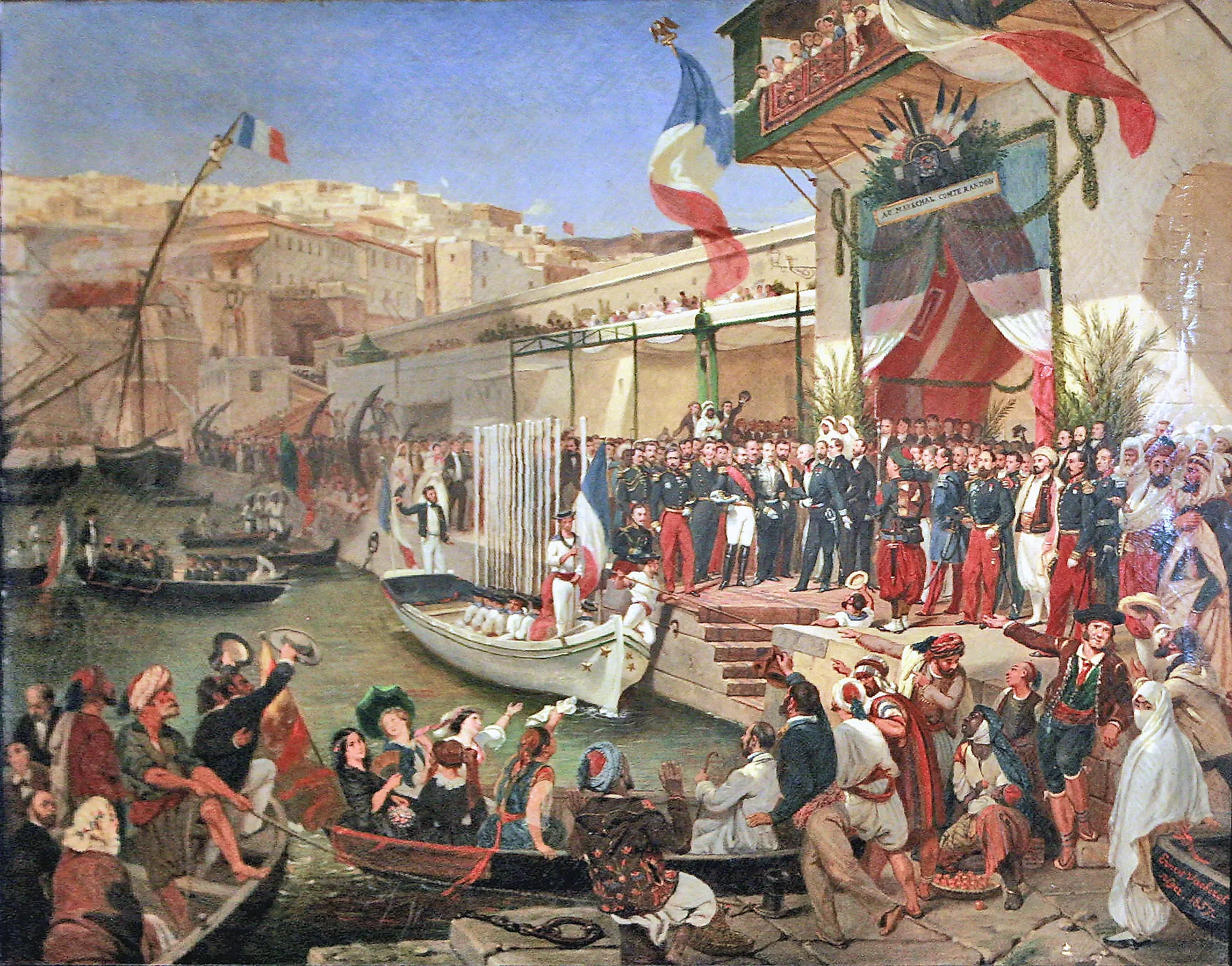
The Former French Colonies
The French Empire began in the early 16th century under King Henery IV. It reached its height during the 19th century under Emperor Napoleon III. The empire then began to unravel after his defeat in the Franco-Prussian War. It finally ended after World War I, and the French colonies overseas became independent countries over time.
The French Colonization Of North America

French colonization of North America started along the banks of the Bay of Fundy, where Samuel de Champlain helped to found Port Royal, which is located in modern-day Nova Scotia. In 1608, Champlain founded the city of Quebec, which served as a base for French expansion into the interior of North America. The French established several colonies and trading posts in North America, including Acadia, Montreal, Louisiana, and New France. The French were, however, less successful than the British in colonizing North America. This was due in part to the fact that they did not have as many settlers come over from Europe. The French also had a difficult time dealing with the Native Americans who were already living in the area.
French Colonies In The Caribbean

The first permanent French colony in the Caribbean was Saint-Pierre. This settlement was founded by Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc in 1635 on the island of Martinique in the Lesser Antilles. It was the first settlement, but many more would soon follow. In 1638, France acquired Saint Lucia from the British, and in 1664, the French founded Saint-Domingue on the western tip of the island of Hispaniola. The colony quickly became a profitable sugar-producing plantation. However, unfortunately, its economy was based on slave labor. And in 1791, enslaved people in Saint-Domingue revolted against their French overlords. The Haitian Revolution lasted for over a decade and resulted in the death of thousands of people, but it was the necessary first step in securing their independence. Haiti became its own sovereign nation in 1804.
French Colonies In Africa

The French first began colonizing Africa in the 17th century, although they did not start having a significant presence on the continent until the 19th century. By 1900, the French had colonies in present-day Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso, Guinea, Ivory Coast, and Benin, just to name a few. The French colonies in Africa were generally quite small, except for Algeria and the Congo. Most colonies were located along the coast or in river valleys, where the climate was more hospitable, and transportation was easier.
French Colonies In Southeast Asia
It was in the mid-1800s that the French began to establish a presence in Southeast Asia. By the early 1900s, they had secured control over Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos. These colonies would remain under French rule for nearly a century. The Vietnamese people resisted French rule, and there were several uprisings against the colonial regime. However, the French were able to maintain control. In 1863, the French Empire established control over Cambodia. They did this to prevent Vietnam from annexing the country. In 1884, they annexed Cambodia, making it a colony. The Cambodian people also resisted French rule, and there were several uprisings against the colonial regime. However, the French did not relinquish control.
The Legacy Of French Colonialism
The legacy of French colonialism is complex and multi-faceted and is still felt today in many parts of the world. The countries that were once under French rule often bear the marks of that period, both in terms of physical infrastructure and social and economic development. In some cases, the legacy of French colonialism has been a positive one. The French colonialists brought with them a wealth of knowledge and experience and helped develop many countries that are now thriving. However, there is also a dark side to the legacy of French colonialism, where some French colonialists were brutal rulers and left a legacy of oppression and exploitation.
The Positive And Negative Aspects Of French Colonialism
The positive and negative aspects of French colonialism are both well-documented. On the one hand, France brought a great deal of modernization to its colonies, particularly in infrastructure and education. Additionally, the French were generally more tolerant of local cultures and traditions than other colonial powers. However, the unfortunate reality is that French colonialism was also marked by a high degree of exploitation, both of natural resources and of human labor. Additionally, the French government was often reluctant to grant political autonomy to its colonies, leading to several nationalist uprisings.
France's Current Relationship With Its Former Colonies

France's current relationship with its former colonies varies depending on the colony in question. In general, France maintains strong economic and political ties with most of its former colonies. For example, France is one of the top investors in Africa and has a large number of troops stationed in various African countries. Additionally, many African leaders have been educated in France and regularly visit the country. Some of France's former colonies, such as Algeria and Morocco, have also become close allies. In recent years, however, there has been some tension between France and some of its former colonies over issues such as immigration and trade. Nonetheless, the overall relationship between France and its former colonies remains strong.
While the French were not the first Europeans to colonize parts of the world, their intercontinental impact was significant. The French established settlements in North America, the Caribbean, Africa and Asia and played a major role in the development of those regions. French explorers and traders interacted with natives from around the world, helping to shape the cultures of both groups. The French also left a lasting mark on the landscape, with place names and architecture that reflect the country's influence. In the end, however, the French could not maintain their grip on their vast empire. Today, many reminders of French colonization remain around the globe.
| List Of Former French Colonies |
|---|
| Albreda |
| Anguilla |
| Annam |
| Antigua and Barbuda |
| Cambodia |
| Chandernagore |
| Cochinchina |
| Colonial Mauritania |
| Colony of Niger |
| Dahomey |
| Dominica |
| France Antarctique |
| France Equinoxiale |
| French Algeria |
| French Cameroons |
| French Chad |
| French Comoros |
| French concessions in Shanghai |
| French Congo |
| French Guiana |
| French Guinea |
| French Madagascar |
| French Mandate for Syria and Lebanon |
| French protectorate in Morocco |
| French protectorate of Tunisia |
| French Seychelles |
| French Somaliland |
| French Sudan |
| French Togoland |
| French Upper Volta |
| Gabon |
| Grenada |
| Haiti |
| Ile-Royale |
| Iles Malouines |
| Isle de France |
| Ivory Coast |
| Karikal |
| Kwang Chou Wan |
| Laos |
| Mahe |
| Malagasy Protectorate |
| Montserrat |
| Nevis |
| New France |
| New Hebrides |
| Newfoundland |
| Niger |
| Oubangui-Chari |
| Pondicherry |
| Saint Bathelemy |
| Saint Christophe |
| Saint Croix |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines |
| Saint-Domingue |
| Saint-Dominigue |
| Sainte-Lucia |
| Sint Eustatius |
| Tobago |
| Tonkin |
| Upper Senegal and Niger |
| Vietnam |
| Yanaon |