What Is La Nina?

La Niña, a Spanish phrase meaning “the little girl,” is a weather phenomenon that is the straight reverse of El Niño, which is also Spanish and means “the little boy.” Sometimes, people have described La Niña as the anti-El Niño or El Viejo (the old man). This phenomenon has an impact on the weather patterns of all the regions of the world. In some places, this phenomenon causes extensive droughts while in some places it leads to the formation of deadly storms.
Impacts of La Niña
Temperature
La Niña happens when there is a significant drop in the temperatures of the sea surface in the central Pacific Ocean. When these temperatures hit lower-than-normal levels, which usually happens during the later stages of fall and the early stages of winter, a ripple effect is felt all around North America and other parts of the world. These lower-than-normal temperatures are usually between 37.4°F and 41°F
Rainfall
In some parts of the world, such as Southeast Asia in nations like India, the phenomenon leads to increased rainfall. Consequently, the agricultural activities in these areas benefit and flourish. For example, in March 2008, the temperatures dropped to around 35.6°F, which caused massive amounts of rainfall in countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines. The increase in rainfall also increases the risk of landfall risks to countries like China.
Floods
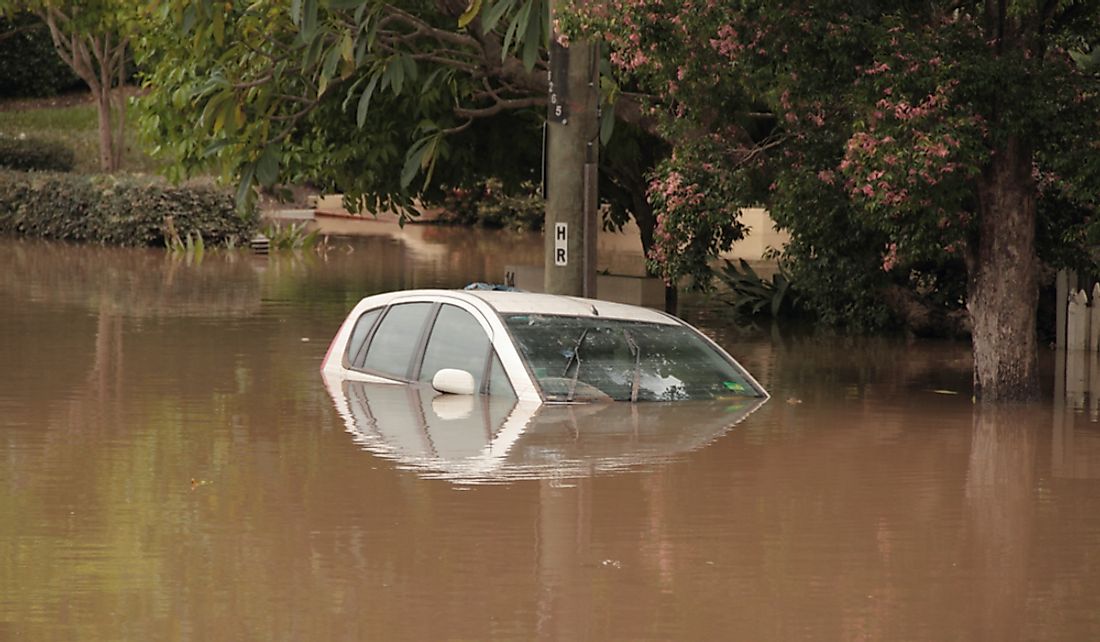
Destructive floods is another consequence of this occurrence. For instance, the 2010 La Niña led to the formation of destructive floods in certain regions of Australia such as Queensland. In 2010 Queensland experienced the most destructive floods of all time that led to the displacement of more than 10,000 people and damages worth well over $2 billion. Bolivia has also had a similar experience in the past.
Droughts
While the occurrence leads to wetter-than-normal conditions in certain parts of the world, it causes the direct opposite effect in other parts. The reduced temperature around the Central Pacific leads to reduced formations of clouds, which causes a subsequent drop in rainfall. This situation is also true for areas in the tropical South American west coast, the Gulf Coast of the US, and the low-lying regions of South America.
In East Africa, the dry conditions between December and February are caused by this phenomenon. The severity and period of these conditions are all dependent on how severe La Niña is in that year. In recent times, the unpredictability of the weather patterns means that the weather conditions are unpredictable and random compared to previous times.
La Niña in the United States
In the United States, La Niña causes more rainfall in the Pacific Northwest while the Northeast has spells of below-average temperatures. The southern tier usually experiences mild dry conditions. Other parts such as California also endure periods of dryness as La Niña prevents the delivery of snow and rain by storms. The aforementioned storms are experienced mostly in the northern parts of the US and the western and northwest parts of Canada.
Relationship Between La Niña and El Niño
A common misconception is that La Niña has to happen immediately after the occurrence of an El Niño. While this is not entirely false, the likelihood of an El Niño transitioning to a La Niña is higher should the former be strong.