The Great Lakes Ranked By Size
The Great Lakes are a series of five interconnected freshwater lakes that span Canada and the United States. The five lakes, Lake Superior, Lake Huron, Lake Michigan, Lake Erie, and Lake Ontario, hold 21% of the Earth’s freshwater, spanning 94,250 mi2 (244,106 km2) and holding 5,439 cubic miles of water. These vast lakes formed approximately 14,000 years ago due to climate warming and glacial melting.
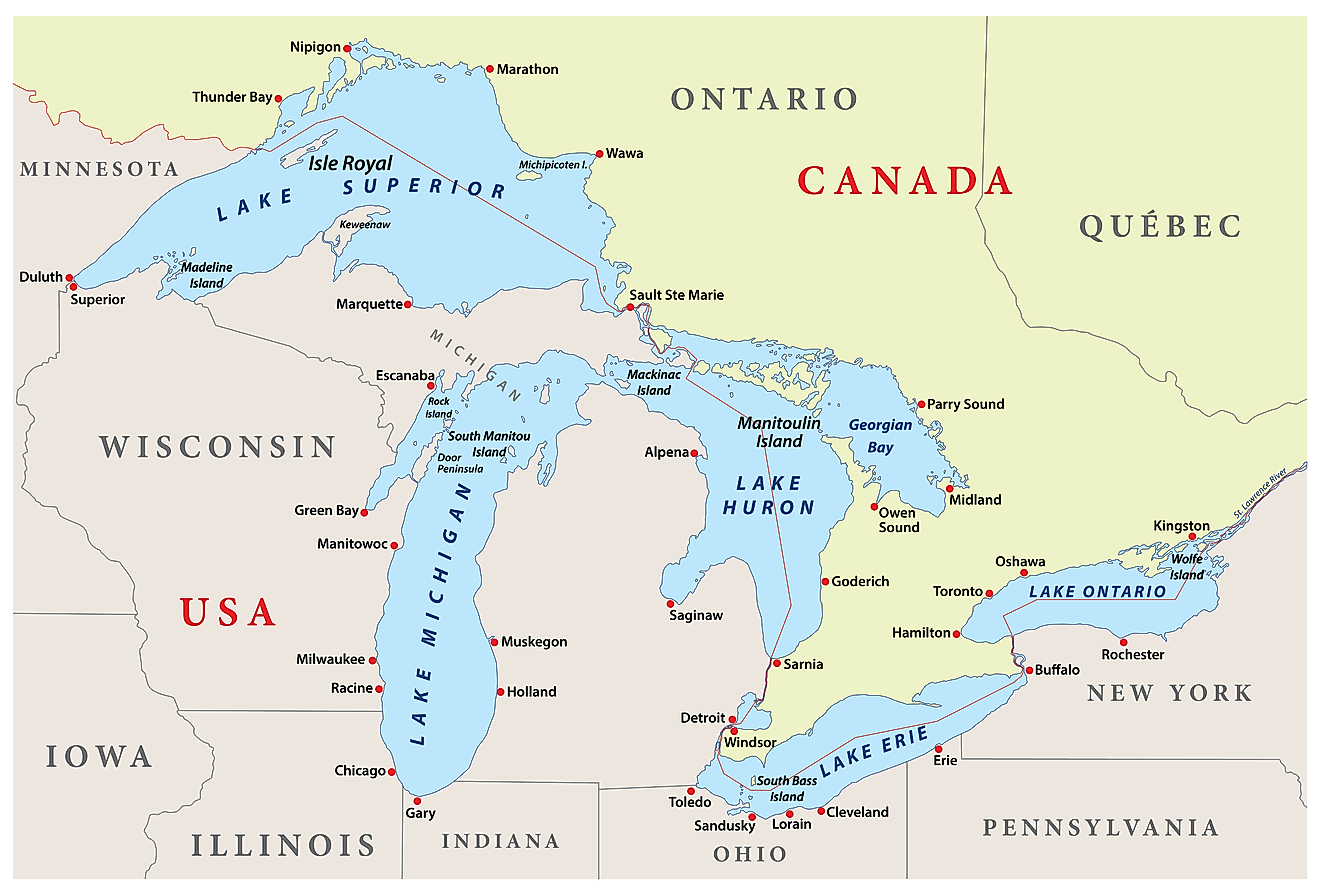
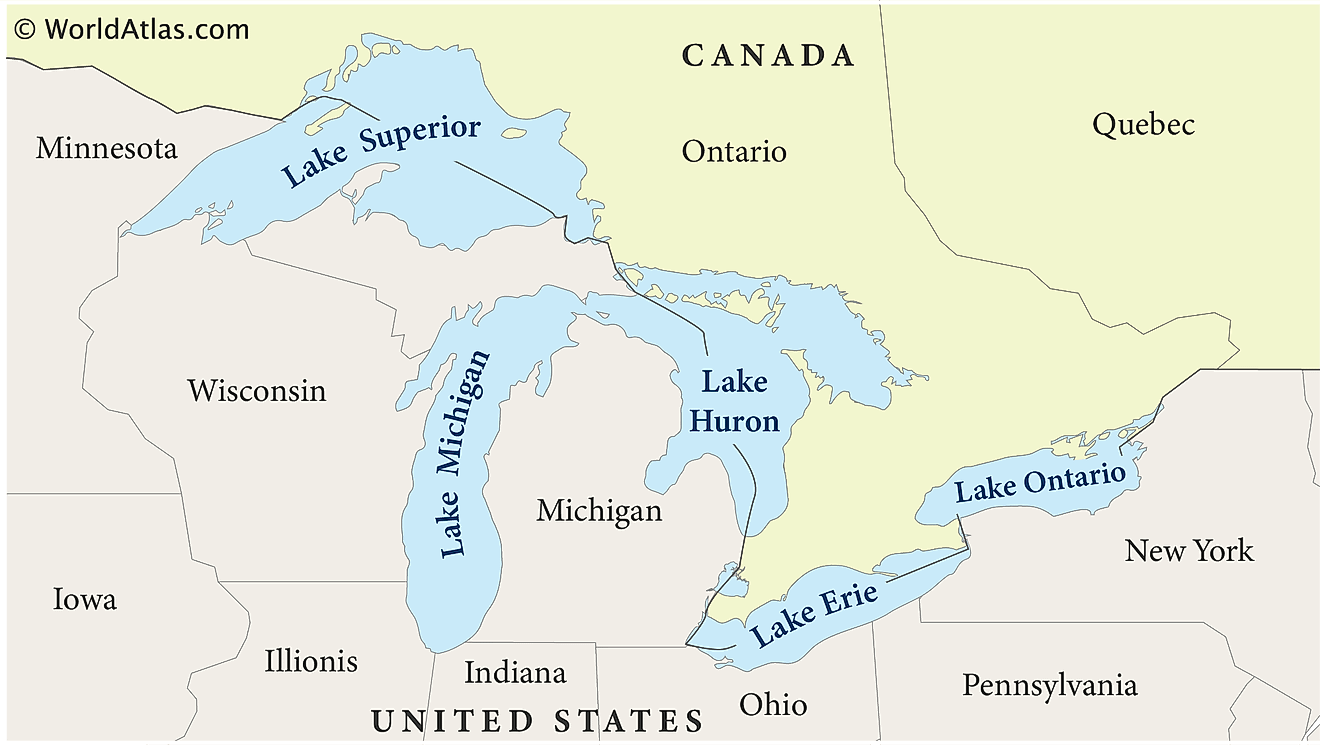
Lake Superior, the largest by both volume and depth, surpasses the size of South Carolina. It is followed by Lake Michigan, the second-largest by volume and third-largest by area, notable for being the only Great Lake entirely within the U.S. borders. Lake Huron ranks third in volume and second in area. Lake Erie, in contrast, is the smallest by volume and the shallowest of the lakes. Finally, Lake Ontario is the second-smallest in volume, and the smallest in area, and it is significantly lower in elevation compared to the other lakes.
1. Lake Superior - 31,700 mi2 (82,102 km2)
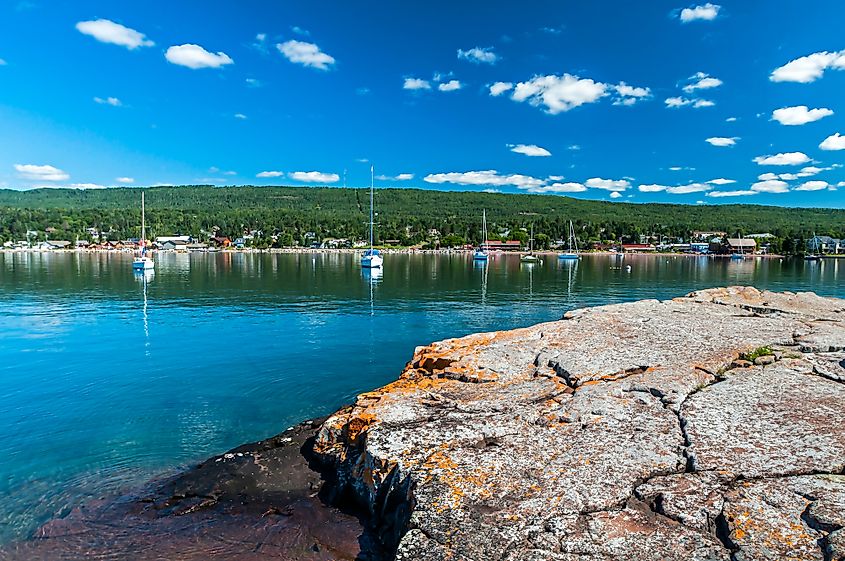

Spanning 31,700 mi2 (82,102 km2), Lake Superior is the largest of the Great Lakes and the northwesternmost in the group. It shares its shores with Minnesota, Wisconsin, Ontario, and Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. Globally, it holds the title of the largest freshwater lake by area and is second in size only to the Caspian Sea. To put its size into perspective, Lake Superior is comparable to Austria and three times larger than Massachusetts. Lake Superior stretches 350 miles at its longest point and spans 160 miles at its widest.
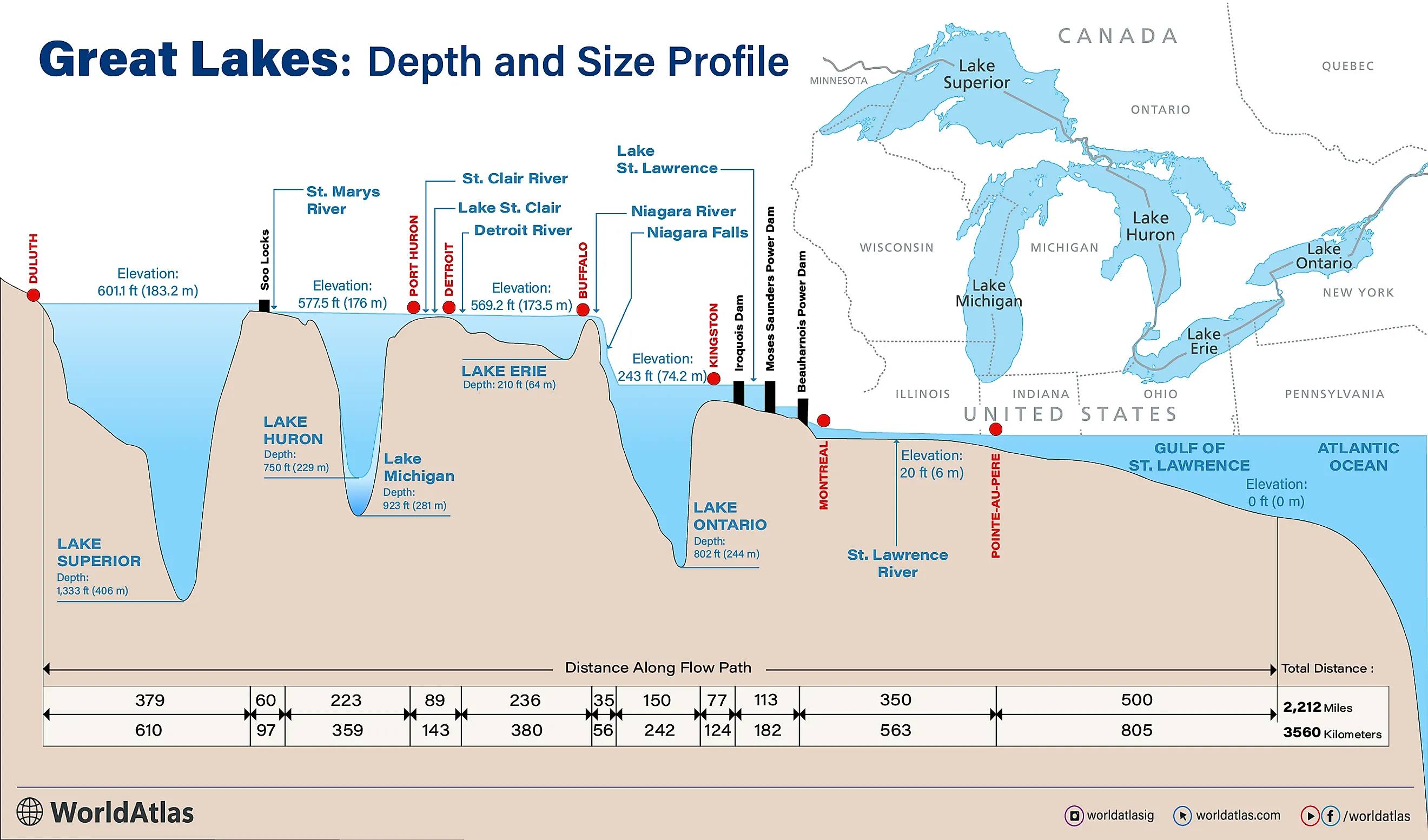
Lake Superior averages a depth of 483 feet and reaches a maximum depth of 1,333 feet, holding a total of 2,900 cubic miles of water. To put this number into perspective, it would take 191 years to empty the lake at its current outflow rate without any replenishment. As part of the Great Lakes Waterway, Lake Superior serves as a vital transportation route for goods like iron ore, grain, and other manufactured materials. However, these routes are typically closed from January to March due to thick ice.
2. Lake Huron - 23,000 mi2 (59,569 km2)

Covering approximately 23,000 mi2 (59,569 km2), Lake Huron is the second largest of the Great Lakes and is located in the middle of the Great Lakes group. It borders only Michigan and the Canadian province of Ontario. Connected to Lake Superior by the St. Marys River and to Lake Michigan by the Straits of Mackinac, Lake Huron plays a key role in linking the Great Lakes system. Its name, given by French explorers, honors a local Indigenous group that historically inhabited the region.
Lake Huron is approximately twice the size of Belgium and half the size of Pennsylvania, with roughly 14,000 square miles in Ontario and 9,000 in Michigan. Despite being the second-largest Great Lake by area, it ranks third in volume, holding 850 cubic miles of water. The lake has an average depth of 195 feet and reaches a maximum depth of 750 feet. Georgian Bay extends from its northeastern end, while Manitoulin Island separates the bay and the North Channel from the main body of the lake.
3. Lake Michigan - 22,300 mi2 (57,756 km2)

Lake Michigan, bordering Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, and Indiana, spans about 22,300 mi2 (57,756 km2), making it the third-largest Great Lake by area. However, with 1,180 cubic miles of water, it ranks as the second largest by volume. Of the five Great Lakes, Lake Michigan is the only to be located completely within the United States. The lake stretches 307 miles at its longest point and 118 miles at its widest, covering an area roughly the size of Croatia and half the size of Ohio.
On average, Lake Michigan is 279 feet deep, with a maximum depth of 925 feet, while its deepest point, Chippewa Basin, lies in the northern half. Green Bay in the northwest and Grand Traverse Bay in the northeast are its two largest bays. Lake Michigan’s major inflows include the Fox, Grand, St. Joseph, and Milwaukee Rivers, while its primary outflows are the Strait of Mackinac and the Calumet and Chicago Rivers.
4. Lake Erie - 9,910 mi2 (25,666 km2)

Covering approximately 9,910 mi2 (25,666 km2), Lake Erie borders Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, and Ontario, making it the fourth-largest Great Lake by area. However, with a volume of just 119 cubic miles, it is the smallest in terms of water volume. It is also the shallowest of the Great Lakes, averaging 62 feet deep and reaching a maximum depth of 210 feet. The lake is named after the Erie people, who historically lived along its southern shore.
The name Erie is derived from the Iroquoian word erielhonan, meaning "long tail," or possibly from eri, meaning "cherry tree." Lake Erie’s main inflow is the Detroit River, while its natural outflow is the Niagara River. It is also connected to Lake Ontario via the Welland Canal. The environmental health of Lake Erie has been of concern for decades, with pollution, overfishing, eutrophication, and algae blooms all posing threats to the natural ecosystem.
5. Lake Ontario - 7,340 mi2 (19,010 km2)

Lake Ontario, the smallest of the Great Lakes by area, is bordered by the Canadian province of Ontario and New York State. The lake, named after the province, serves as the outlet for the Great Lakes system, connecting to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. Its primary inflow is the Niagara River. Covering 7,340 mi2 (19,010 km2), Lake Ontario holds 393 cubic miles of water and has the lowest elevation of the Great Lakes at 243 feet above sea level.
Lake Ontario stretches 193 miles in length and 53 miles in width. Its average depth is 283 feet, with a maximum depth of 802 feet. Within the lake, there are several inhabited islands, including Galloo Island, Little Galloo Island, Amherst Island, Association Island, and Waupoos Island. There are also over 100 beaches spread along the shores.
Final Thoughts
The Great Lakes stand as a testament to the geological forces that shaped North America, offering unparalleled natural resources and economic significance. Together, they form a vital freshwater system that sustains millions of people, supports diverse ecosystems, and facilitates commerce across the region. Yet, as much as they are a source of pride and utility, they also remind us of the responsibility to protect and preserve their ecosystems for future generations. Whether admired for their vastness or relied upon for their resources, the Great Lakes are an enduring part of the continent’s identity.
Great Lakes Ranked By Size
| Name | Bordering State/Province | Area (mi2) | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior | Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan (Upper Peninsula), Ontario | 31,700 | 82,102 |
| Huron | Michigan, Ontario | 23,000 | 59,569 |
| Michigan | Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, Indiana | 22,300 | 57,756 |
| Erie | Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York, Ontario | 9,910 | 25,666 |
| Ontario | New York, Ontario | 7,340 | 19,010 |