Who Won World War 1?
The Allies (led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia until 1917, Italy after 1915, and the United States after 1917) won World War One. This left the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire) as the losers. The outcome of this conflict was enormously consequential. Indeed, the formal peace treaty, the Treaty of Versailles, contributed to mass social and economic unrest in Germany, paving the way for the rise of Nazism.
The War

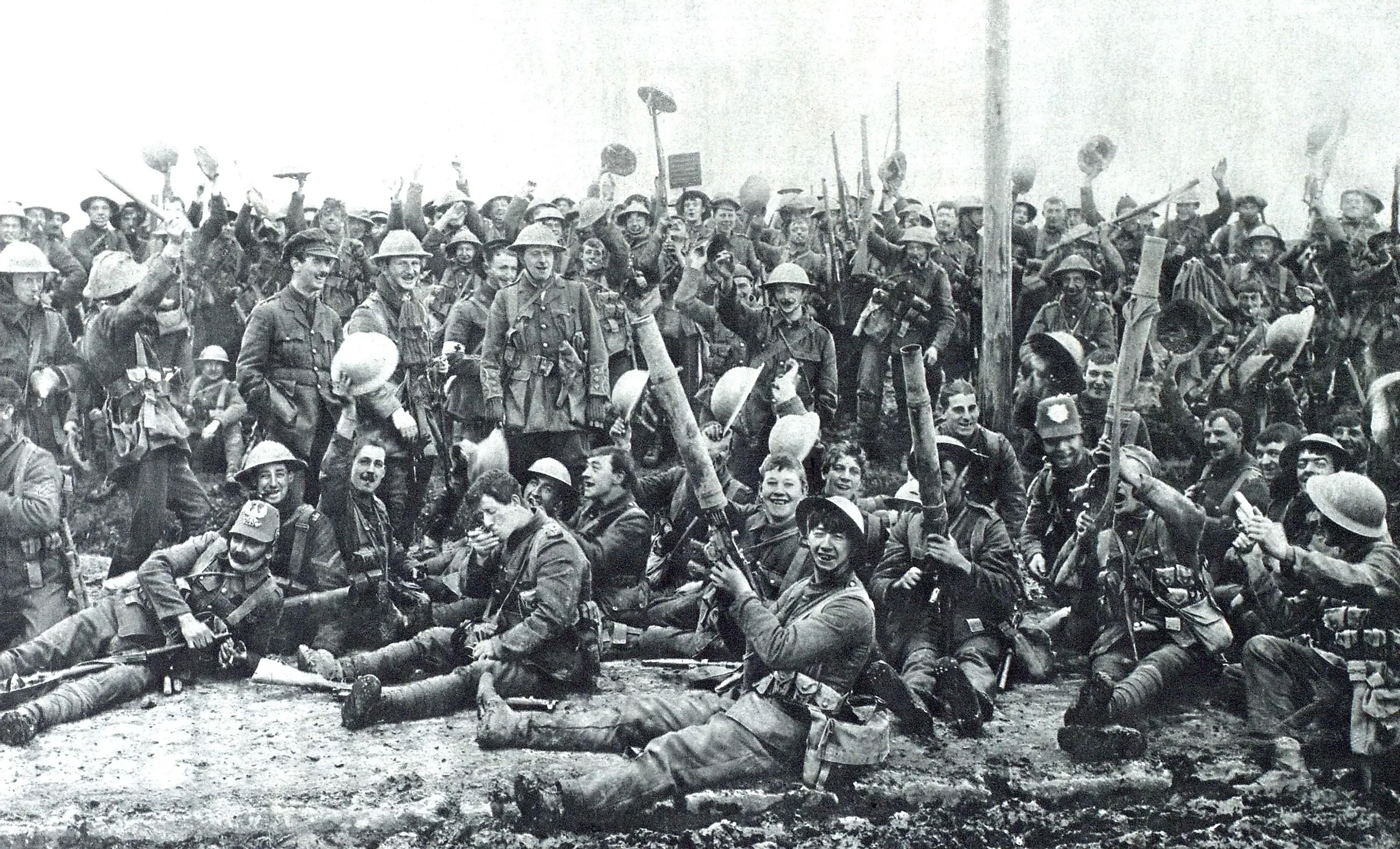
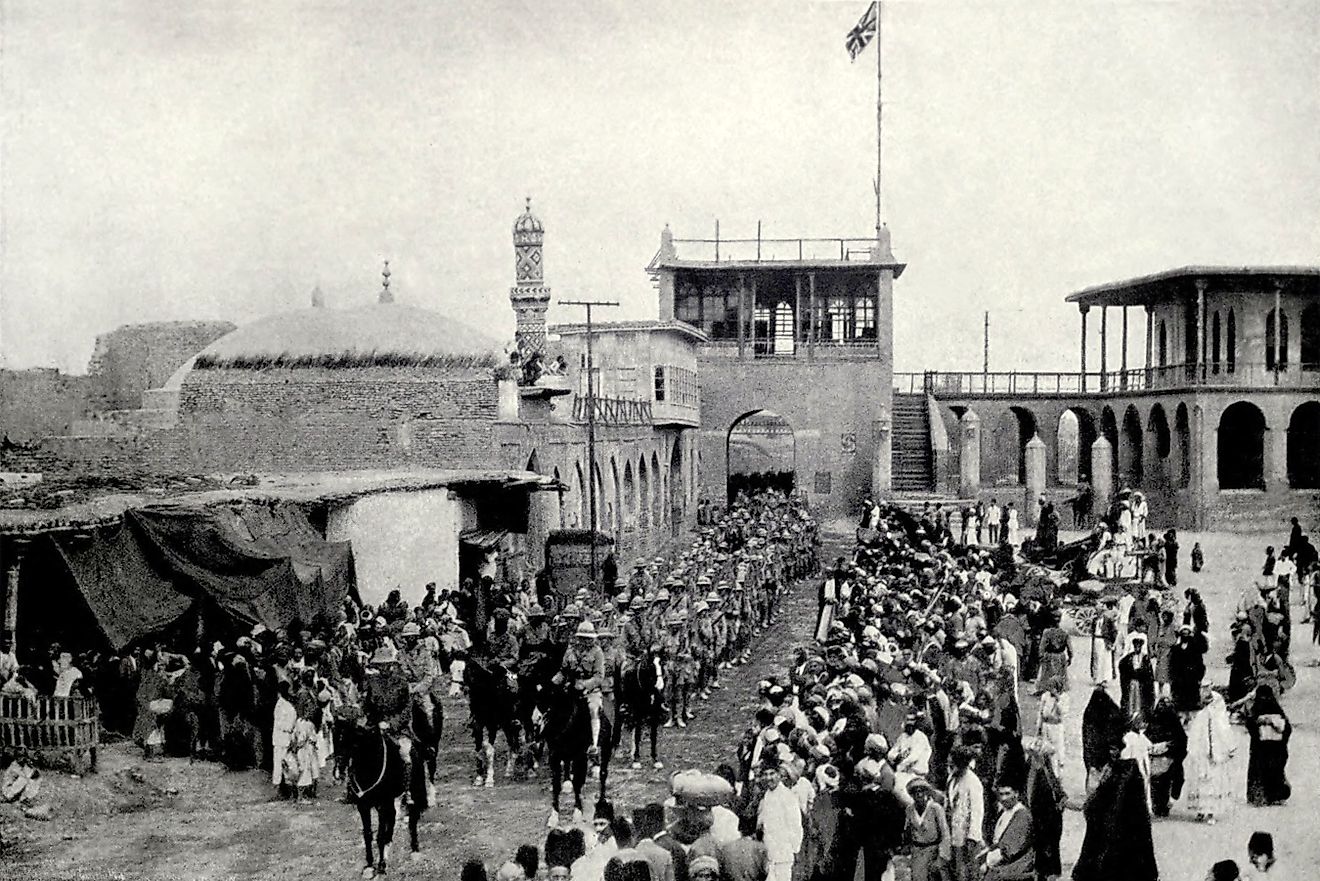
World War One began on June 28, 1914, when Archduke of Austria-Hungary Franz Ferdinand was assassinated in Sarajevo. This event set off a chain reaction that resulted in the major European powers going to war with each other. The subsequent four years were a bloodbath. On the Western Front, trench warfare created a stalemate, making it so millions of men and boys died fighting for minuscule territorial gains. The story in Eastern Europe was much the same, with the poorly trained Russian Army suffering untold numbers of casualties. In the Middle East, the Ottomans fought on four fronts, beating the British in Gallipoli and the Russians in the Caucasus. However, they were unable to beat the British in Iraq, Palestine, and Egypt. In total, between 15 to 23 million were killed in World War One, and about 23 million were injured.
The End Of The War

By 1917, both the Allies and the Central Powers were facing significant problems. The new Bolshevik government pulled Russia out of the war, leaving the United Kingdom and France without a key ally. As for the Central Powers, with the United States about to enter the conflict on the side of the Allies, the Germans knew they needed to launch a major attack to win the war. This resulted in the German Spring Offensive in the spring of 1918. Despite initial steady progress, logistical issues and the American entry into the war ultimately hindered the campaign. The Allies subsequently pushed back the Germans during the Hundred Days Offensive from August to November. When combined with domestic unrest in Germany and the aforementioned Ottoman failures, this resulted in an armistice being signed on November 11, 1918, ending the war with the Allies as the winners and the Central Powers as the losers.
The Treaty of Versailles

As the dust from the war settled, the major European powers began discussing a formal peace treaty. Negotiations started in January 1919, and the Treaty of Versailles was presented to the German delegates five months later. It was incredibly draconian, forcing Germany to give up all of its colonies and a major portion of its European territory, reducing its military to 100,000 soldiers, and making the country pay billions of dollars in reparations. Despite being widely seen as unfair, Germany nonetheless signed the treaty on June 28 after the Allies threatened to invade.
As for the Ottomans, the end of the war was catastrophic. It saw the major European powers partition the empire, resulting in its end in 1922. The French got what is now modern-day Lebanon and Syria, whereas the British got Iraq, Jordan, and Palestine. Moreover, the French, British, and Italians also had an interest in Turkey. However armed resistance by Turkish nationalists forced them to recognize an independent Turkish state.
The Aftermath

The Treaty of Versailles contributed to significant instability in Germany. For instance, it was the main cause of hyperinflation in the 1920s since the German government printed money to pay the reparations. Thus, by November 1923, one American dollar was worth 4.2 trillion Reichsmarks. This monetary instability led to political instability, with the Nazis attempting a coup in Munich that same year. While the German economy recovered in the second half of the 1920s, the stock market crash of October 1929 capitulated Germany back into economic despair. When combined with the memories of the hyperinflationary period, this contributed to even more anger and discontent towards the German government, contributing to Hitler and the Nazis' rise to power in 1933.
In conclusion, the Allies won World War One. The resulting peace process led to unfair punishments for the Germans and the Ottomans. Moreover, it contributed to the increasing popularity of fascism in Germany, helping Adolf Hitler become chancellor.