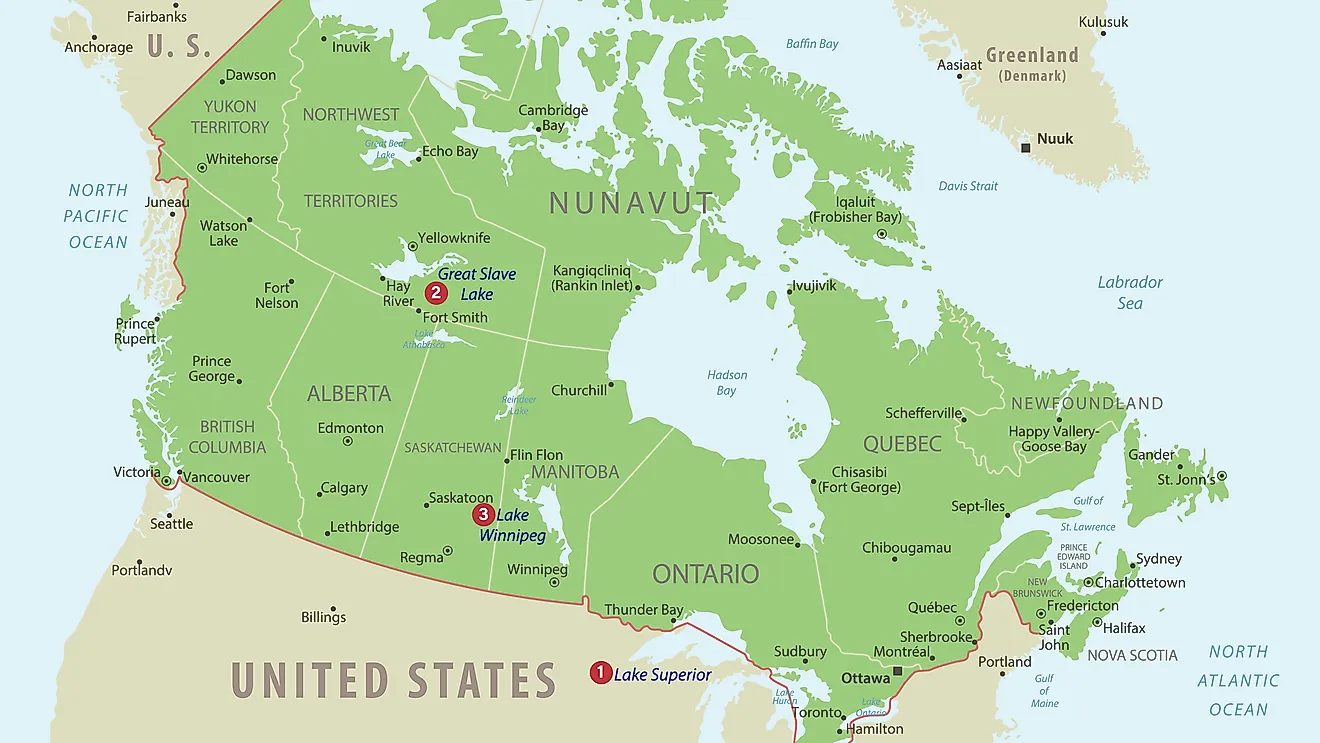
The Largest Lakes In Australia
Australia is a vast and arid landscape generally associated with desert ecosystems or coastal regions. It does, however, have many large lakes throughout its territories. Due to the climate, most of these lakes are saline, and/or endorheic. Their water levels fluctuate with the seasons, and the heat in dry season means salt levels are high in most areas. Here is a compiled list of the 8 largest Lakes in Australia by state/territory:
| State/Territory | Lake | Area (in km2) |
|---|---|---|
|
South Australia |
Lake Eyre (salt) |
9690 |
|
Western Australia |
3494 |
|
|
Northern Territory |
Lake Amadeus (salt) |
1032 |
|
New South Wales |
542 |
|
|
Tasmania |
272 |
|
|
Queensland |
220 |
|
|
Victoria |
209 |
|
|
Australian Capital Territory |
7.2 |
|
Lake Eyre/Kati Thanda (South Australia)
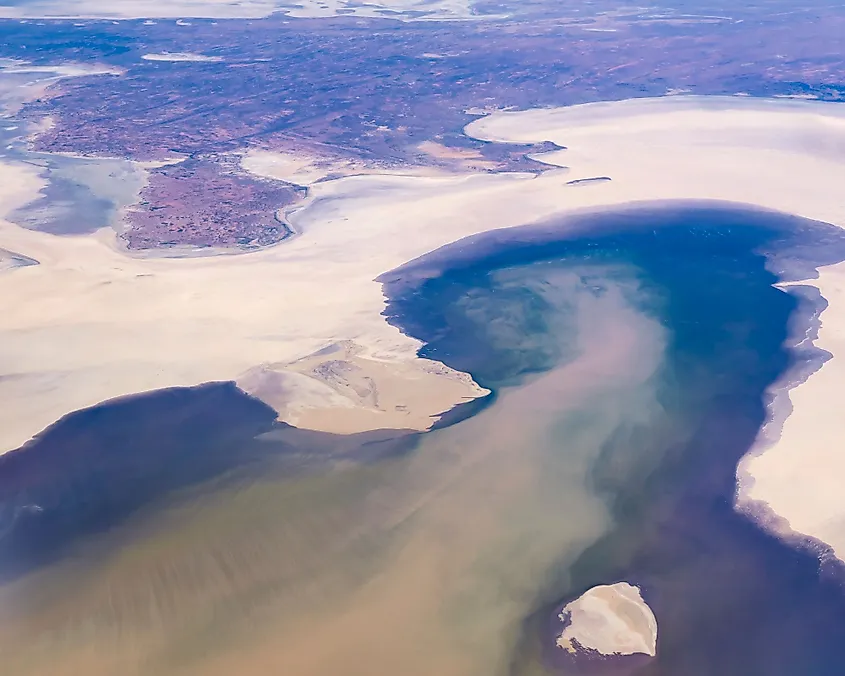

Officially referred to as Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre, Lake Eyre is situated in South Australia and covers an area of 9690 sq. km. Lake Eyre is an endorheic and salt lake, which is mainly a dried basin for most of the year but fills with water during wet seasons becoming the largest lake in Australia. Lake Eyre, situated in the Far North region of South Australia, also sits at approximately 15 meters below sea level, which is considered the lowest natural point in Australia. Since the lake has a very low water level in dry seasons and is highly saline, it does not sustain much permanent wildlife other than phytoplankton. When it is filled in the wet season, it becomes a popular stopping place for several migratory birds. Some of the notable birds like Australian pelicans, banded stilts, Caspian terns, Red-necked avocets, red-necked stints, sharp-tailed sandpipers, silver gulls, etc are found here when the lake is at its highest levels. Lake Eyre also falls under two protected areas: the Elliot Price Conservation Park and the Kati Thanda-Lake Eyre National Park both of which ensure the conservation and protection of the lake and its wildlife.
Lake Mackay (Western Australia)
Also referred to as Wilkinkarra by the native Pintupi people, Lake Mackay is another ephemeral salt lake in Australia, and one of many lakes that are found in the Pilbara and the northern portion of Western Australia’s Goldfields-Esperance region and the Northern Territory. The lake’s location within the Great Sandy Desert means that it often has very low water levels, but when full, it measures an average of 3,494 square kilometers, making it the largest lake in Western Australia. The lake has a prominent population of algae but is also very saline. The surface of the lake is often white and highly reflective, due to the presence of salt, while the algae create dark patches under the water’s surface.
Lake Amadeus (Northern Territory)
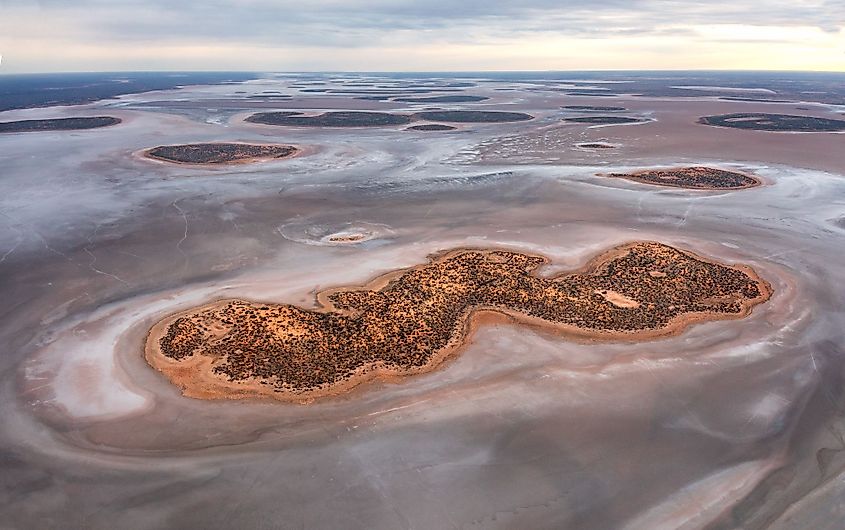

Lake Amadeus is another vast salt lake that is situated in the southwestern corner of Australia’s Northern Territory, approximately 50km to the north of Uluru/Ayers Rock. The lake covers an area of 1032 sq. km and forms a part of the larger Amadeus Basin. Lake Amadeus has a length of 180km and a maximum width of 10km, making it Northern Territory’s largest salt lake. The region where the lake is situated is exceptionally arid, and the lake contains more than 600 million tonnes of salt, making it an extremely saline lake. The harsh conditions and high salinity of the lake make it a relatively hostile environment for wildlife.
Lake Garnpung (New South Wales)
Covering an area of 542 sq. km, Lake Garnpung forms a part of the Willandra Lakes region in the western part of the Australian state of New South Wales. The lake is situated at an elevation of 106m above sea level. The Garnpung Lake is located about 27km to the north of Lake Mungo National Park.
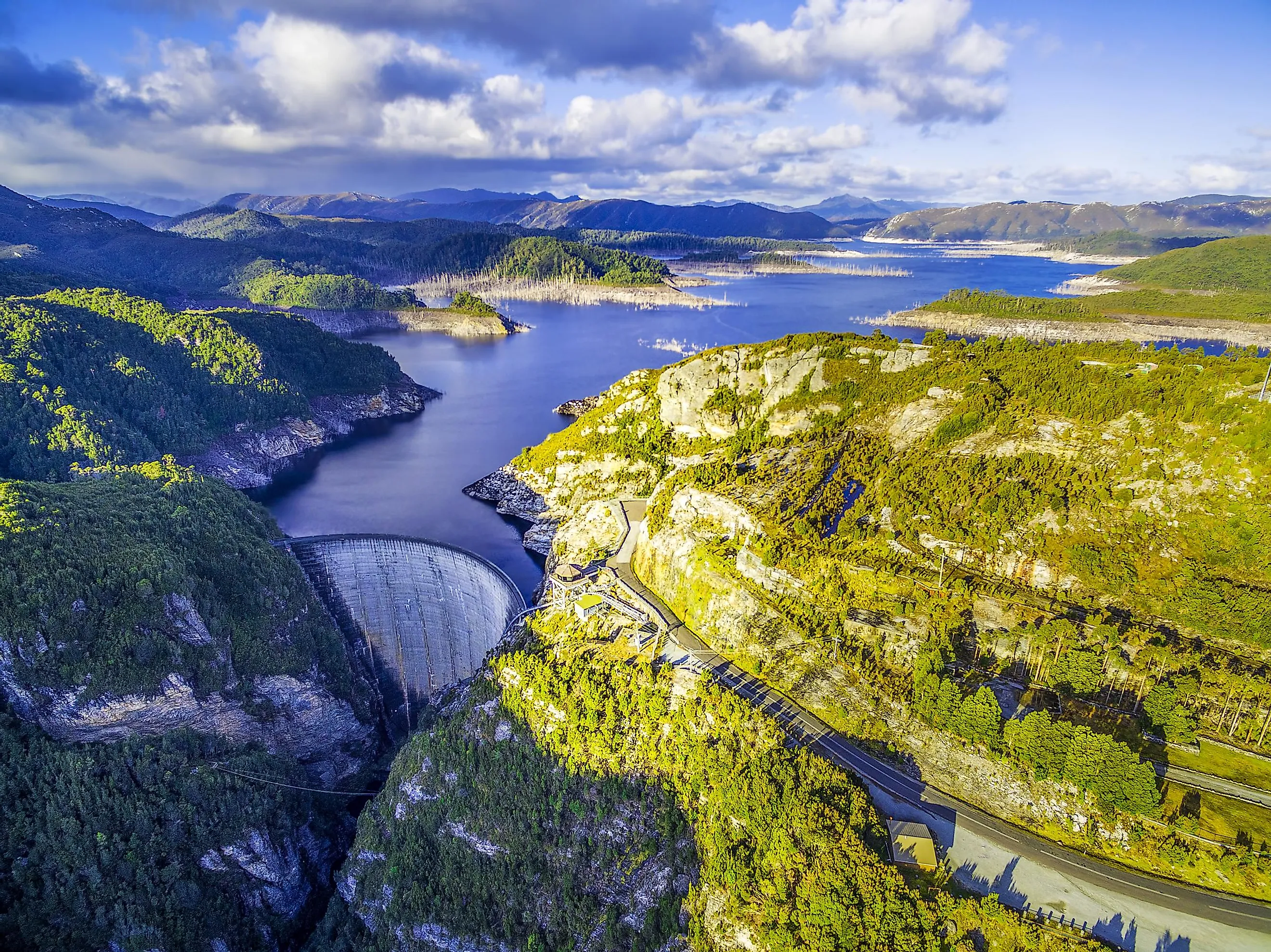
Lake Gordon (Tasmania)
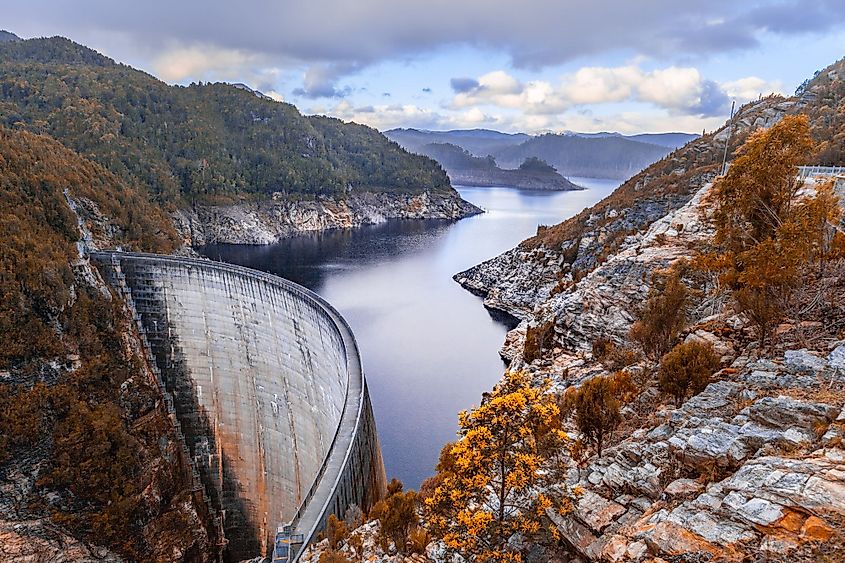

Lake Gordon is an artificial reservoir created by the damming of the Gordon River by the 140m high Gordon Dam. The reservoir is located in the southwest region of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Covering an area of 278 sq. km, Lake Gordon is considered the largest lake in Tasmania that has a catchment area of 1,280 sq. km and a storage capacity of 12.5 cubic kilometers of water. The McPartlans Pass Canal links Lake Gordon with Lake Pedder. The reservoir was built in 1974 and is currently managed by Hydro Tasmania.
Lake Dalrymple (Queensland)
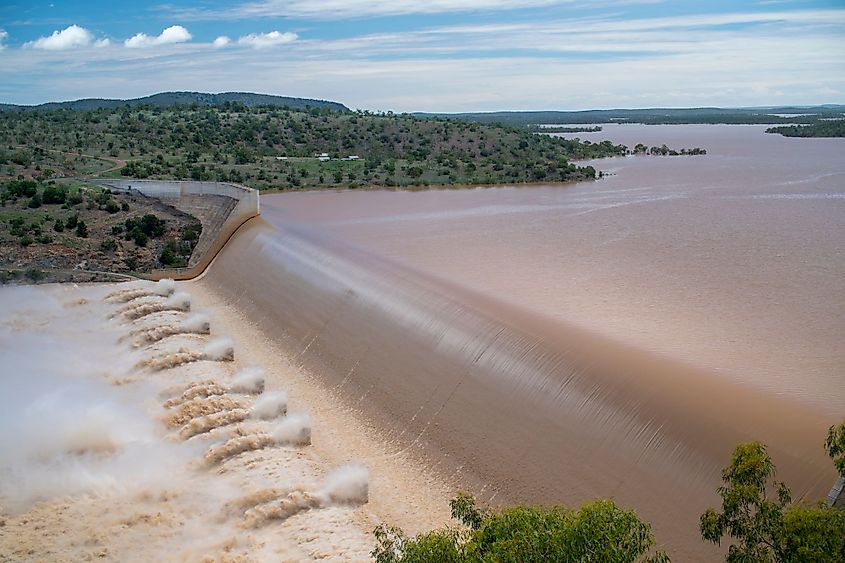

Lake Dalrymple is a man-made reservoir created by the damming of the Burdekin River by the 876m long Burdekin Falls Dam. The reservoir is situated in the southwestern part of Ayr and Home Hill towns in the northern portion of the Australian state of Queensland. Lake Dalrymple covers an area of 224 sq. km and has a catchment area of 114,220 sq. km. The lake has a maximum storage capacity of 1,860,000 megalitres of water. Lake Dalrymple is situated at an elevation of 154m and the waters of the lake reaches a maximum depth of 40m. Lake Dalrymple serves as a popular tourist destination and offers many recreational activities such as fishing, boating, water sports, etc for its visitors.
Lake Corangamite (Victoria)
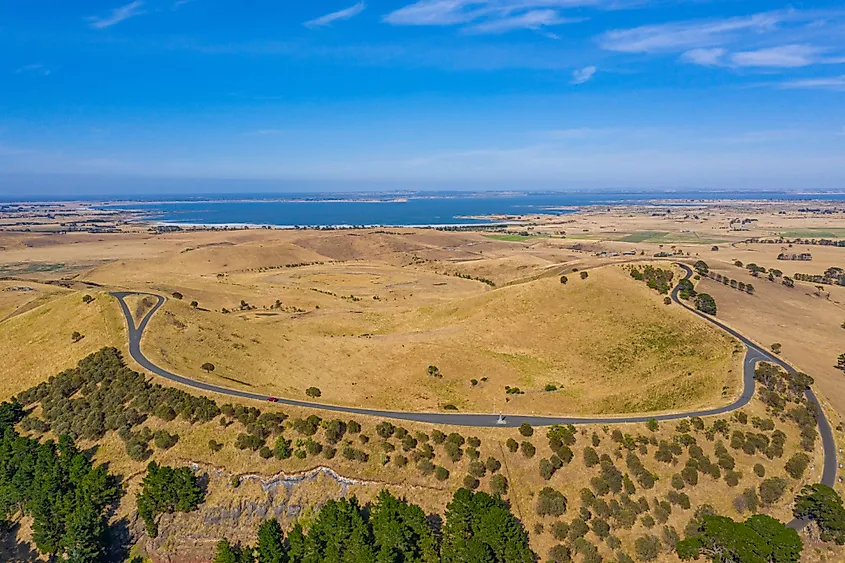

Also referred to as Kronimite by the indigenous people, Lake Corangamite is a hypersaline endorheic lake that is situated close to the city of Colac in the Western District of the Australian state of Victoria. Covering an area of 209 sq. km, Lake Corangamite is considered the largest permanent saline lake in Australia, which has a length of 150km, an average depth of 5m, and reaches a maximum depth of 7m. The lake forms a part of Victoria’s Western District Lakes that have been designated as “wetlands of international importance” under the Ramsar convention. Lake Corangamite Complex has also been recognized by BirdLife International as an Important Bird Area as it often supports an internationally significant number of waterbirds.
Lake Burley Griffin (Australian Capital Territory)
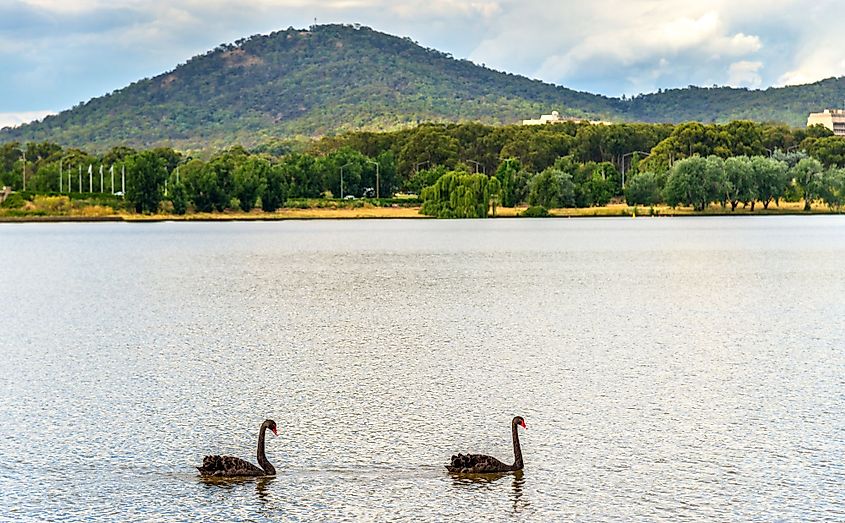

Lake Burley Griffin is a man-made reservoir that has been created by the damming of the Molonglo River by the 319m long Scrivener Dam. The lake is situated in the heart of the Australian capital city of Canberra. Covering an area of only 7.2 sq. km, Lake Burley Griffin is 11km long and has a maximum width of 1.2km. The lake reaches a maximum depth of 18m at its deepest point that is situated close to the Scrivener Dam. Lake Burley Griffin is situated at an elevation of 556m and has a maximum storage capacity of 33,000,000 cubic meters of water. Several important institutions of Australia are situated on the shores of Lake Burley Griffin. In the warmer months, the lake serves as a popular tourist destination and offers many recreational activities like fishing, rowing, sailing, canoeing, paddle-boating, etc. At present, there are seven islands in Lake Burley Griffin. The lake has been named in the honor of Walter Burley Griffin – the famous American architect who designed the city of Canberra.