How Are Ancient Roman Buildings Still Standing?
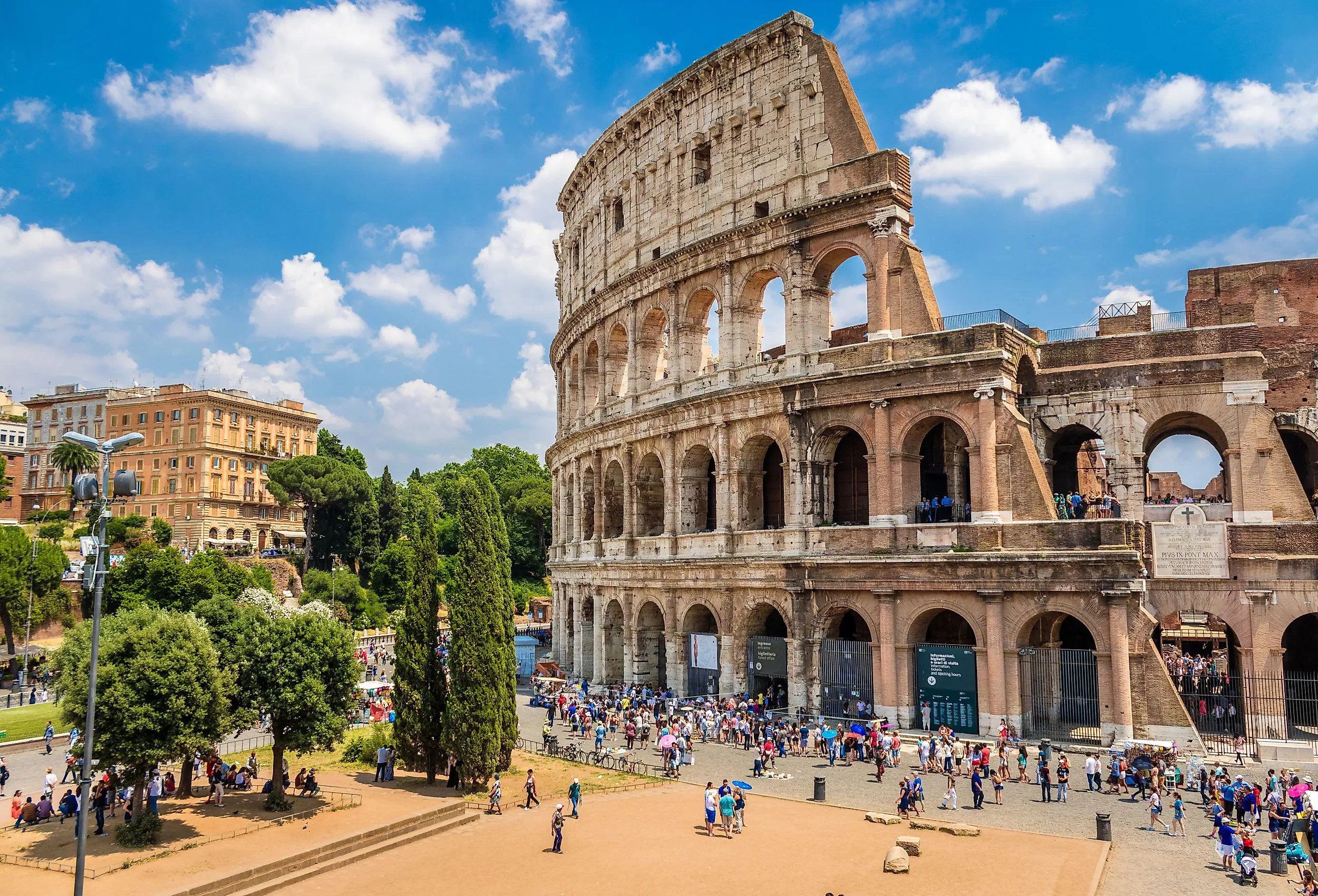
Many people go to Rome to see the remains of buildings that are thousands of years old. These buildings still stand, such as the Colosseum and Pantheon, and are a stunning display of ancient Roman achievements and technology. Some more modern buildings are already deteriorating. The fact that ancient Roman buildings are outlasting modern-day buildings is a strange phenomenon. This has led scientists to look more deeply into how the ancient Roman's built their buildings and how they are still standing. Scientists have studied the materials of the buildings and looked at historical texts, hoping to uncover the Roman's secrets.
Explore what humans know so far about ancient Roman building technology and how these magnificent buildings are still standing today.
Where Are These Buildings Today
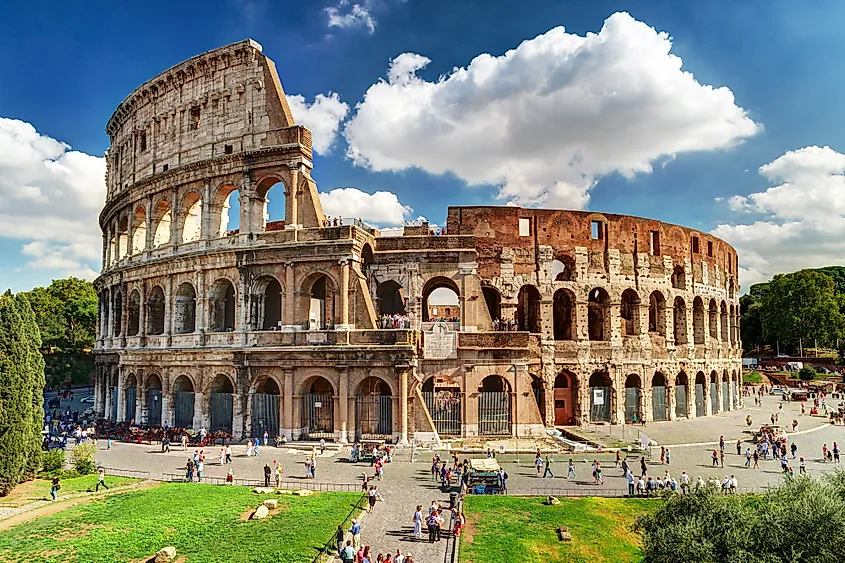

Ancient Rome covered a different area of land than the city of Rome today. Remains of ancient Roman buildings are in modern-day Italy and modern day France. One of the most popular ancient Roman buildings still standing today is the Colosseum. This is one of the most iconic ancient Roman structures and the most theatrical. The Colosseum is in modern day Italy. Another popular Roman site is the Thermes de Cluny in Paris. This was a Roman bathhouse. The ancient Romans have many other impressive buildings still standing today.
Pouring Concrete
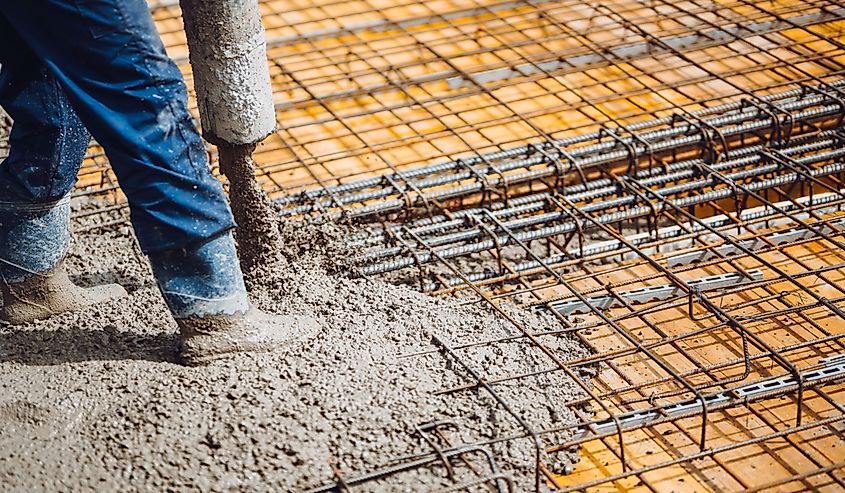

Given that buildings in Rome date back over 2,000 years, the Romans clearly knew how to make a building last. Ancient Roman buildings withstood earthquakes, floods, and military conflicts. Researchers believe the secret to the Romans' strong buildings was a combination of ingenious design and a unique concrete formula. The ancient Romans didn't invent concrete, but they had a special formula for it.
The Romans used a mix of materials including burnt limestone, volcanic sand, water, and gravel to facilitate chemical reactions that bind the components together. This process, known as the pozzolanic reaction, is named after the city of Pozzuoli. Once the concrete was mixed, they poured it over wooden molds to form the desired structures.
Modern Day Concrete
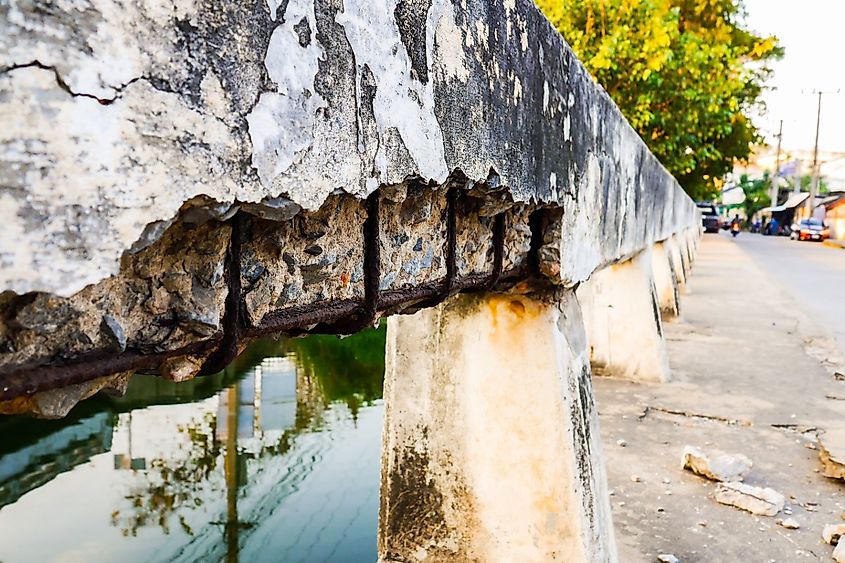

The ancient Roman methods for using concrete are similar to today's methods. Today, most concrete is a mixture called portland cement. This is a combination of silica sand, limestone, clay, chalk, and other minerals, baked at a high temperature and then crushed into a fine powder. This creates a rocky aggregate with a range of grain sizes, from sand to chunks of stone. Mixing these materials together makes the concrete strong. Adding water to the mixture binds all the ingredients together. Unlike Roman concrete, modern concrete dries significantly faster but uses steel rebar to reinforce construction. This steel, used to strengthen concrete, also weakens it over time as the metal corrodes.
Roman concrete is different than modern day concrete in a couple of ways. An important difference is that the concrete was not mixed as thoroughly. However, researchers believe this was intentional since the Romans wanted the concrete to have self-healing properties.
The Secret Ingredient
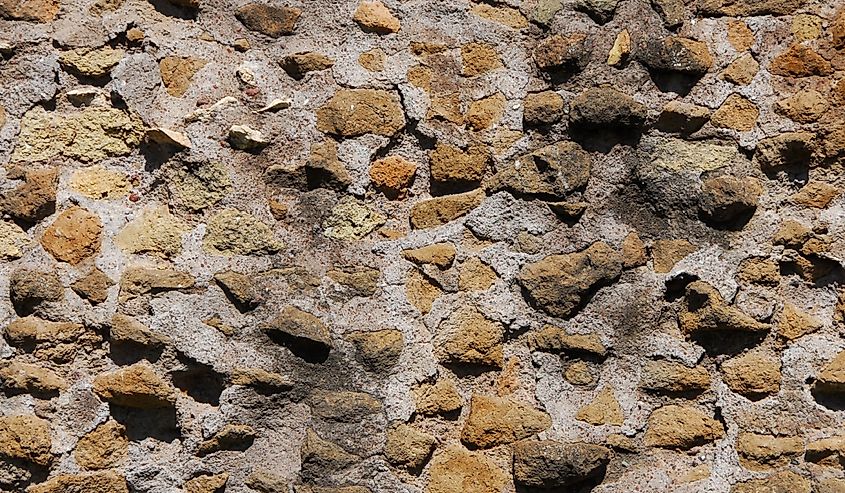

An amazing feat of ancient Roman concrete is its self-healing capabilities. Over time, water can erode concrete; however, ancient Roman buildings have survived floods. While humans don't know for sure, some scientists today think the secret ingredient in ancient Roman concrete is lime chunks. One study published by a civil and environmental engineer found that the chunks of lime studded throughout the Roman concrete are not evenly distributed.
Initially, scientists thought the Romans' concrete issues were due to improper mixing. However, some researchers now believe it was intentional. The lime chunks serve as a water-resistant barrier. When cracks occur, water infiltrates the concrete and reaches the lime pockets. The reaction between lime and water then fills in the damaged areas, providing a protective effect.
Carbon Emissions

Beyond the resilience of Roman concrete, Roman concrete also had a smaller carbon footprint, something humans can learn from. Today, cement production accounts for up to 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions by some estimates. The cement today doesn't last as long as the cement the Romans used. Often, modern-day cement crumbles away in a few decades. Studying ancient Roman methods for building allows us the opportunity to hopefully improve our own building methods.
Can't Use the Building Techniques for Skyscrapers
Ancient Roman construction techniques and materials are remarkable, but many are not suitable for modern buildings. For example, Roman concrete could fail to support heavy loads, risking the collapse of tall structures like skyscrapers without adequate support. Nonetheless, researchers are exploring new projects that incorporate the ancient Roman "self-healing" concrete, which could potentially transform construction practices. Start-up companies such as Masic are actively working to develop and utilize this innovative concrete.
Even though the ancient Romans are thousands of years behind us, they are remembered today for their strong structures. They serve as an inspiration for researchers and might even help us improve our building techniques in the future. These buildings also show the value of learning about past civilizations and other cultures.