy beaches, and rocky outcrops.
3. Lake Michigan: 1,640 miles (2,639 kilometers)
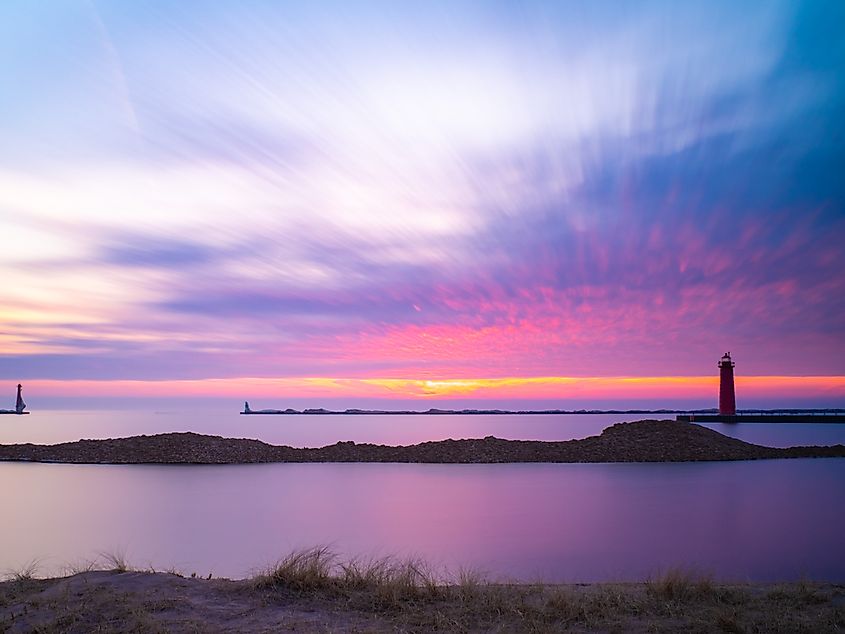

Lake Michigan is the third-largest of the Great Lakes and the only one entirely within the United States. It has a coastline on Michigan to the north and east, Indiana to the southeast, Illinois to the southwest, and Wisconsin to the west. Lake Michigan’s 1,640 miles (2,639 kilometers) of coastline has more coastal wetlands than any other of the Great Lakes.
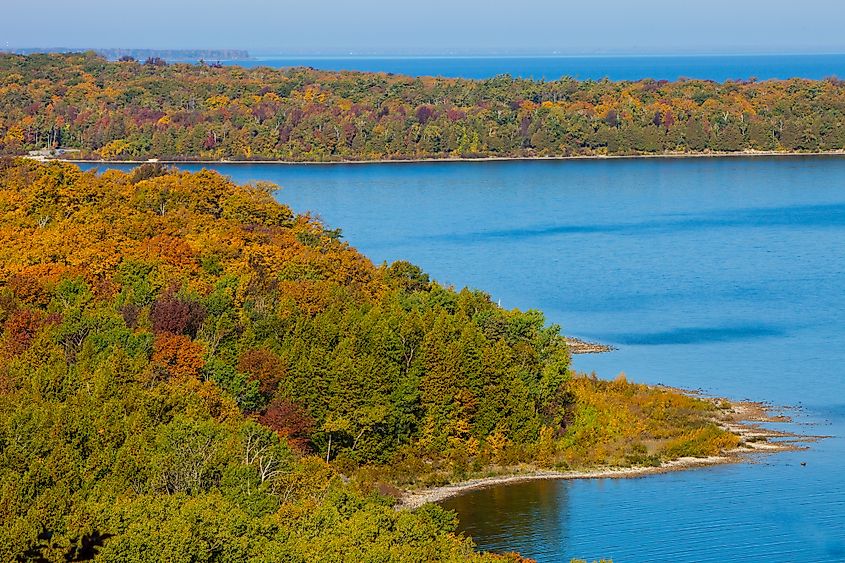

Its coastline is composed of forests, sandy beaches, bluffs, and limestone bedrock. The northern portion particularly features Silurian dolomite rock, believed to be over 400 million years old, whereas the southern portion is characterized by large sand dunes, moraines, and drumlin fields formed by the last glacial retreat over 3,000 years ago.
4. Lake Erie: 871 miles (1,402 kilometers)
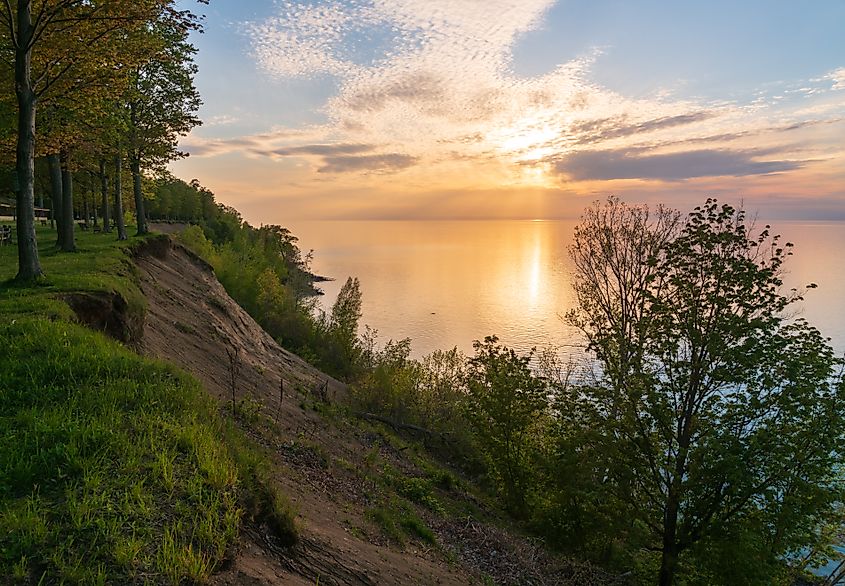

Lake Erie is the fourth-largest of the Great Lakes and forms a boundary between the United States and Canada. Subsequently, its entire northern coast is in Ontario, whereas Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York are on its east, south, and west shores. Lake Erie is the southernmost and shallowest of the Great Lakes, and its productive waters and coastal wetlands support a rich diversity of fish, birds, and other wildlife. Its sandy shores provide crucial stopover grounds for migratory birds and butterflies each year.
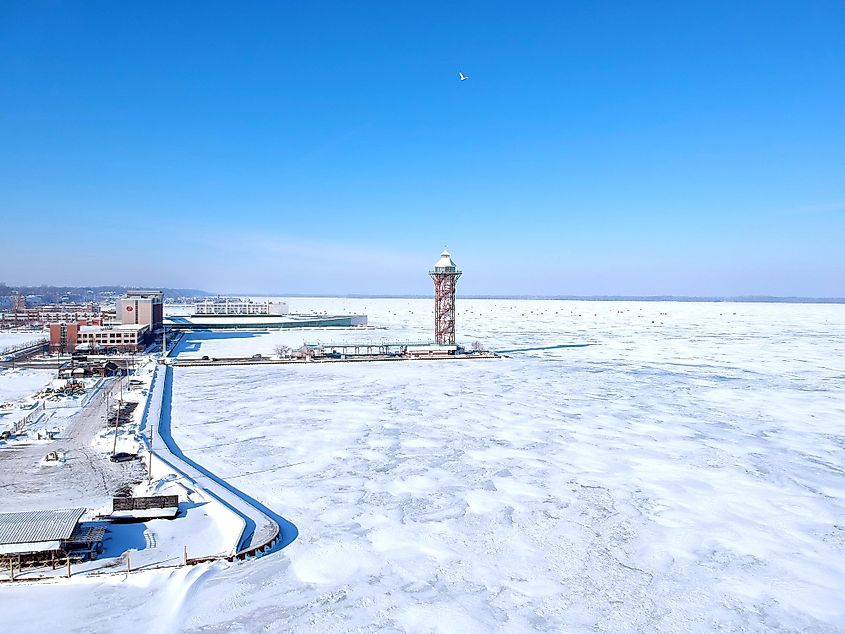

Lake Erie’s eastern and western shores are composed of clay and silt deposits, which supply minerals to surrounding communities, including salt mines and what has long been recognized as the largest sandstone quarry in the world in Ohio. Lake Erie’s nutrient-dense soils aid in the production of concord grapes, earning the nickname “The Lake Erie Concord Grape Belt” and supporting the largest vine culture in North America outside of California.
5. Lake Ontario: 712 miles (1,146 kilometers)
Lake Ontario is the smallest and easternmost of the Great Lakes. It has a coastline on Ontario in the north, and on New York to the south. Its 712 miles (1,146 kilometers) of coastline is composed of low bluffs and narrow beaches. Along the coast of Lake Ontario, there are 2,000 islands and 100 different beaches, which include the most extensive freshwater sand dune in New York.
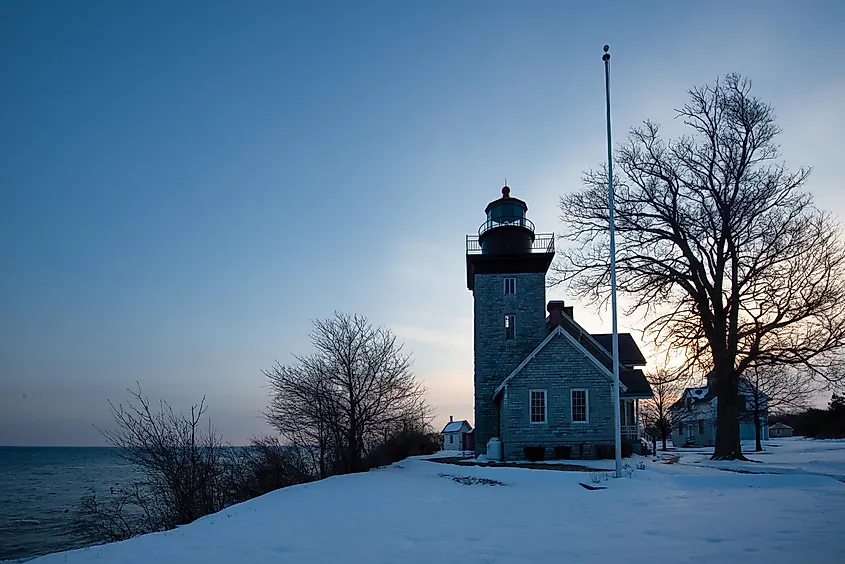

Expansive sand dunes on its east shore have created an isolated coastal environment which includes wetlands and barrier beaches that provide ample habitat for the Piping Plover, an endangered shorebird. Furthermore, Lake Ontario’s eastern shore has ample nesting habitat for other species of resident and migratory coastal bird species.

As the largest chain of freshwater lakes in the world, the Great Lakes have earned their name and their reputations. Due to stressors like development, agriculture, and road density, the Great Lakes ecosystems are at risk. While the southern region of the Great Lakes is significantly more developed and populated, the northern region is undeveloped, and its varying climate, soils, and geography create crucial habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species on its coastlines.