What Type Of Government Does Kenya Have?

What Type Of Government Does Kenya Have?
The Republic of Kenya is one of the countries in East Africa and a member of the East African Community. It borders Uganda, Tanzania, South Sudan, Somali, Ethiopia, and the Indian Ocean. Kenya covers a total area of 581,309 square kilometers and has an estimated population of 45 million people of different ethnicity and culture. Kenya attained her independence in 1963 from the British Colonial rule and gained internal self-rule on December 12, 1963. It became a republic twelve months later on December 12, 1964, with the Late Jomo Kenyatta being the first Kenyan President.
Administrative Divisions
Before the promulgation of the new constitution in 2010, Kenya was divided into eight provinces under the administration of the provincial commissioner. The provinces were further divided into lower administrative divisions of districts and divisions which were under the administration of the district commissioners and district officers respectively. However, with the current constitution, Kenya is divided into 47 counties which form the first-order division. The counties are further divided into sub-counties. The counties are headed by the governors while the sub-counties or wards are headed by the Member of County Assembly. The country is also subdivided into 290 constituencies whose representatives form the national assembly.
The National Government
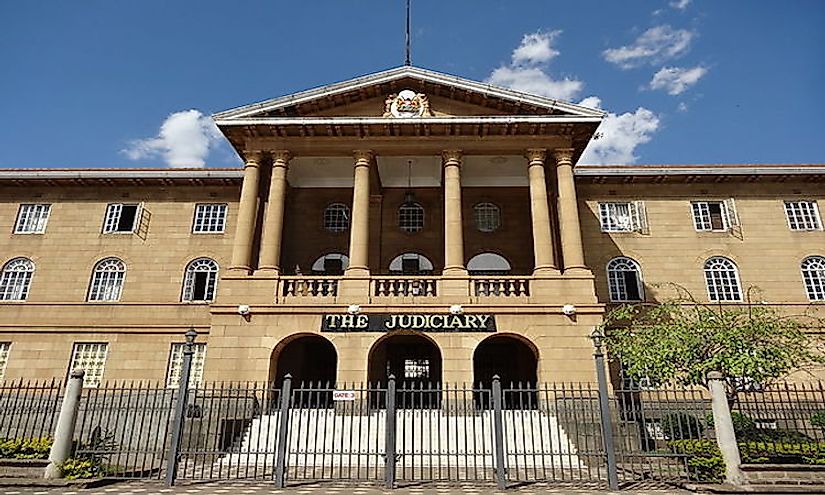
Kenya functions under a devolved system of government with two levels of government; the national and the county government. The National government comprises of the Judiciary, the Executive, and the Legislature. The executive arm of government is headed by the president who is elected for a maximum of two five-year terms. The president, who exercises executive powers, is the head of both the state and the government. He works with a cabinet comprising of the deputy president and 22 cabinet secretaries who are in charge of various ministries. The executive is in-charge of policy formulations and implementation of various government projects. The legislative powers are vested on the Senate and the National Assembly. The two houses play an oversight role as well as debating of bills before the presidential ascent. The legislative assemblies are headed by the Speakers of the two houses. The Judiciary, which is independent of the other two arms of government, is headed by the Chief Justice who is also presides the Supreme Court which has the responsibility of interpreting the Constitution and whose decisions are final and cannot be challenged.
The County Government
The county government is the second level of government under the Kenya’s constitution. There are 47 county governments headed by the governors who are also elected for a maximum of two five-year terms. Just like the president, governors also appoint county executives who are in-charge of the various county portfolios including health, infrastructure, finance, and other sectors of development. The governors are responsible for the management of county resources including revenue collections and supervision of the development projects. The county assembly which comprises of the elected ward representatives together with the Senate plays an oversight role and is also responsible for budgeting and approval of projects to be carried out by the county government.
The Current Government
The two levels of government are formed after every general election which is conducted every five years. The current government is the first under the new constitution since the old constitution provided for only one level of government, the national government, which was headed by the President. Kenya is set for elections in August 2017 where a new government for the two levels is expected to be formed.