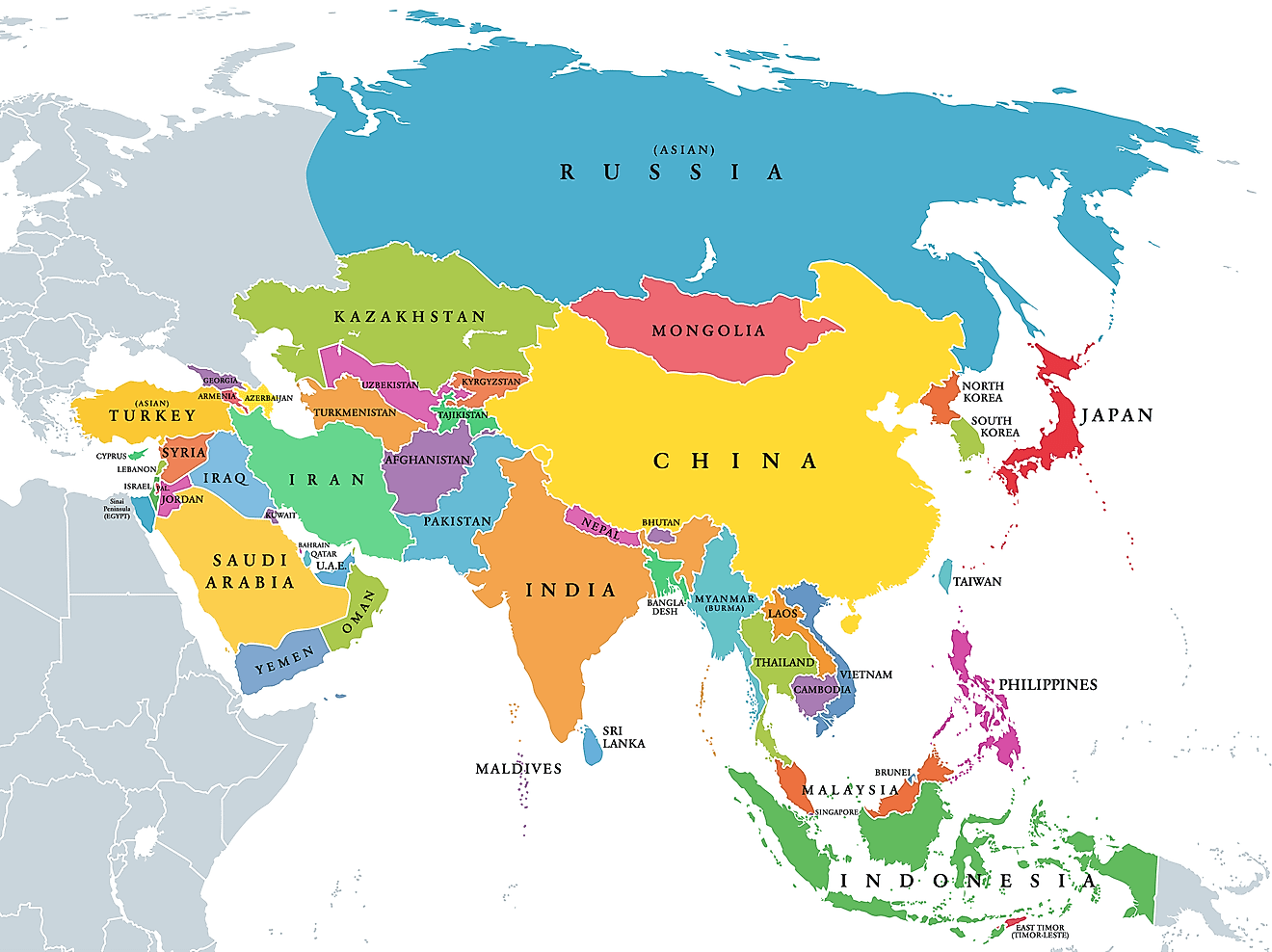
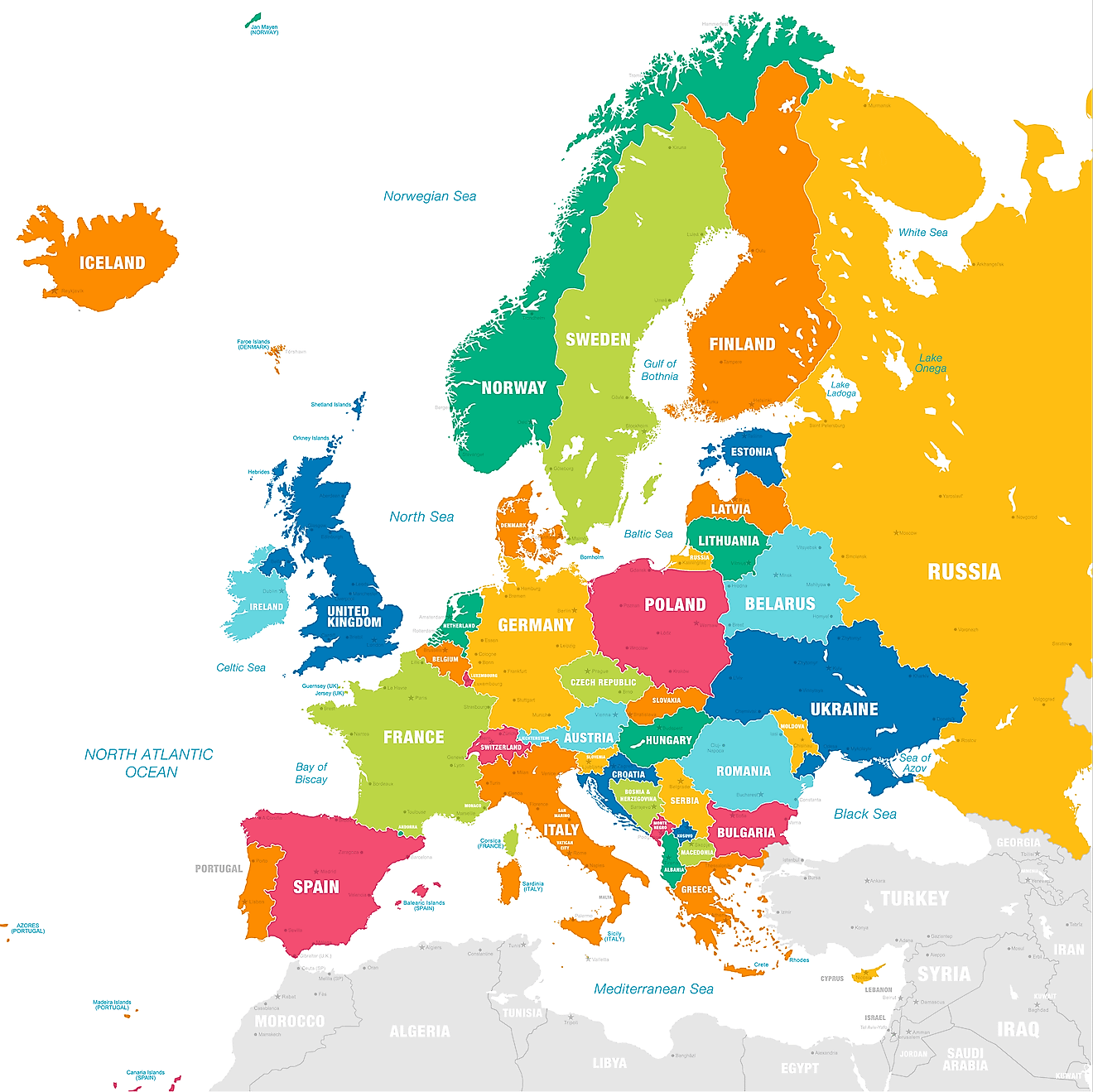
The Geoscheme of the United Nations
The United Nations Geoscheme, a tool widely utilized by organizations and governments, promotes a detailed worldview by fragmenting continents into more manageable portions. Although initially designed for statistical purposes by the United Nations Statistics Division, its application has extended beyond this original intent. The Geoscheme also serves as a reference point for the Universal Periodic Review, a process that has witnessed some countries pressuring others into alignment - a concerning trend. To further grasp this tool's significance, one must first review and understand the Geoscheme's inner mechanics, then consider a few comparisons with other methods, and last, take note of its use cases and capacity for impact. Click here for a quick view of the table: All countries organized by Geoscheme classification.
The UN Geoscheme And Other Classification Systems
The UN Geoscheme is one of many systems that observe the world's continents and territories. It categorizes countries and regions based on geographic and geopolitical criteria, providing a framework for statistical analysis. Other methods, such as the CIA World Factbook, offer a different approach.
The CIA World Factbook is more comprehensive and provides detailed information on various topics, offering a broader understanding of each country. It includes facts about their geography, demographics, government, economy, and more. Produced by the CIA, an agency of the United States government, its information may have a particular perspective or emphasis.
The World Bank regional classification is another widely used method for categorizing countries and regions. It is used mainly in the context of economic and development analysis, and it may not encompass all geopolitical or cultural considerations.
The UN Geoscheme, instead, is part of the M49 system, a classification system that provides a standard framework for categorizing and organizing countries and regions worldwide. Assigning numerical codes and acronyms, it offers a more scientific approach focused on its primary statistics purpose.
Impact Of Geoscheme On International Politics And Economy

The UN Geoscheme is used in statistical case studies to provide a standardized framework for organizing and analyzing data at regional and global levels, from providing advice on climate change challenges to ensuring consistency and interoperability in reporting and analysis to enabling all kinds of comparisons between territories. The UN Geoscheme can also contribute to regional cooperation and collaboration in addressing human rights issues. Policymakers and stakeholders can use this information to identify similarities and differences in human rights practices, policy approaches, and challenges between regions.
The Universal Periodic Review (UPR) actively employs the UN Geoscheme as a differentiation between regions and subregions during the periodic confrontations of policymakers; it is created and maintained by the United Nations. Its impact, though, is not always achieved fairly. The troubling trend of Western countries using the UPR system to pressure other regions and countries to change their laws is a recurring problem. During the review, countries are compared to others to determine the next step in implementing a standard line in policymaking. In some cases, Western countries put pressure on developing countries to align and change their laws on complicated topics such as abortion, human rights, and SOGI (UN acronym for LGBTQ+) freedom. However, these aforementioned countries, such as the United States, are still in the process of determining their own stances on these topics, so their influence could push sensitive issues either way.
The UN Geoscheme can have a significant economic impact. This standard system has influenced Australia, Israel, Türkiye, and Russia. It plays a crucial role in trade, investment, and development cooperation and can affect their economic ties and partnerships with neighboring nations. Similarly, for countries spanning multiple regions like Türkiye or Russia, the UN Geoscheme classification plays a role in influencing their economic policies, access to markets, and overall economic development.
How Regions And Subregions Are Grouped
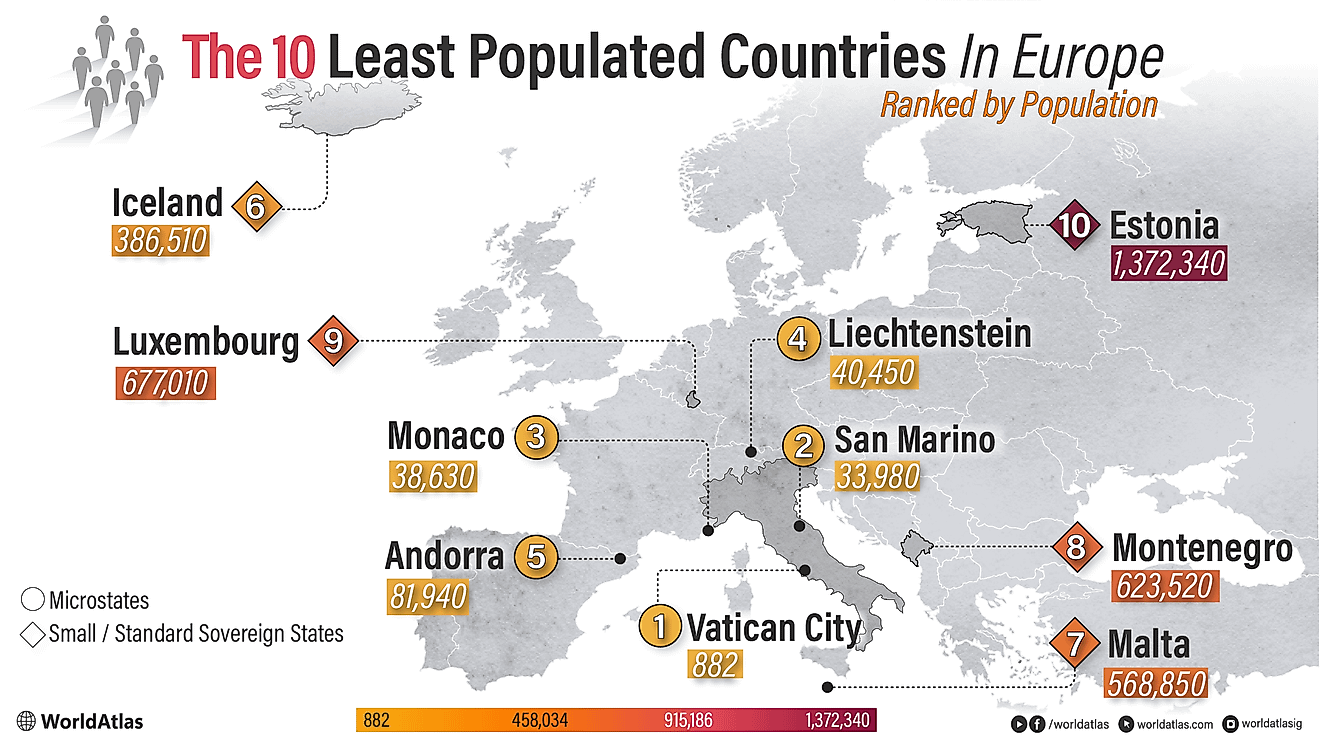
The UN Geoscheme groups areas into regions and subregions based on continental boundaries and geographical proximity, aligning regions with the continents of Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe, and Oceania. Also, it takes into account existing regional groupings and organizations. It considers regional initiatives, alliances, and organizations that countries participate in. This criterion reflects the geopolitical and collaborative dynamics among nations within a specific region. Interestingly some subregions are furtherly divided into intermediate regions. For example, Sub-Saharan Africa hosts four intermediate regions: Eastern Africa, Middle Africa, Southern Africa, and Western Africa.
Additionally, cultural, historical, and political factors can influence the classification of areas. Countries with shared cultural or historical backgrounds, linguistic connections, or affiliations may be grouped. Economic integration and trade patterns between countries that engage in significant regional trade or are part of economic integration agreements can also influence the classification. For trivia, Antarctica is the only geographical region comprising no sub-regions or country-level areas (despite attempts at territorial claims from various countries).
Ultimately, the UN Geoscheme balances geographic, geopolitical, and socio-economic factors in defining regions and subregions. Some of these factors are dynamic and might need adjustments in the future to reflect evolving situations.
Transcontinental Countries
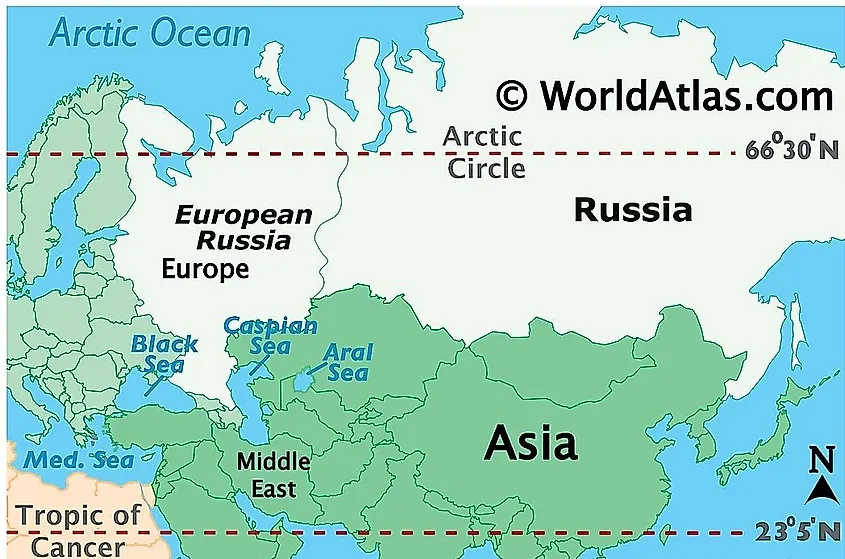
The UN Geoscheme classifies some areas and countries into specific subregions or regions despite them spanning multiple continents. Also, political dynamics and historical affiliations can contribute to the transcontinental classification. These countries that straddle more than one continent are known as transcontinental or intercontinental, despite their categorization as one-or-the-other. Transcontinental countries can be contiguous or non-contiguous. They are contiguous when they span directly over more than one continent, and they are non-contiguous when a portion of the territory is separated by a body of water or by other countries. For example, Egypt occupies a part of Asia despite being classified only as African. The Russian Federation, Türkiye, Georgia, Kazakhstan, and Azerbaijan all span both Asia and Europe; for Russia, it is considered as part of Eastern Europe for statistical simplicity. Furthermore, Panama, Colombia, Trinidad and Tobago, and Venezuela are both contiguously and non-contiguously over the North America and South America boundary.
The UN Geoscheme provides a standardized system for organizing and analyzing data, facilitating statistical reporting, and regional analysis. Many organizations use it as their standard classification system to investigate the world and differentiate its regions. While it does not directly impact geopolitics or policymaking, it indirectly influences these areas through the UPR. However, it is essential to recognize that the geopolitical landscape is complex and multifaceted, and the UN Geoscheme is just one tool among many used to understand the diverse dynamics of our world.
All Countries And Areas Organized By The Regions, Sub-Regions, And Intermediate Regions Of The UN Geoscheme
| Country or Area | Intermediate Region | Sub-region | Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antarctica | |||
| Algeria | Northern Africa | Africa | |
| Angola | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Benin | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Botswana | Southern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| British Indian Ocean Territory | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Burkina Faso | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Burundi | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Cabo Verde [Cape Verde] | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Cameroon | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Central African Republic | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Chad | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Comoros | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Congo [Republic of the Congo] | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Côte d'Ivoire [Ivory Coast] | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Djibouti | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Egypt | Northern Africa | Africa | |
| Equatorial Guinea | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Eritrea | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Eswatini [Swaziland] | Southern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Ethiopia | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| French Southern Territories | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Gabon | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Gambia | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Ghana | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Guinea | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Guinea-Bissau | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Kenya | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Lesotho | Southern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Liberia | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Libya | Northern Africa | Africa | |
| Madagascar | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Malawi | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Mali | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Mauritania | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Mauritius | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Mayotte | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Morocco | Northern Africa | Africa | |
| Mozambique | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Namibia | Southern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Niger | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Nigeria | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Réunion | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Rwanda | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Saint Helena [Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha] | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Sao Tome and Principe | Middle Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Senegal | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Seychelles | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Sierra Leone | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Somalia | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| South Africa | Southern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| South Sudan | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Sudan | Northern Africa | Africa | |
| Togo | Western Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Tunisia | Northern Africa | Africa | |
| Uganda | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| United Republic of Tanzania | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Western Sahara | Northern Africa | Africa | |
| Zambia | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Zimbabwe | Eastern Africa | Sub-Saharan Africa | Africa |
| Anguilla | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Antigua and Barbuda | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Argentina | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Aruba | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Bahamas | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Barbados | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Belize | Central America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Bermuda | Northern America | Americas | |
| Bolivia (Plurinational State of) | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Bouvet Island | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Brazil | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| British Virgin Islands | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Canada | Northern America | Americas | |
| Cayman Islands | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Chile | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Colombia | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Costa Rica | Central America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Cuba | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Curaçao | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Dominica | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Dominican Republic | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Ecuador | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| El Salvador | Central America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Falkland Islands (Malvinas) | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| French Guiana | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Greenland | Northern America | Americas | |
| Grenada | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Guadeloupe | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Guatemala | Central America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Guyana | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Haiti | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Honduras | Central America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Jamaica | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Martinique | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Mexico | Central America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Montserrat | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Nicaragua | Central America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Panama | Central America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Paraguay | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Peru | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Puerto Rico | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Saint Barthélemy | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Saint Lucia | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Saint Martin (French part) | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Saint Pierre and Miquelon | Northern America | Americas | |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Sint Maarten (Dutch part) | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Suriname | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Trinidad and Tobago | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Turks and Caicos Islands | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| United States of America | Northern America | Americas | |
| United States Virgin Islands | Caribbean | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Uruguay | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of) | South America | Latin America and the Caribbean | Americas |
| Afghanistan | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| Armenia | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Azerbaijan | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Bahrain | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Bangladesh | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| Bhutan | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| Brunei Darussalam | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Cambodia | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| China | Eastern Asia | Asia | |
| China, Hong Kong Special Administrative Region | Eastern Asia | Asia | |
| China, Macao Special Administrative Region | Eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Cyprus | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Democratic People's Republic of Korea [North Korea] | Eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Georgia | Western Asia | Asia | |
| India | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| Indonesia | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Iran (Islamic Republic of) | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| Iraq | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Israel | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Japan | Eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Jordan | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Kazakhstan | Central Asia | Asia | |
| Kuwait | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Kyrgyzstan | Central Asia | Asia | |
| Lao People's Democratic Republic | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Lebanon | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Malaysia | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Maldives | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| Mongolia | Eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Myanmar [Burma] | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Nepal | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| Oman | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Pakistan | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| Philippines | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Qatar | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Republic of Korea [South Korea] | Eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Saudi Arabia | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Singapore | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Sri Lanka | Southern Asia | Asia | |
| State of Palestine | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Syrian Arab Republic | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Tajikistan | Central Asia | Asia | |
| Thailand | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Timor-Leste [East Timor] | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Türkiye | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Turkmenistan | Central Asia | Asia | |
| United Arab Emirates | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Uzbekistan | Central Asia | Asia | |
| Viet Nam | South-eastern Asia | Asia | |
| Yemen | Western Asia | Asia | |
| Åland Islands | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Albania | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Andorra | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Austria | Western Europe | Europe | |
| Belarus | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| Belgium | Western Europe | Europe | |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Bulgaria | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| Croatia | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Czechia [Czech Republic] | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| Denmark | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Estonia | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Faroe Islands | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Finland | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| France [French Republic] | Western Europe | Europe | |
| Germany | Western Europe | Europe | |
| Gibraltar | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Greece | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Guernsey | Channel Islands | Northern Europe | Europe |
| Holy See [Vatican City] | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Hungary | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| Iceland | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Ireland | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Isle of Man | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Italy | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Jersey | Channel Islands | Northern Europe | Europe |
| Latvia | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Liechtenstein | Western Europe | Europe | |
| Lithuania | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Luxembourg | Western Europe | Europe | |
| Malta | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Monaco | Western Europe | Europe | |
| Montenegro | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Netherlands | Western Europe | Europe | |
| North Macedonia | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Norway | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Poland | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| Portugal | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Republic of Moldova | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| Romania | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| Russian Federation | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| San Marino | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Sark | Channel Islands | Northern Europe | Europe |
| Serbia | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Slovakia | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| Slovenia | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Spain | Southern Europe | Europe | |
| Svalbard and Jan Mayen Islands | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Sweden | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| Switzerland | Western Europe | Europe | |
| Ukraine | Eastern Europe | Europe | |
| United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | Northern Europe | Europe | |
| American Samoa | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| Australia | Australia and New Zealand | Oceania | |
| Christmas Island | Australia and New Zealand | Oceania | |
| Cocos (Keeling) Islands | Australia and New Zealand | Oceania | |
| Cook Islands | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| Fiji | Melanesia | Oceania | |
| French Polynesia | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| Guam | Micronesia | Oceania | |
| Heard Island and McDonald Islands | Australia and New Zealand | Oceania | |
| Kiribati | Micronesia | Oceania | |
| Marshall Islands | Micronesia | Oceania | |
| Micronesia (Federated States of) | Micronesia | Oceania | |
| Nauru | Micronesia | Oceania | |
| New Caledonia | Melanesia | Oceania | |
| New Zealand | Australia and New Zealand | Oceania | |
| Niue | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| Norfolk Island | Australia and New Zealand | Oceania | |
| Northern Mariana Islands | Micronesia | Oceania | |
| Palau | Micronesia | Oceania | |
| Papua New Guinea | Melanesia | Oceania | |
| Pitcairn [Pitcairn Islands] | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| Samoa | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| Solomon Islands | Melanesia | Oceania | |
| Tokelau | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| Tonga | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| Tuvalu | Polynesia | Oceania | |
| United States Minor Outlying Islands | Micronesia | Oceania | |
| Vanuatu | Melanesia | Oceania | |
| Wallis and Futuna Islands | Polynesia | Oceania |