What Is Acid Rain?
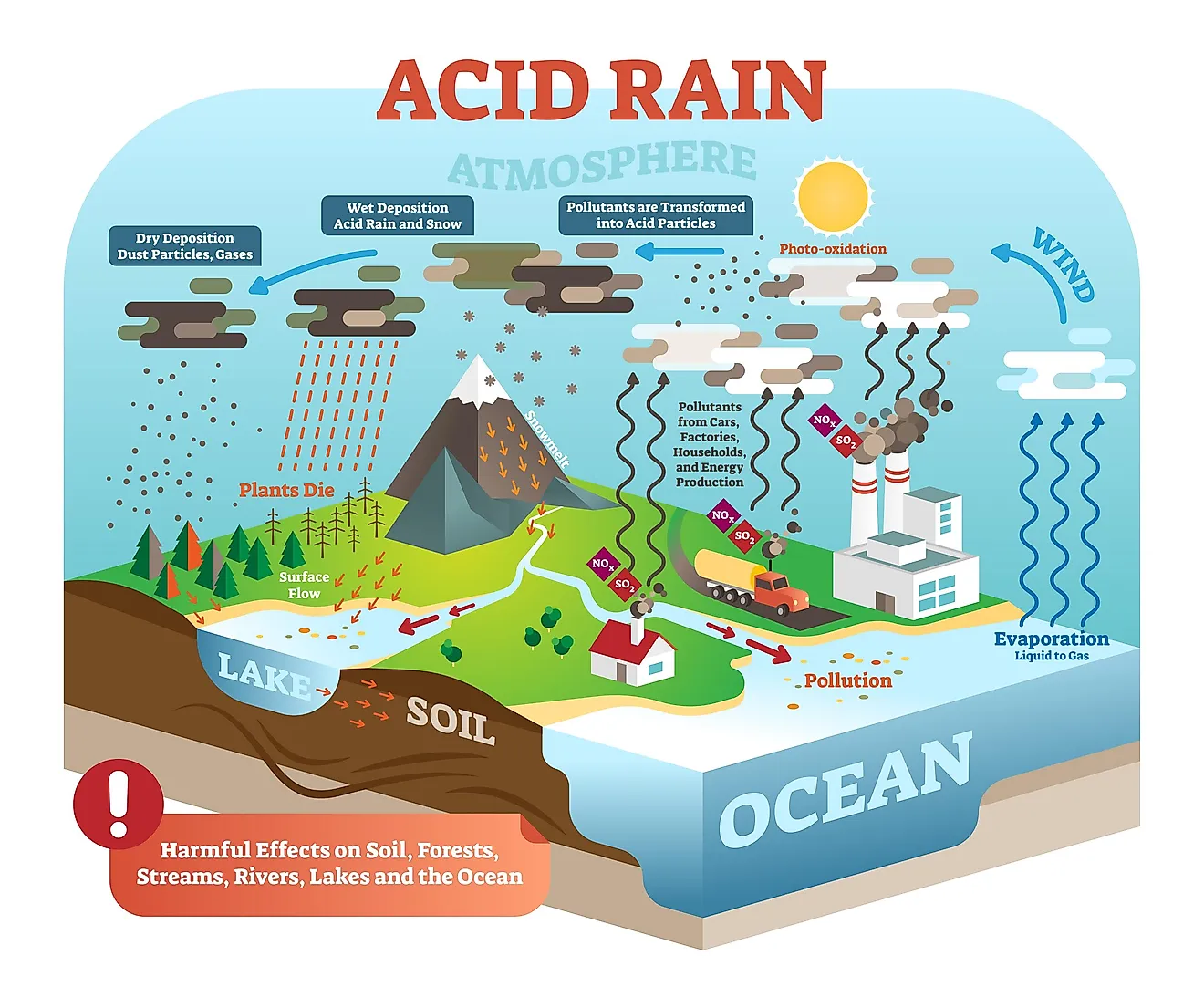
Acid rain is rainfall with a significantly altered ph. It mainly occurs due to atmospheric pollution and can be very harmful to both human-made objects and natural ecosystems, especially lakes and forests.
How Acidic Is Acid Rain?
Acid rain is atmospheric precipitation mixed with pollution elements that produce acids as reacting with the natural atmospheric gases and water, which causes the rain to become more acidic. Mainly, scientists detect high levels of nitric and sulfuric acids. The pH of ''normal'' rain is 5.6, which is slightly acidic (pure water has a pH of 7), but acid rains can have pH lower than 5, and even 4 in the areas with a lot of cars and industrial pollution.
What Causes Acid Rains?
Decaying vegetation and erupting volcanoes can, on occasion, release some chemicals that would affect the rain acidity, but the leading cause of acid rains is human activity. The main cause is the burning of fossil fuels and coal: their waste gases contain a lot of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Coal-burning power plans, transportation, and large industrial facilities are the main contributors.

Although acid-rain gases originate in the industrialized areas, they can be carried for great distances by the atmospheric movement and end up deposited over the fields and forests. Furthermore, when the acid rain pollutes water, it penetrates the soil and enters underground waters.
What Is The Impact Of Acid Rain?
The environment can sometimes adapt to the changing water acidity by changing its biosystem towards plants and animals that can exist in more acidic conditions. However, it also means losing many unique biomes, such as in the Rocky Mountains and some parts of the northwest and the southeast US.
Some fish and aquatic animals that reproduce in water have difficulties adjusting to growing acidity. Evergreen forests suffer the most among plants. Dead and crippled trees are a typical sight in areas regularly affected by acid rains. Acid can leech or change nutrients in the soil that plants need to grow, or change them so drastically that they can no longer be absorbed.
Buildings And Monuments Also Suffer From Acid Rains
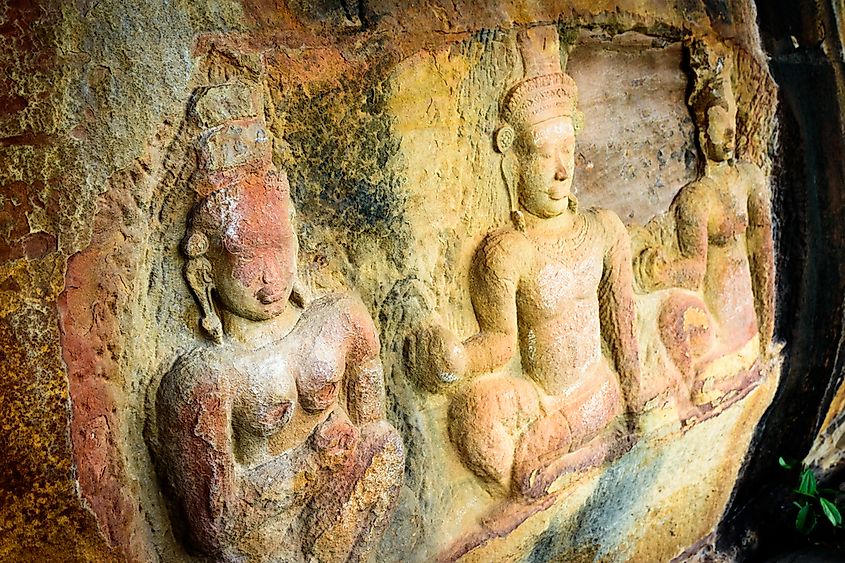

Acid precipitation dissolved stone or alters its appearance. Pollution and acid rain accelerate the corrosion of buildings and monuments, causing concern about the loss of historical buildings. Even sandstone is affected, but marble and limestone, often used for the architecture of importance, suffer the most. When acids in polluted air react with the calcite in those materials, it dissolves, and surfaces become eroded, lose its gloss, color, and delicate carvings.
What Regions Have The Most Acid Rain?
The Northeastern United States suffer from heightened acidity the most due to the dense population, high numbers of large cities, and distribution of the power plants and industrial production. The winds and storms bring pollution from those areas to the Midwest. China, which uses a lot of coal, has done a great job of cutting the sulfur dioxide emissions, which has decreased 75% during the last decade. India, however, increased its emissions by 50%. Poland is one of the examples where acidic rains have destroyed forests.
What Can Be Done To Stop Acid Rains?
As long as fuel fossils remain in widespread use, acid rains will be a problem. The only way to stop acid rains is by decreasing the release of the gases and pollutants that cause it by burning fewer fossil fuels. The US is working on implementing the Clean Air Act of 1990, attempting to drive sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides down. But recovery will likely take a long time since the chemical composition of the soil and groundwater, affected by the acid rains, is not a speedy process.