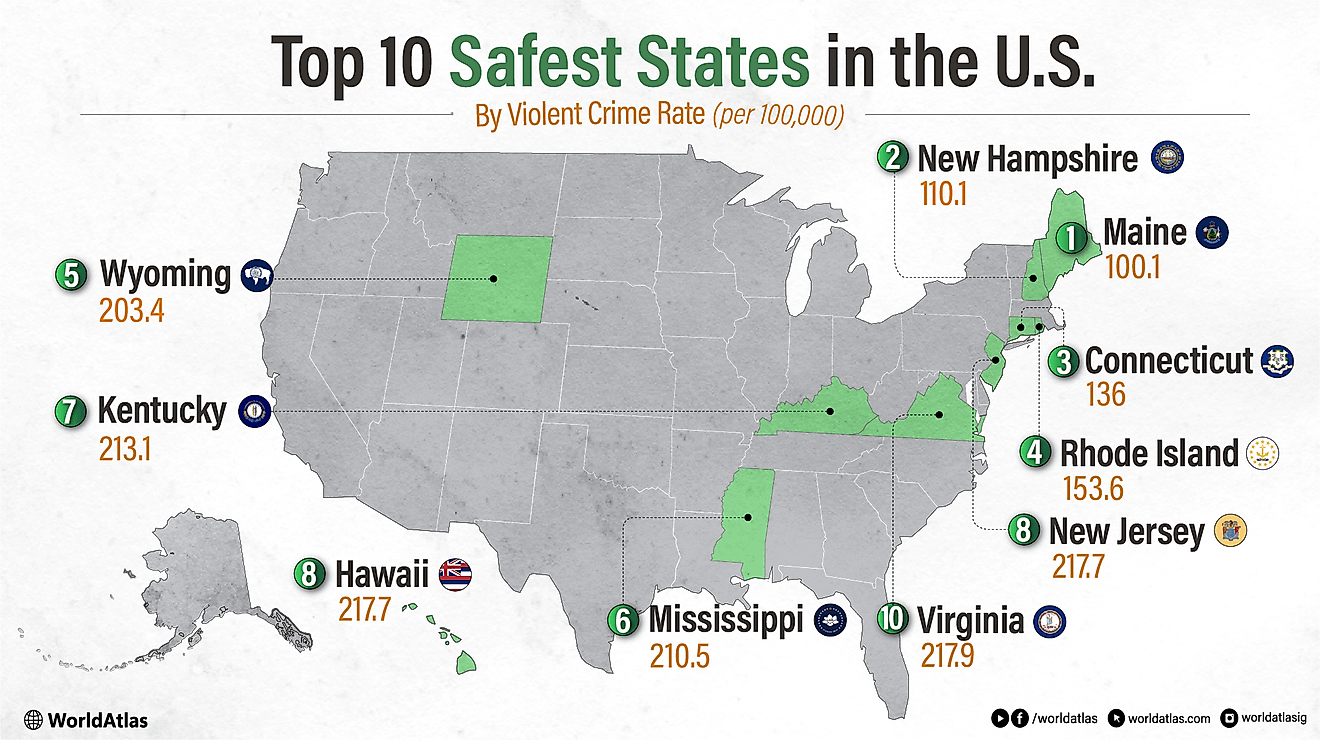
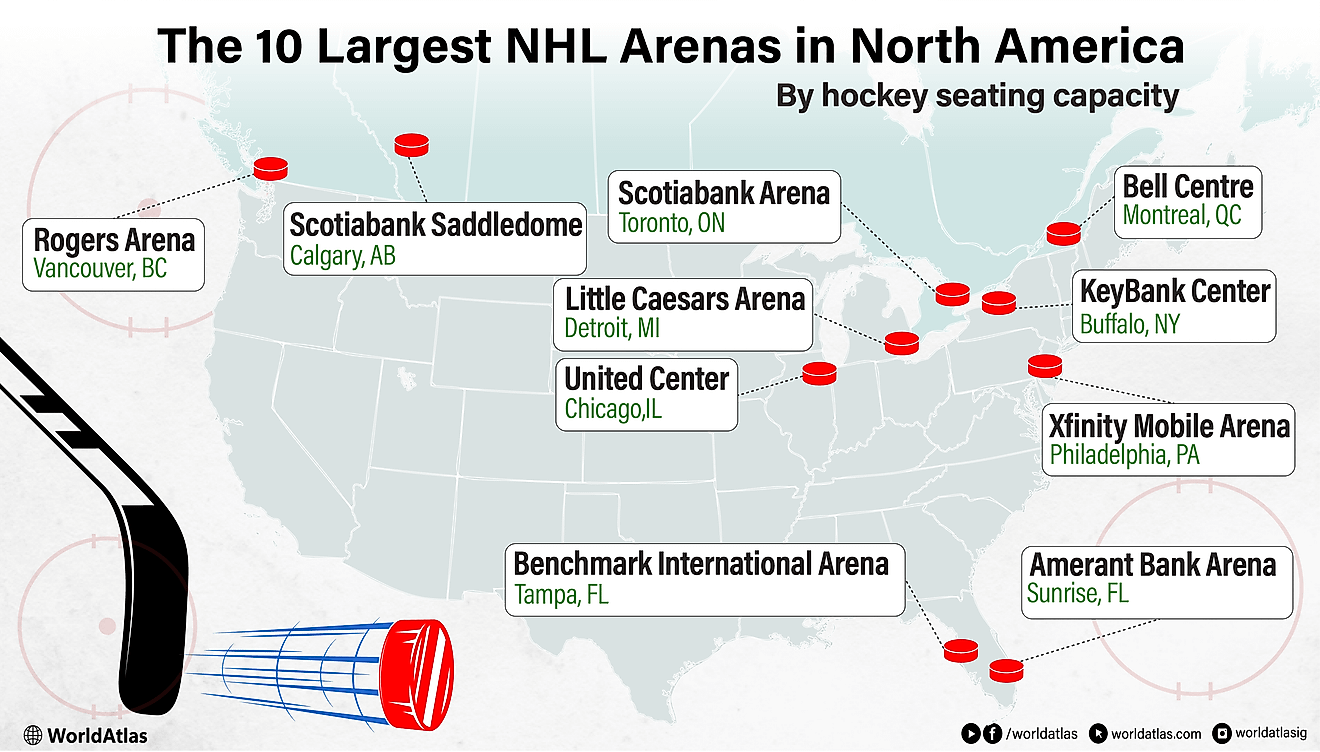
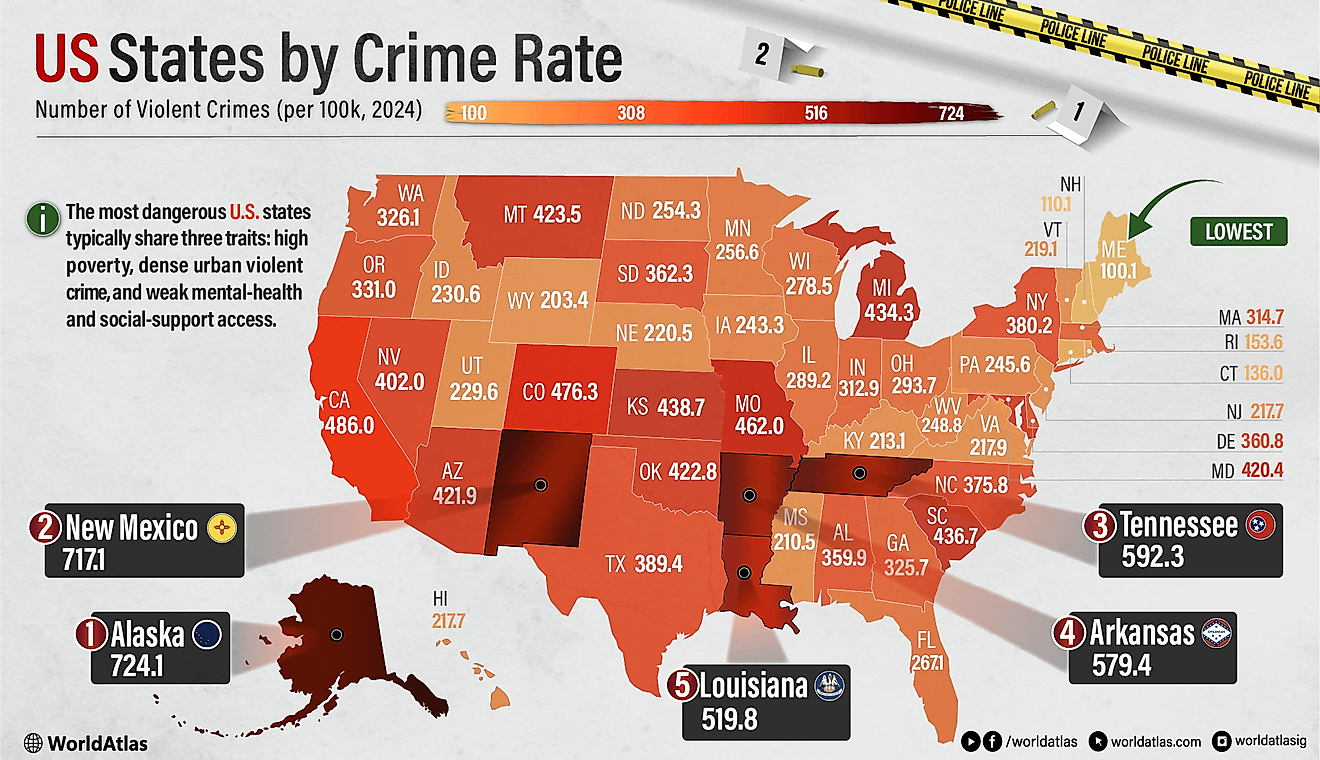
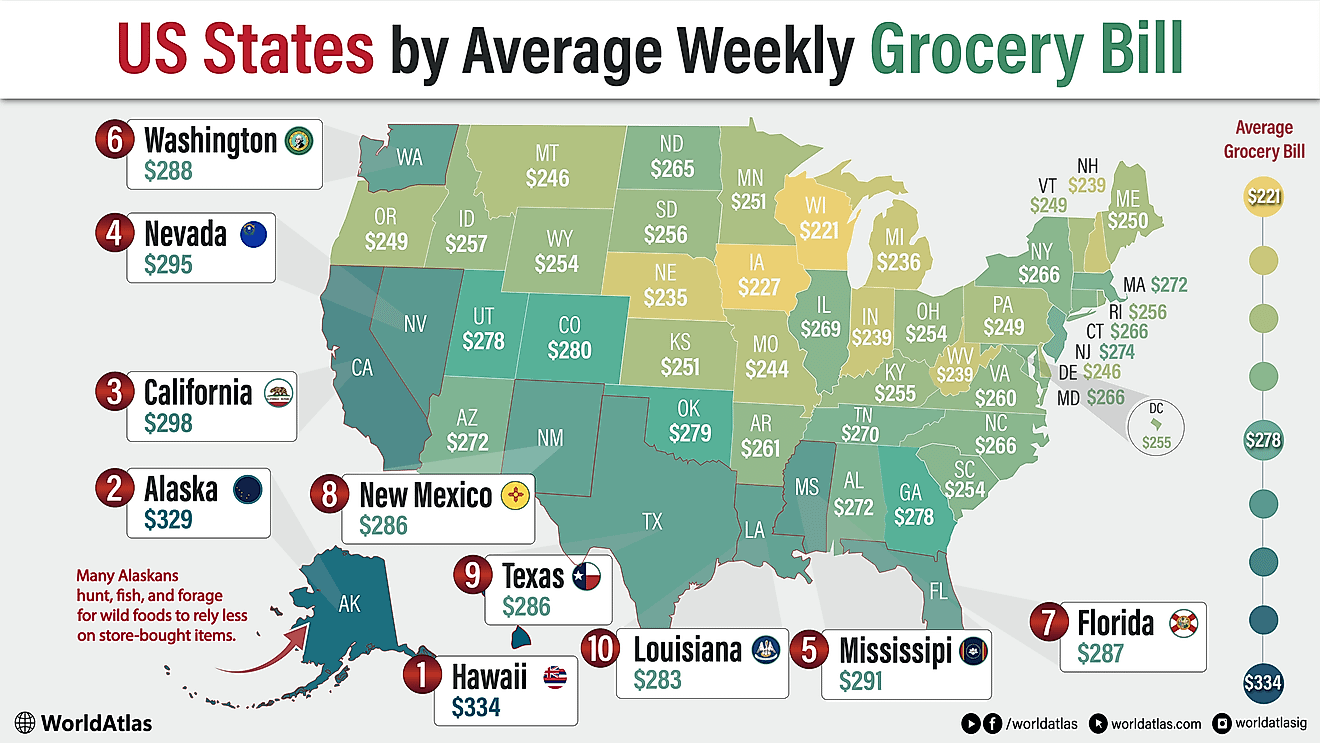
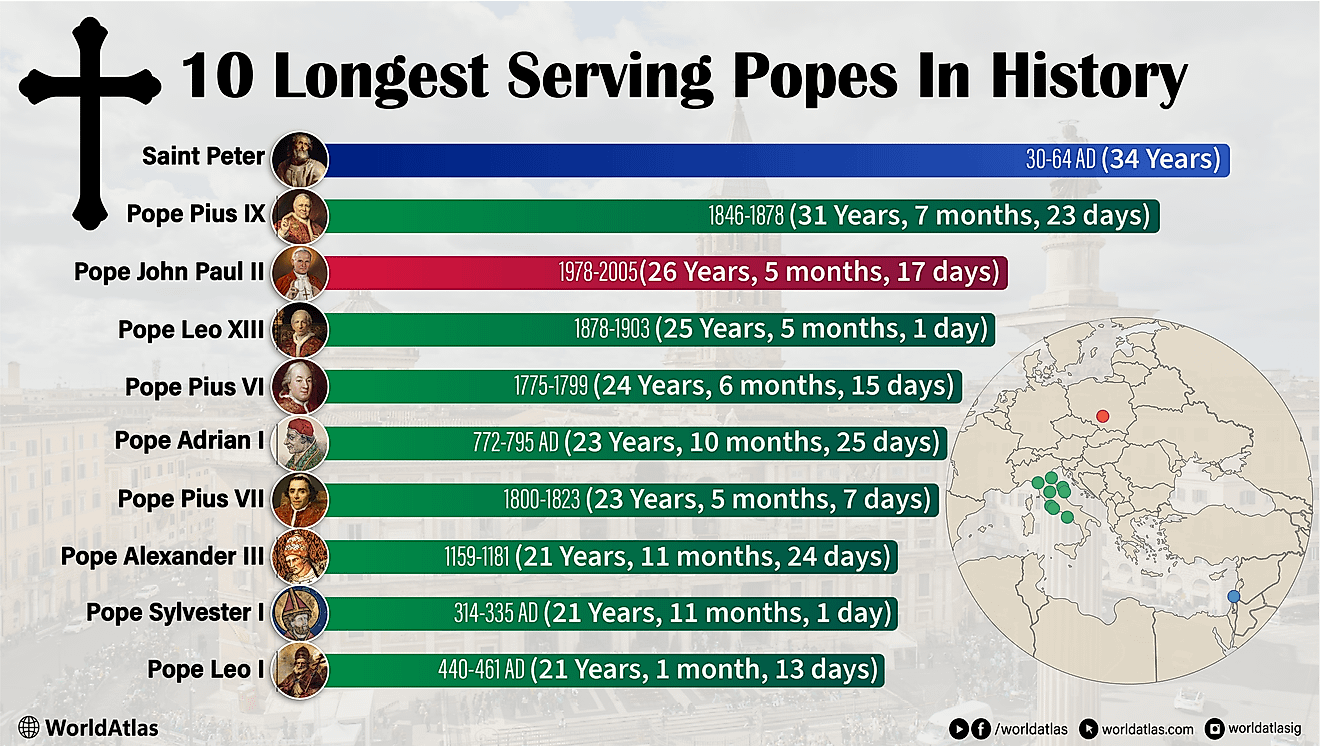
10 Countries Where Women Far Outnumber Men
While 105 boys are typically born for every 100 girls, factors like life expectancy and immigration have led some countries to have a higher proportion of women in their populations. As per a report released by the United Nations Population Division in July of 2024, some of the countries with the highest percentage of women in their populations are Moldova, with 53.98%; Latvia, with 53.68%; Armenia, with 53,61%, and Russia with 53.57%.
The 10 Countries With The Largest Proportion of Women
| Rank | Country | Percentage of Women |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Moldova | 53.98% |
| 2 | Latvia | 53.68% |
| 3 | Armenia | 53.61% |
| 4 | Russia | 53.57% |
| 5 | Ukraine | 53.50% |
| 6 | Georgia | 53.40% |
| 7 | Belarus | 53.40% |
| 8 | Lithuania | 52.85% |
| 9 | Tonga | 52.59% |
| 10 | Serbia | 52.51% |
1. Moldova - 53.98%
While 53.98% of Moldova's population is women, the country still faces significant challenges regarding gender equality. Despite higher female enrollment in tertiary education, women's participation in the labor force remains notably lower than men's, with a 10% gap. Additionally, two-thirds of unemployed individuals between the ages of 15 and 29 are women, highlighting persistent barriers in the workforce. Traditional gender norms are largely responsible for Moldova’s low rate of women’s workforce participation, with women receiving an unequal share of household and childcare responsibilities.
2. Latvia - 53.68%

With 53.68% of the population as women, Latvia’s high percentage of women can largely be attributed to general health. Under 43 years old, there are actually more men than women in the population, while after 65, there are twice the number of women than men. This discrepancy after the age of 65 is a result of poor male health, with men having a much lower life expectancy. Men are about three times more likely to smoke, with 31% of the male population smoking compared to just 10% of the female population. Men are also slightly more likely to be obese or overweight, with 62% of men being overweight or obese compared to 57% of women.
3. Armenia - 53.61%
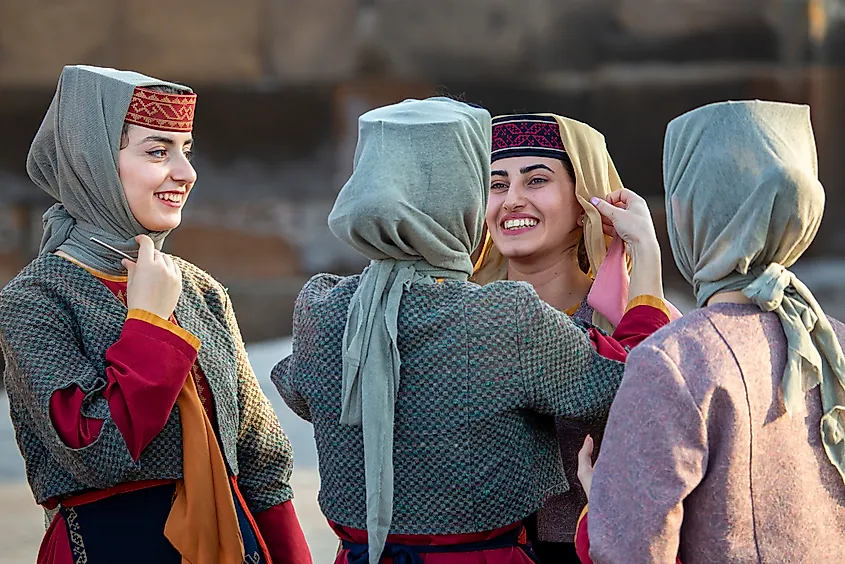

The high percentage of women in Armenia’s population, 53.61%, can largely be attributed to the fact that many Armenian men leave to go abroad in search of better work. However, despite a large female population, women continue to face barriers in the workforce and political sphere. While women represent 56% of those with higher education, their influence in the government and political sectors remains low. Women hold fewer than 10% of local governance positions and make up up just 24% of Armenia’s parliament. Additionally, the percentage of women participating in the workforce is considerably lower, with about 12% fewer women working than men.
4. Russia - 53.57%
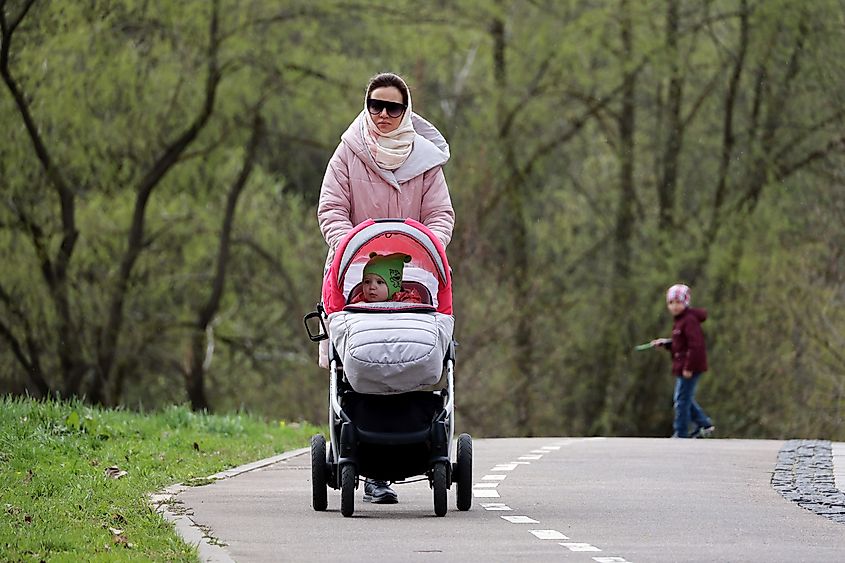

Russia has had a high percentage of women in its population since the 1950s, when many Soviet men died during World War II. This historical event continues to shape the population today, as Russia's relatively high life expectancy results in older generations being predominantly female. Additionally, due to health issues such as alcoholism, suicide, and diseases, men in Russia generally have lower life expectancies than women. Women born between 2010 and 2015, for example, have a projected life expectancy of 75.6 years, compared to men born in the same period, of just 64.2 years. This gap results in a lower percentage of men in older generations.
5. Ukraine - 53.50%
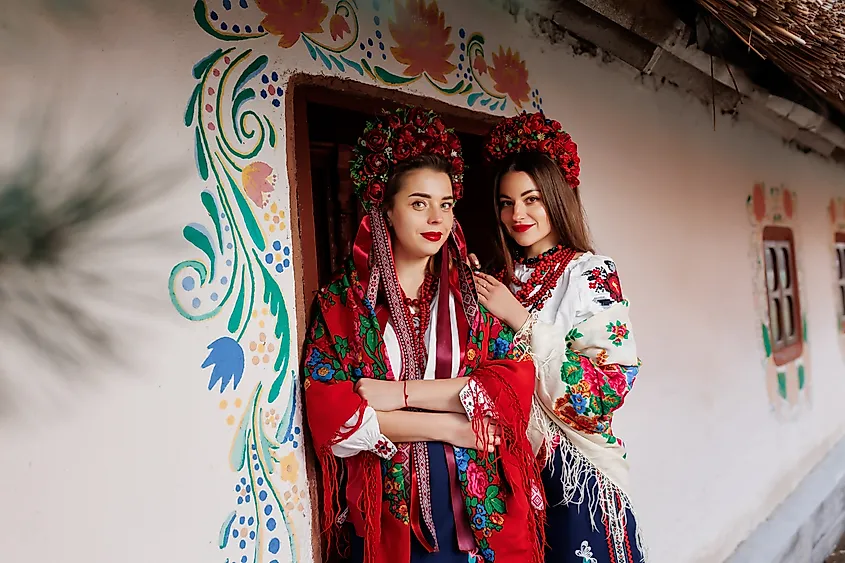

Similar to Russia, women in Ukraine have a higher life expectancy than men, which greatly contributes to the higher number of women in their population. As of 2021, the life expectancy for women in Ukraine is 75.3 years of age, which is nearly a decade longer than that of men in the country, at 66.3. Regarding higher education, women in Ukraine are generally very educated, with 60% of women in the country holding higher education degrees. Despite their educational achievements, Ukrainian women continue to face challenges in the workforce, representing 80% of the unemployed population.
6. Georgia - 53.40%
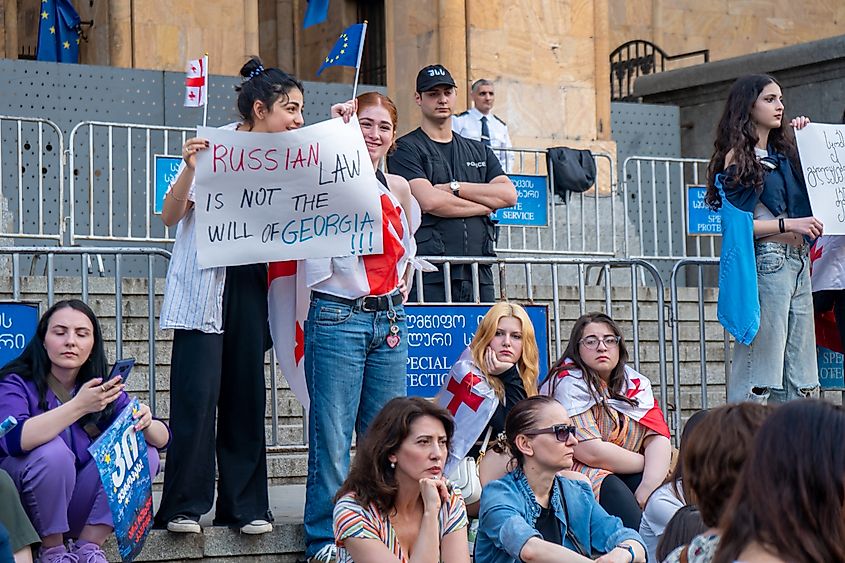

Georgia’s high number of women, composing 53.4% of the total population, can largely be attributed to two factors: immigration and life expectancy. With 56% of Georgians emigrating abroad being men, the country is left with a slightly higher proportion of women. Additionally, similar to other countries with a high female population, women have a higher life expectancy than men. As of 2023, Georgian men have a life expectancy of 70.6 years, which is significantly lower than that of women in the country, at 79.4 years, resulting in older generations being predominantly female.
7. Belarus - 53.40%

Although women represent 53.4% of Belarus's total population, the country remains deeply patriarchal, with significant gender inequality. On average, for example, a Belarusian woman earns about 80% of what a man does. However, unlike some of the other countries on this list, Belarus stands out, with women making up 54% of the workforce, more closely reflecting the country's overall gender distribution. One factor that largely influences the proportion of women to men in the country is life expectancy: As of 2021, life expectancy for women in Belarus is 78 years, exactly ten years higher than that of men.
8. Lithuania - 52.85%

Life expectancy and refugee immigration are two major factors that have led to Lithuania’s high percentage of women, making up about 52.85% of the population. Lithuanian women, on average, live nine years longer than Lithuanian men, largely due to health factors such as smoking, drinking, diet, and exercise. In fact, two-thirds of the country’s population over the age of 65 are women. In recent years, a record number of Ukrainian refugees arriving in Lithuania has further affected gender disparities in the country, with 32,000 of the 54,000 refugees received being women.
9. Tonga - 52.59%

With women making up 52.59% of the population, Tonga ranks as the ninth country worldwide with the highest female-to-male ratio. Regarding life expectancy, as of 2021, women in Tonga have a life expectancy of 75.3 years, which is about five years higher than the men’s average life expectancy of 70.2 years. Since childhood, Tongan society often socializes boys to practice riskier habits such as smoking, fighting, and wrestling, all of which are generally not socially accepted behaviors for girls. In terms of gender equality, Tonga ranks 115th globally on the Gender Inequality Index, with a score of 0.462 as of 2022.
10. Serbia - 52.51%

Serbia has the tenth highest proportion of women to men in the world, with 52.51% of the population consisting of women. Despite over half the population being women, women are underrepresented in the workforce, accounting for just 45.5% of workers. Serbian women are disproportionately affected by discrimination and domestic violence, with half reporting experiences of domestic abuse. Life expectancy is a relevant factor that influences gender population distribution. Serbian women, as of 2021, have a life expectancy of 75.6 years, compared to men of just 70 years.
Final Thoughts
While several factors contribute to the higher proportion of women compared to men in these countries, life expectancy stands out as a major factor, with men often engaging in behaviors more detrimental to their health. As health organizations address these concerns, populations may achieve a more balanced gender ratio, particularly in older age groups. Despite having a larger percentage of women, many of these countries still face lower female representation in the workforce and political spheres, emphasizing the ongoing need to advocate for greater gender equality continuing to move forward.
The Countries And Territories With More Women Than Men
| Rank | Country | Percentage of Women |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Republic of Moldova | 53.98% |
| 2 | Latvia | 53.68% |
| 3 | Armenia | 53.61% |
| 4 | Russian Federation | 53.57% |
| 5 | Ukraine | 53.50% |
| 6 | Georgia | 53.40% |
| 7 | Belarus | 53.40% |
| 8 | Lithuania | 52.85% |
| 9 | Tonga | 52.59% |
| 10 | Serbia | 52.51% |
| 11 | Estonia | 52.50% |
| 12 | El Salvador | 52.50% |
| 13 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 52.44% |
| 14 | Antigua and Barbuda | 52.41% |
| 15 | Zimbabwe | 52.38% |
| 16 | Portugal | 52.36% |
| 17 | Mayotte | 52.27% |
| 18 | Bahamas | 52.21% |
| 19 | Holy See | 52.22% |
| 20 | Central African Republic | 52.11% |
| 21 | Saint Kitts and Nevis | 52.08% |
| 22 | Barbados | 52.06% |
| 23 | Hungary | 52.01% |
| 24 | Nepal | 51.91% |
| 25 | French Guiana | 51.89% |
| 26 | Montenegro | 51.88% |
| 27 | Niue | 51.84% |
| 28 | Croatia | 51.78% |
| 29 | Sri Lanka | 51.61% |
| 30 | Bulgaria | 51.60% |
| 31 | Greece | 51.56% |
| 32 | Romania | 51.56% |
| 33 | Poland | 51.54% |
| 34 | Kiribati | 51.54% |
| 35 | France | 51.53% |
| 36 | Mozambique | 51.52% |
| 37 | Uruguay | 51.51% |
| 38 | Mexico | 51.50% |
| 39 | Anguilla | 51.40% |
| 40 | Lebanon | 51.39% |
| 41 | North Macedonia | 51.37% |
| 42 | South Africa | 51.35% |
| 43 | Kazakhstan | 51.32% |
| 44 | Lesotho | 51.30% |
| 45 | Guyana | 51.30% |
| 46 | Thailand | 51.26% |
| 47 | Rwanda | 51.25% |
| 48 | Malawi | 51.22% |
| 49 | Japan | 51.19% |
| 50 | Slovakia | 51.17% |
| 51 | Namibia | 51.16% |
| 52 | Italy | 51.16% |
| 53 | Monaco | 51.05% |
| 54 | Bermuda | 51.04% |
| 55 | Tokelau | 51.06% |
| 56 | Cambodia | 51.02% |
| 57 | Vietnam | 51.02% |
| 58 | Azerbaijan | 51.00% |
| 59 | Mauritania | 50.98% |
| 60 | Turkmenistan | 50.96% |
| 61 | Cook Islands | 50.94% |
| 62 | Eswatini | 50.91% |
| 63 | Tajikistan | 50.90% |
| 64 | Spain | 50.90% |
| 65 | San Marino | 50.83% |
| 66 | Nicaragua | 50.82% |
| 67 | Kosovo (under UNSC res. 1244) | 50.81% |
| 68 | South Sudan | 50.81% |
| 69 | Bangladesh | 50.80% |
| 70 | Brazil | 50.78% |
| 71 | Austria | 50.78% |
| 72 | United Kingdom | 50.77% |
| 73 | Belgium | 50.71% |
| 74 | Czechia | 50.69% |
| 75 | New Caledonia | 50.68% |
| 76 | Colombia | 50.65% |
| 77 | Eritrea | 50.65% |
| 78 | Cuba | 50.64% |
| 79 | Jersey | 50.64% |
| 80 | Germany | 50.62% |
| 81 | Guinea-Bissau | 50.60% |
| 82 | Falkland Islands (Malvinas) | 50.59% |
| 83 | Saint Lucia | 50.58% |
| 84 | Finland | 50.58% |
| 85 | Costa Rica | 50.58% |
| 86 | Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of) | 50.57% |
| 87 | Dem. People's Republic of Korea | 50.57% |
| 88 | Saint Pierre and Miquelon | 50.57% |
| 89 | Guernsey | 50.56% |
| 90 | Albania | 50.56% |
| 91 | Kyrgyzstan | 50.56% |
| 92 | Guinea | 50.56% |
| 93 | Tunisia | 50.55% |
| 94 | Trinidad and Tobago | 50.54% |
| 95 | Jamaica | 50.53% |
| 96 | Angola | 50.53% |
| 97 | Zambia | 50.51% |
| 98 | Ireland | 50.50% |
| 99 | Haiti | 50.49% |
| 100 | Isle of Man | 50.48% |
| 101 | United Republic of Tanzania | 50.44% |
| 102 | Uganda | 50.42% |
| 103 | Djibouti | 50.42% |
| 104 | Guatemala | 50.41% |
| 105 | Sudan | 50.40% |
| 106 | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 50.39% |
| 107 | Australia | 50.39% |
| 108 | Argentina | 50.38% |
| 109 | Fiji | 50.37% |
| 110 | Canada | 50.34% |
| 111 | Switzerland | 50.34% |
| 112 | Liechtenstein | 50.33% |
| 113 | Netherlands | 50.33% |
| 114 | Burundi | 50.33% |
| 115 | New Zealand | 50.33% |
| 116 | Chile | 50.30% |
| 117 | Micronesia (Fed. States of) | 50.30% |
| 118 | State of Palestine | 50.30% |
| 119 | Denmark | 50.29% |
| 120 | Kenya | 50.28% |
| 121 | Dominican Republic | 50.27% |
| 122 | Sao Tome and Principe | 50.27% |
| 123 | Peru | 50.26% |
| 124 | Gibraltar | 50.24% |
| 125 | Israel | 50.23% |
| 126 | Gambia | 50.21% |
| 127 | Myanmar | 50.20% |
| 128 | Burkina Faso | 50.19% |
| 129 | Cameroon | 50.16% |
| 130 | Ecuador | 50.14% |
| 131 | Sierra Leone | 50.13% |
| 132 | Botswana | 50.13% |
| 133 | Philippines | 50.12% |
| 134 | Mongolia | 50.11% |
| 135 | Liberia | 50.09% |
| 136 | Montserrat | 50.09% |
| 137 | Republic of Korea | 50.08% |
| 138 | Türkiye | 50.07% |
| 139 | Ghana | 50.05% |
| 140 | Mauritius | 50.02% |
| 141 | Suriname | 50.01% |
| 142 | Syrian Arab Republic | 50.01% |
| 143 | Congo | 50.00% |