Who Are the Berber People?
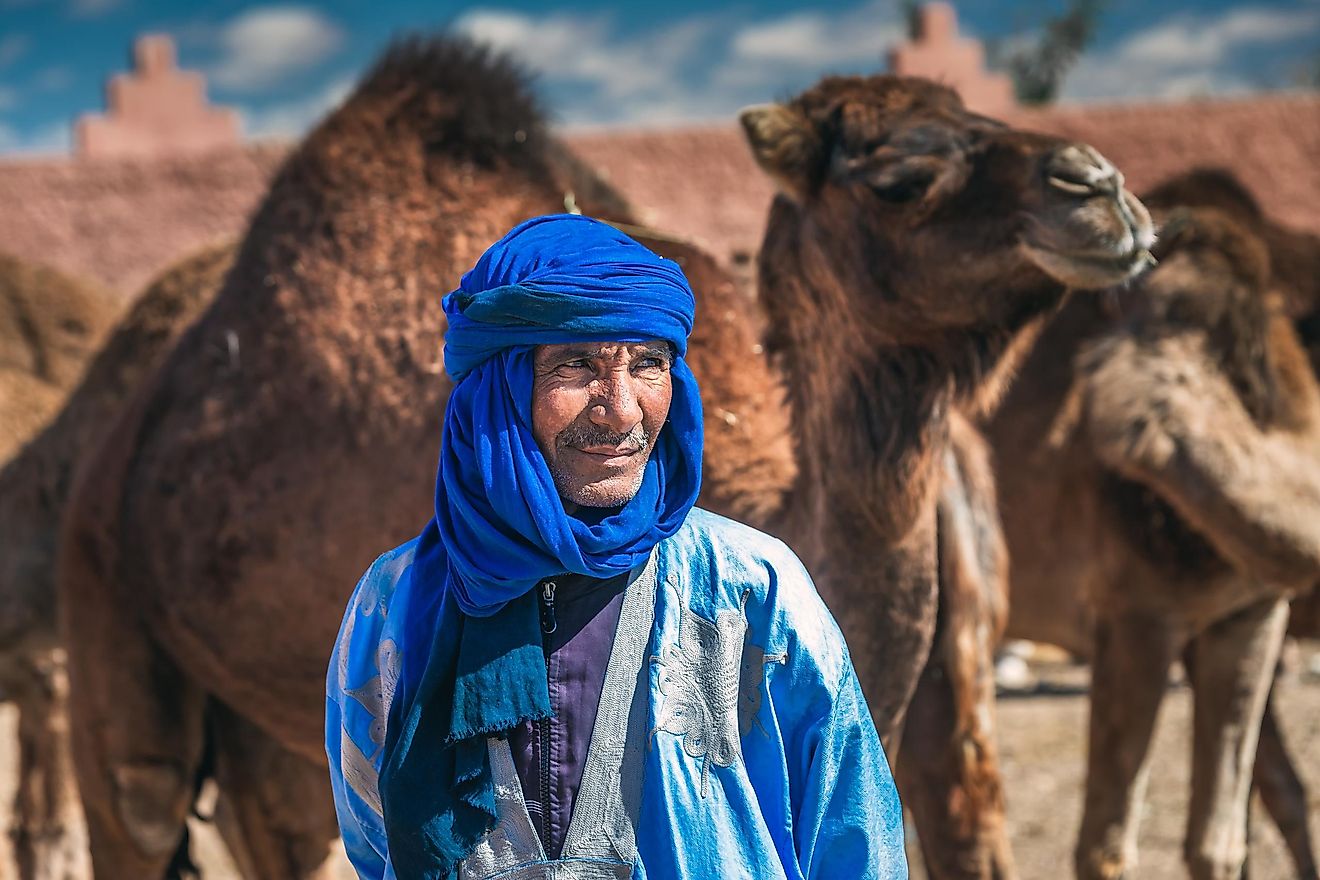

Berber people are an ethnic group indigenous to North Africa, occupying regions stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea. They speak the Berber languages which belong to the Afro-Asiatic language family. There are about 14 million Berber speakers in North Africa today with the majority found in Libya, Algeria, and Morocco. The majority of the population in North Africa is believed to be either Berber in origin or sharing a common ancestry with the Berbers. Berbers are not entirely a homogeneous ethnicity but include a wide range of societies. Berber language, heritage, and history are considered the major unifying factors of the Berber people.
Berber Languages

Berber languages are closely related and belong to the Afro-Asiatic language group. There are hundreds of dialects among the Berber population, but the vast majority of Berbers speak one of seven dominant Berber dialects. It is not possible to ascertain the exact populations of Berber speakers since most of the Maghreb countries do not have language data. It is estimated that 14 to 20 million people in Africa speak the Berber language. Berber languages include Tarifit, common in Morocco, Kabyle in Algeria, and Tashelhyt in Central Morocco. There has been a strong movement by the Berbers to unite all the languages into a single standard known as Tamazight. Other notable Berber languages include Siwa, Zenanga, and Sanhaja.
History And Origin Of The Berber People
Berbers have inhabited North Africa for many years with records suggesting their presence as early as 3000 BCE. The group is first mentioned in Egyptian writings during the Predynastic Period. For several years they inhabited the coast of North Africa. The Berbers interacted with the European colonialists and invaders of the coastal regions of North Africa who left some imprint upon them. The Sudanic empires and pastoralists from East Africa also had a great influence on the Berber people. The Berbers expanded from the coastal areas of North Africa into Sahara, displacing the earlier inhabitants such as the Azer. However, they were assimilated into North Africa by the Arabs as early as the 11th century. The areas in North Africa that retained the Berber language and traditional beliefs such as Morocco and Kabylie were least exposed to the foreign rule.
Demographics
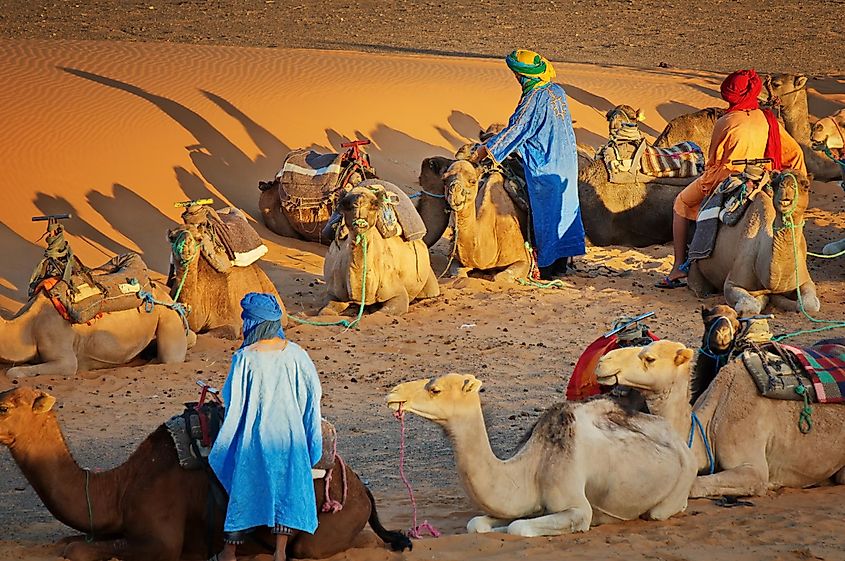

The majority of the Berber people live in Morocco accounting for at least 35% of the population and in Algeria where they form at least 15% of the population. A sizable number of Berbers are also found in Libya and Tunisia. The majority of the North African Arabs also have Berber ancestry. Outside of North Africa, there are about 2.5 million Tuaregs in Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso. Tuaregs are traditionally nomadic Berbers inhabiting the vast Sahara Desert. Berbers are stereotyped in Europe as being nomads. However, the majority of Berbers are mainly farmers occupying the mountains close to the Mediterranean coast. Some notable Berbers include Zinedine Zidane, Augustine of Hippo, and Ziri ibn Manada, the founder of the Zirid Dynasty.
Culture And Religion
Culturally, Berber men take care of migrating livestock with the seasons, seeking water and grass for the animals while women take care of the family. Their social structure is tribal with a leader appointed to lead the tribe. Most of the tribe leaders are men, though many women like Tin Hinan and Tazoughert are known to have governed their tribes. Most of the Berbers are Sunni Muslims but the majority incorporate traditional practices in their worship. Traditional practices tend to dominate rural areas where Berbers outnumber Arabs. Before conversion to Islam, some Berbers had converted to Christianity while others practiced polytheism.