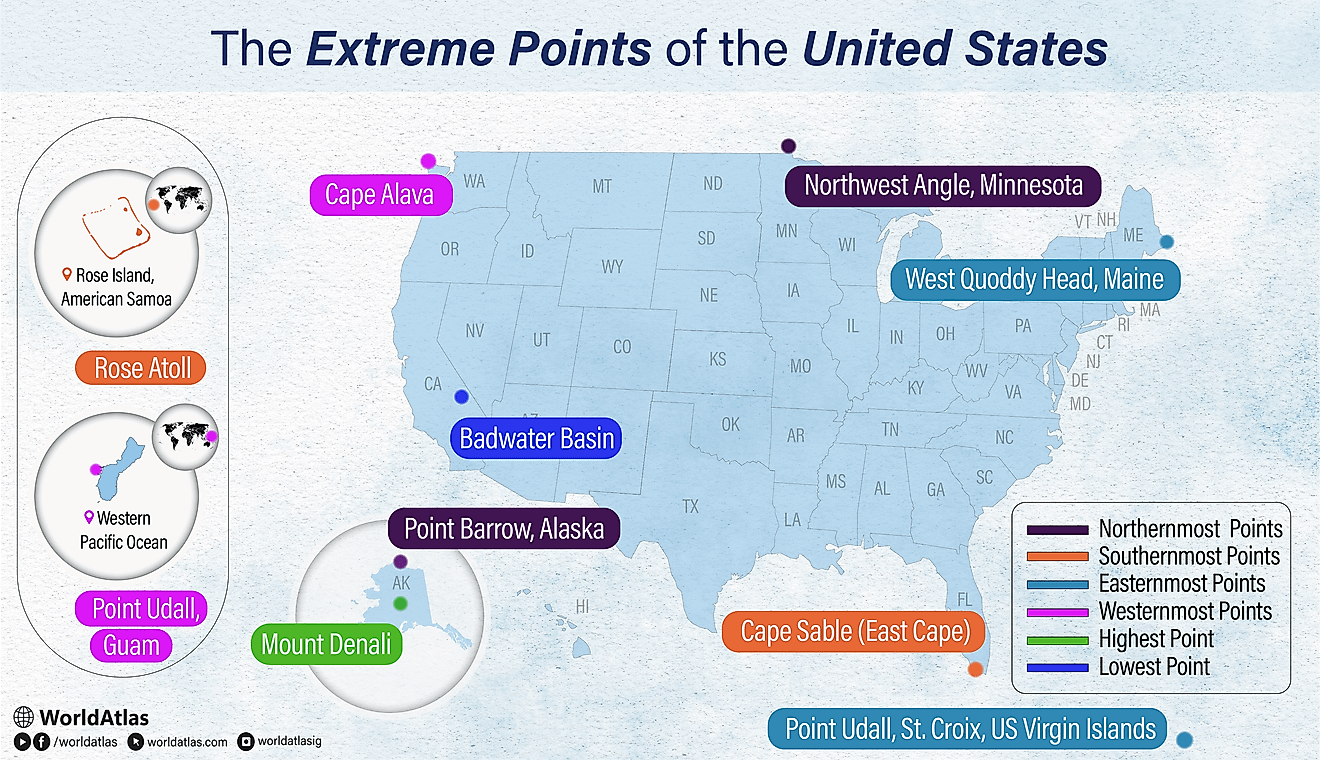
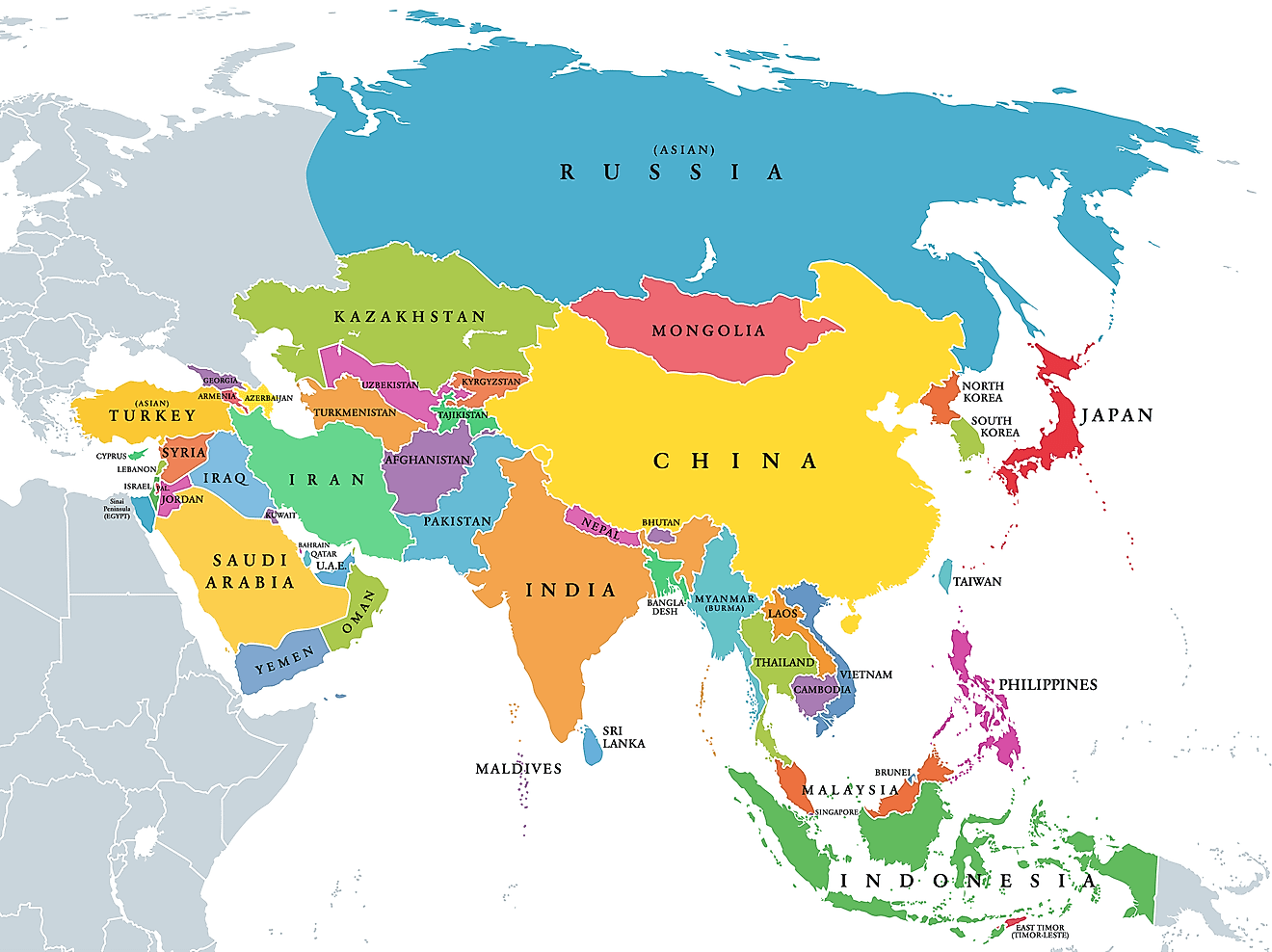
Major Landforms Of The Middle East
The Middle East is a region encompassing parts of eastern Europe, western Asia and northeastern Africa. The borders of this region are defined differently depending on the source, but it is made up of at least 20 countries that bear geographical and cultural similarities.
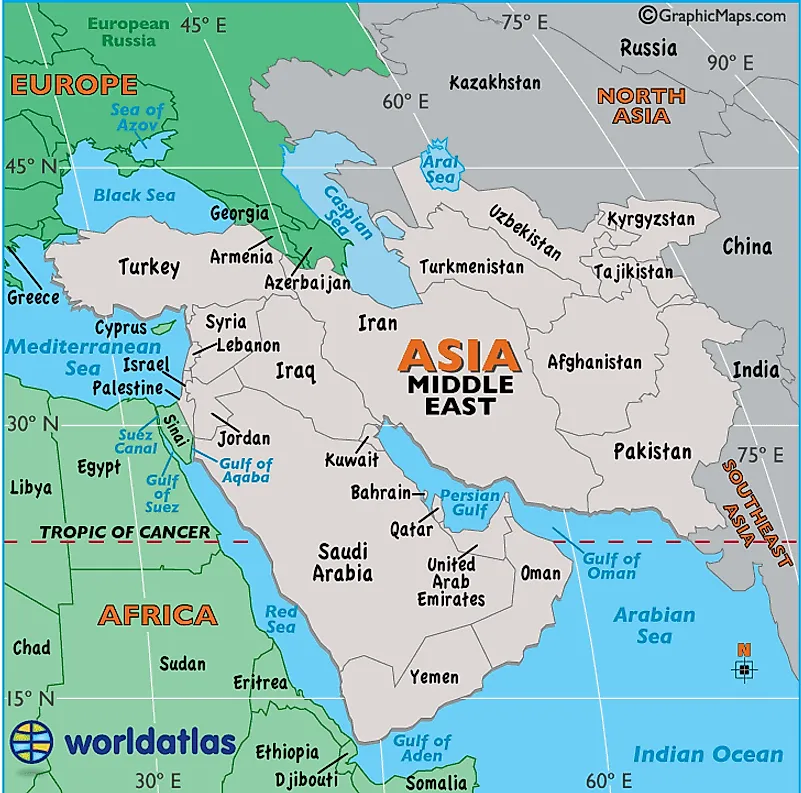
The region's western border is generally considered to be the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. To the south, the Middle East is bordered by the Arabian Sea. To the west, it is bordered by the countries of Kazakhstan, China, and either India or Pakistan. Pakistan is sometimes considered part of the Middle East, but due to its shared history with India, it is also sometimes considered to be part of South Asia. The northern border includes the countries of Turkey, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Kyrgyzstan. Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia are sometimes considered to be part of the Middle East, and sometimes part of Europe. Egypt is also occasionally included in this region.
Geographically, the Middle East is characterized by desert terrain and mountains, and it experiences an arid climate. A description of the major landforms of the region is included below.
Contents:
- Anatolian Plateau
- An-Nafud Desert
- Asir & Hejaz Mountains
- Caucasus Mountains
- Dasht-e Kavir (Kavir Desert)
- Dasht-e Lut (Lut Desert)
- Elburz Mountains
- Hadramawt Mountains
- Hindu Kush Mountains
- Karakum Desert
- Pamir Mountains
- Rub’Al Khali Desert
- Syrian Desert
- Taurus Mountains
- Tien Shan Mountains
- Zagros Mountains
The Major Landforms Of The Middle East
Anatolian Plateau
This barren and arid plateau is located at an elevation of at least 500 m in the central upland region of Turkey. The plateau is surrounded by the Pontic Mountains in the north and by the Taurus Mountains in the south. The plateau region experiences extreme climatic conditions with severely cold winters and hot and dry summers. Due to the extreme temperatures, different occupations like farming are difficult. Nevertheless, several scattered towns and villages cover the entire landscape.
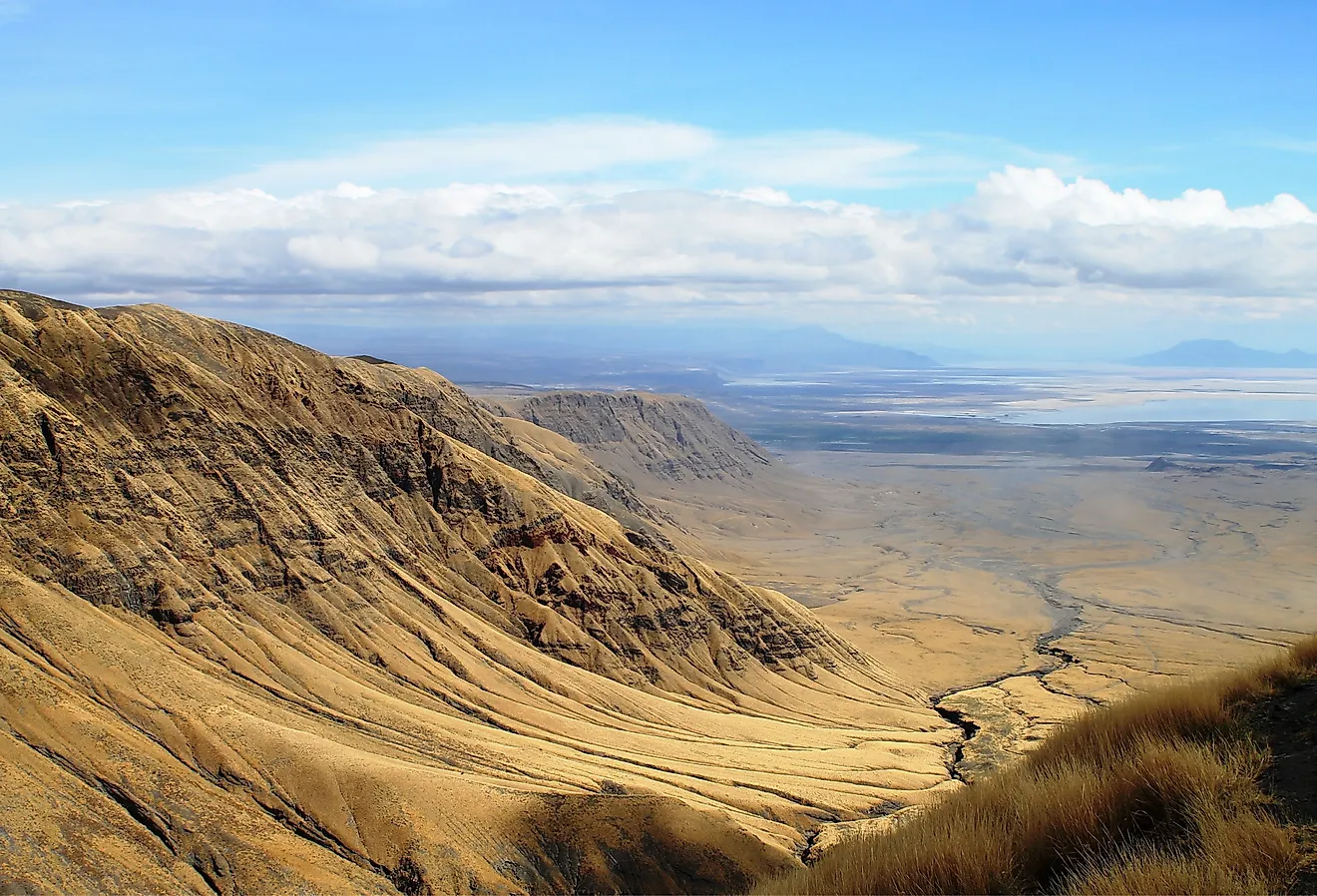
An-Nafud Desert

Covering an area of about 65,000 sq. km, the An-Nafud Desert is positioned in the northern portion of the Arabian Peninsula in the north-central part of Saudi Arabia. Often referred to as the Great Nafud, it is the second largest expanse of the Arabian Desert. An-Nafud Desert is noted for its gigantic sand dunes, some of which reach more than 30 m.
Asir & Hejaz Mountains
The western coast of the Arabian Peninsula comprises two mountain ranges, namely the Hejaz (Hijaz) Mountains in the north and the Asir Mountain in the south. These lower mountain ranges run along Saudi Arabia’s border with the Red Sea and have an elevation of about 1,829 to 2,130m.
Caucasus Mountains

These mountains are located between the Caspian Sea in the east and the Black Sea in the west and dominate the landscape of Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Russia. The Caucasus Mountains comprise two separate mountain ranges, namely the Greater Caucasus in the north and the Lesser Caucasus in the south. Situated in the Greater Caucasus mountain range is Mount Elbrus in Russia, which rises to an elevation of 5,642 m and is the highest peak in the Caucasus Mountains.
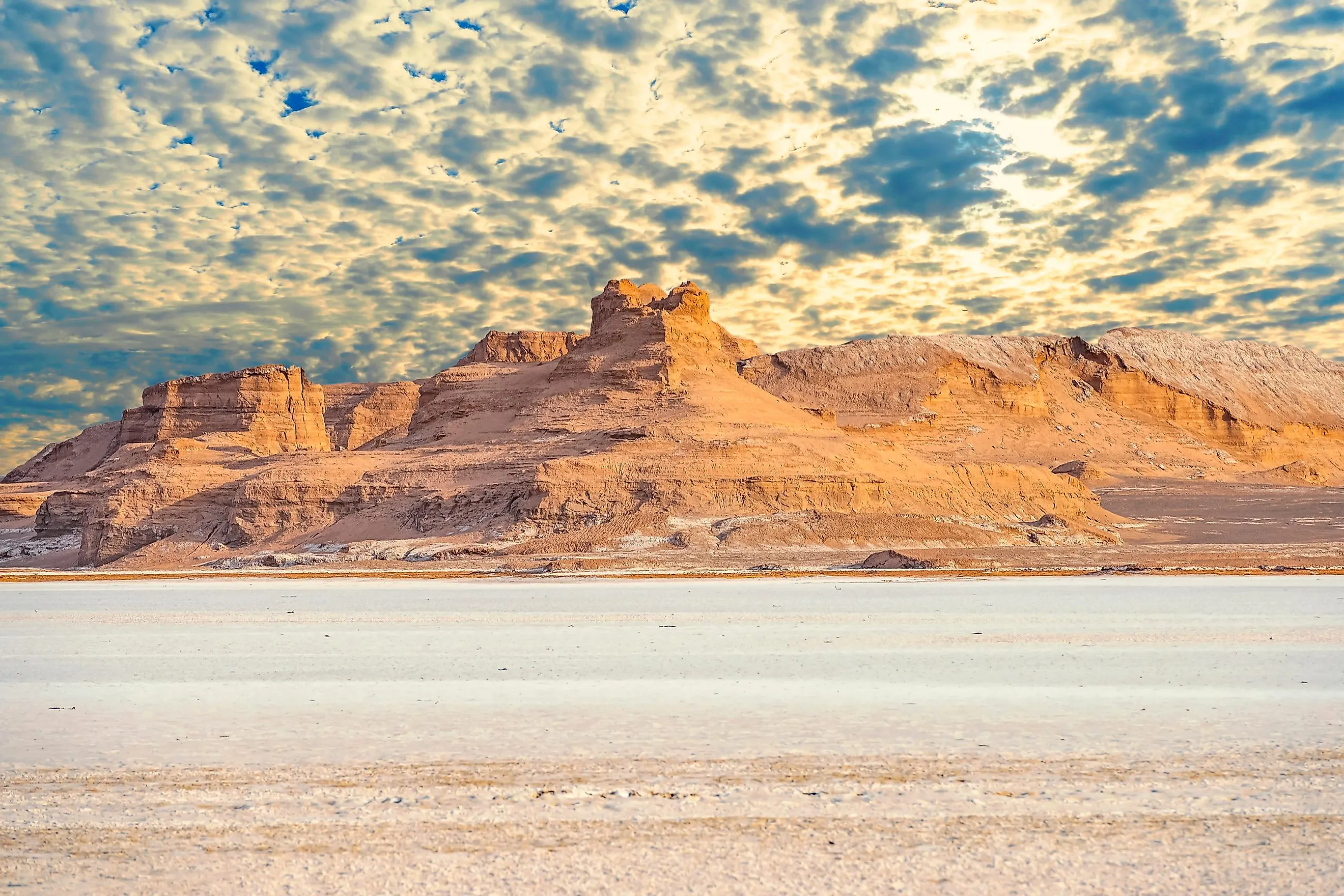
Dasht-e Kavir (Kavir Desert)
Often referred to as the “Great Salt Desert,” this desert is located in the north-central part of Iran, extending from the Elburz Mountain range to the Dasht-e Lut desert. It occupies parts of the Iranian provinces of Isfahan, Khorasan, Semnan, Tehran, and Yazd. The Dasht-e Kavir is the 24th-largest desert in the world, encompassing an area of about 77,600 km2. This large desert is mostly an uninhabited wasteland covered with crusty salt ridges.
Dasht-e Lut (Lut Desert)
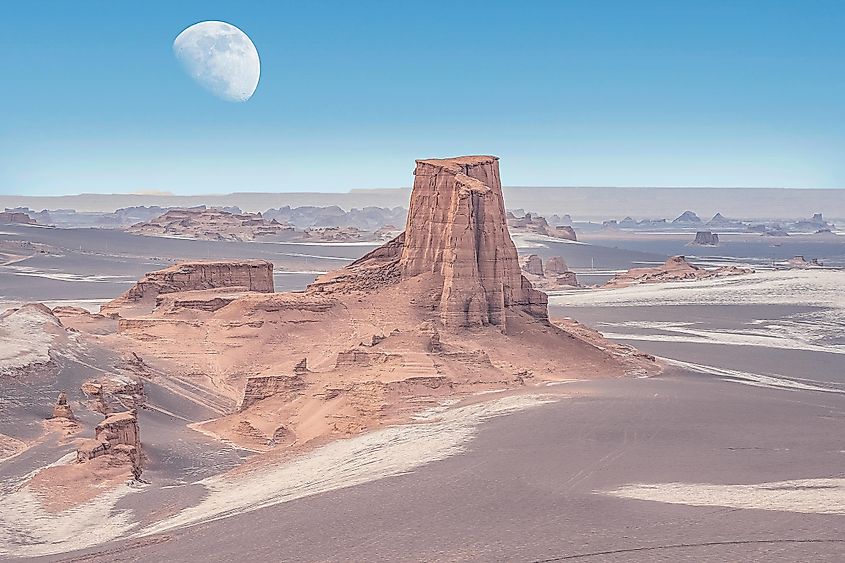

Lut Desert is a large salt desert located in the south-eastern part of Iran in the provinces of Kerman and Sistan and Baluchestan. It is the 25th-largest desert in the world, occupying an area of about 51,800 km2. With surface temperatures reaching as high as 70 °C in the summer months, the Dasht-e Lut desert is considered to be one of the driest and hottest regions on Earth.
Elburz Mountains (or Alborz)
Extending for about 900 km along Iran’s northern border with the Caspian Sea, these mountains separate the Iranian plateau and the Caspian Sea region. The jagged Elburz Mountains have an average height of about 2,750 m, but there are also many peaks in the range exceeding 4,000 m. Mount Damavand, a dormant volcano rising to an elevation of 5,670 m, is the highest point in the Elburz mountain range.
Hadramawt Mountains
Also referred to as the “Mahrat Mountains,” these mountains are located in the east-central part of Yemen, along the shores of the Gulf of Aden. These low mountain ranges have an average height of about 1,000 m, with their highest peak estimated at 2,440 m.
Hindu Kush Mountains
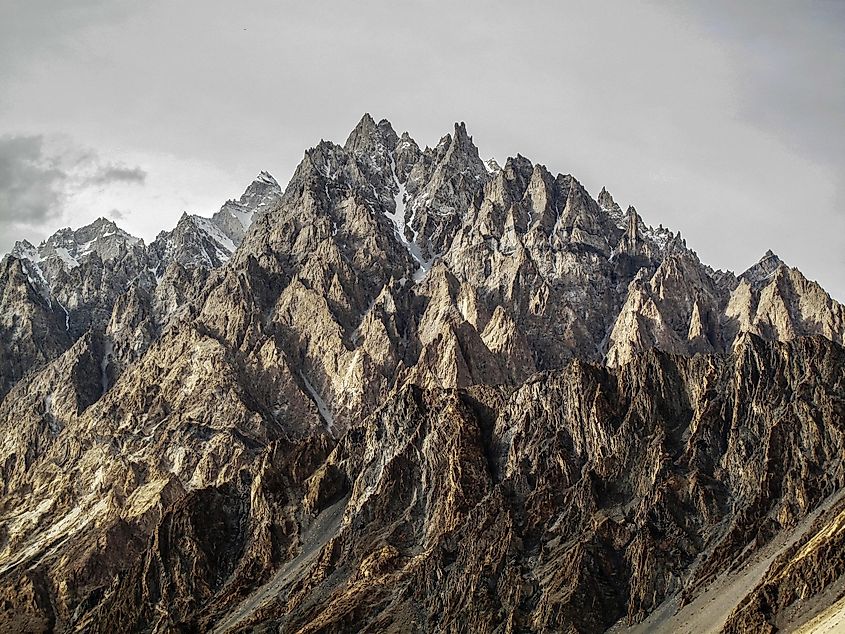

This 800 km-long mountain range in South-Central Asia, stretches from northern Pakistan through Afghanistan and into Tajikistan. These mountains form a natural border between Pakistan and Afghanistan and comprise several high snow-capped peaks. Located in Pakistan’s Chitral district is Tirich Mir, which is the highest peak in the Hindukush Mountain range at an elevation of 7,708 m.
Karakum Desert
Covering about 350,000 km2 in south-central Turkmenistan, this desert is noted for its towering sand dunes which extend in all directions. The Karakum Desert is one of the largest and hottest deserts in Central Asia and also hosts the Darvaza Gas Crater, known as the Gates of Hell or Door to Hell.
Pamir Mountains
Located at the junction of the Himalayas, the Tien Shan, the Kunlun, the Karakoram, and the Hindu Kush mountain ranges is the Pamir Mountain range. These mountains stretch across most of Tajikistan and parts of Afghanistan, Pakistan, and China. Like the Hindu Kush, the Pamir Mountain range also comprises several high snow-capped peaks. Located in the Pamir Mountains is the Ismoil Somoni Peak (Pik Samani), which rises to an elevation of 7,495 m and is the highest point in Tajikistan.
Rub’Al Khali Desert
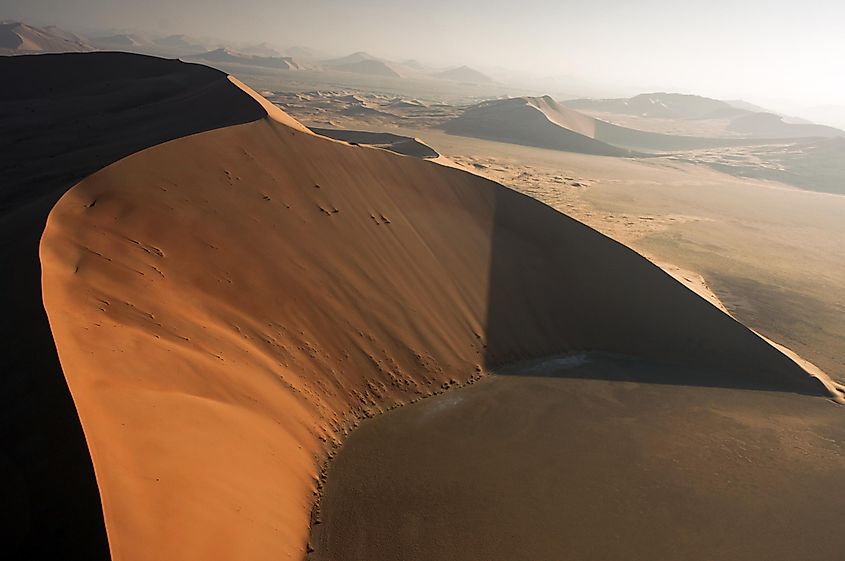

Also known as the “Empty Quarter” and covering an area of about 660,000 sq. km, the Rub’Al Khali Desert is the world’s largest continuous sand desert. The desert occupies the major south-central portion of the Arabian Peninsula, including parts of Oman, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. The desert is noted for its large reddish-brown sand dunes that alternate with sabkhas or interdune salt flats. It is also one of the world’s most hyper-arid regions. The Ad-Dahna is a northern sandy expanse that connects the Rub’Al Khali desert with the An-Nafud desert.
Syrian Desert
At approximately 500,000 km2, the Syrian Desert covers parts of Jordan, Syria, Saudi Arabia, and western Iraq. This arid wasteland receives less than 125 mm of rainfall annually, but Arab nomads inhabit the desert region and have successfully raised camels and cattle. Scattered oases and oil pipelines are common in the desert area.
Taurus Mountains
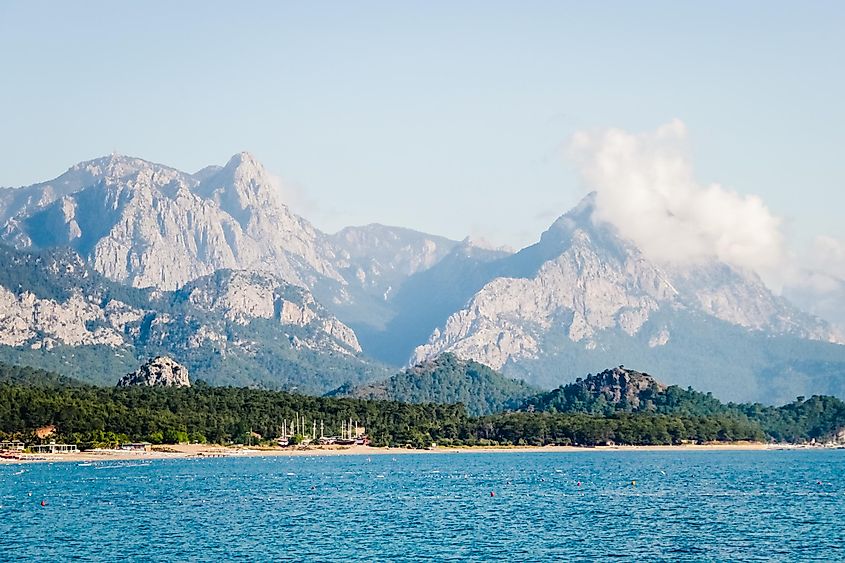

This rugged mountain chain extends across southern Turkey and forms the southern border of the Anatolian Plateau. Located in the Eastern Taurus range is Mount Ararat, an extinct volcano, which rises to an elevation of 5,137 m and is the highest point in the Taurus Mountains. This mountain range also contains important mineral deposits like copper, silver, iron, zinc, arsenic, and lignite.
Tien Shan Mountains
This mountain range stretches across Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, and western China. Situated on the border of Kyrgyzstan and China is Jengish Chokusu Mountain/Pik Pobedy/Victory Peak, which rises to an elevation of 7,439 m and is the highest point in the Tien Shan Mountain range. Also, located in the north-eastern part of the mountain range is Lake Issyk-Kul, which is the world’s highest mountain lake.
Zagros Mountains
The 1,600 km-long Zagros mountain range extends across southeastern Turkey and northern Iraq to the Strait of Hormuz. Located in the central part of the range is Mount Dena, which rises to an elevation of 4,409 m and is the highest point in the Zagros Mountain range.