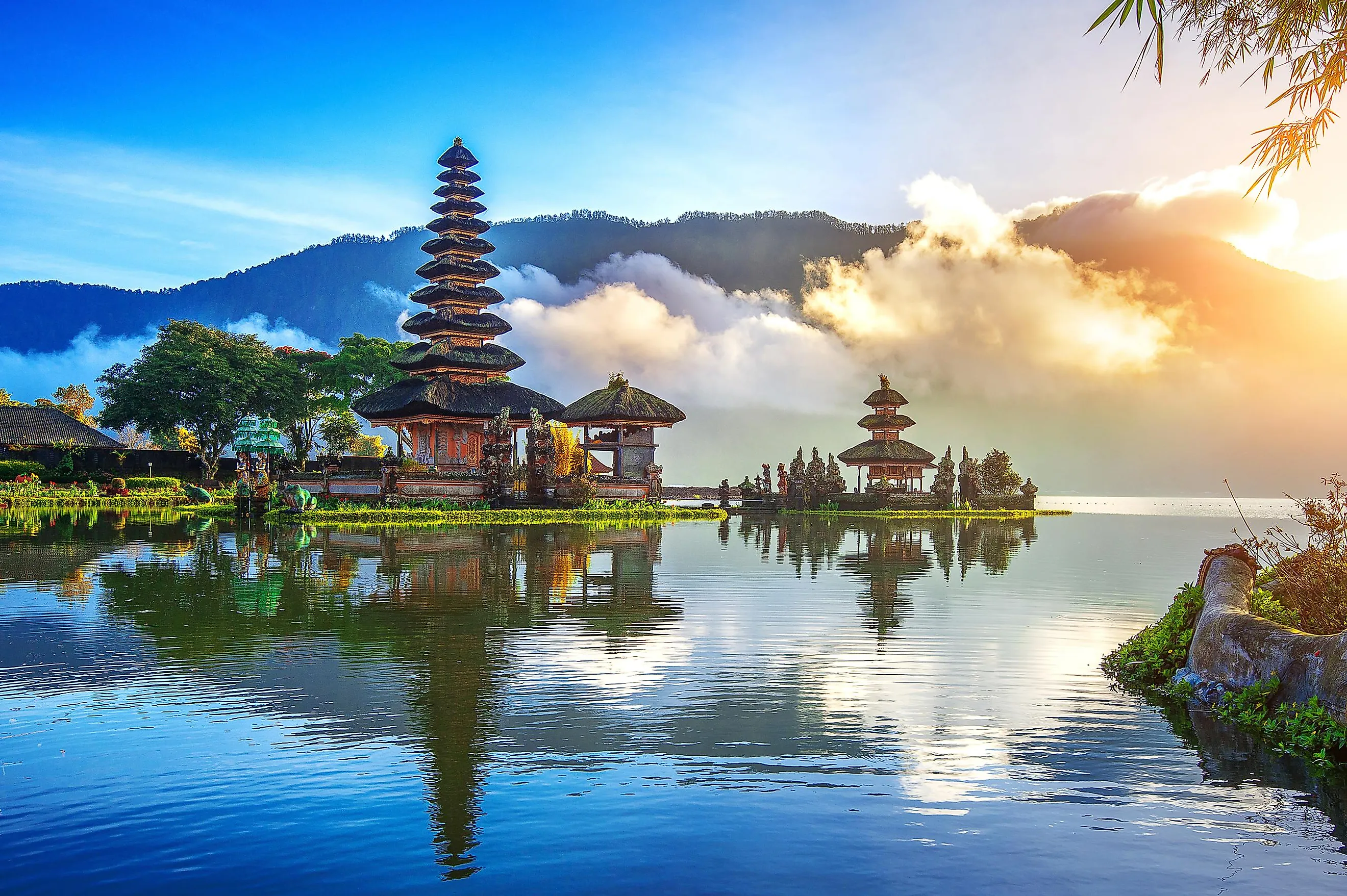
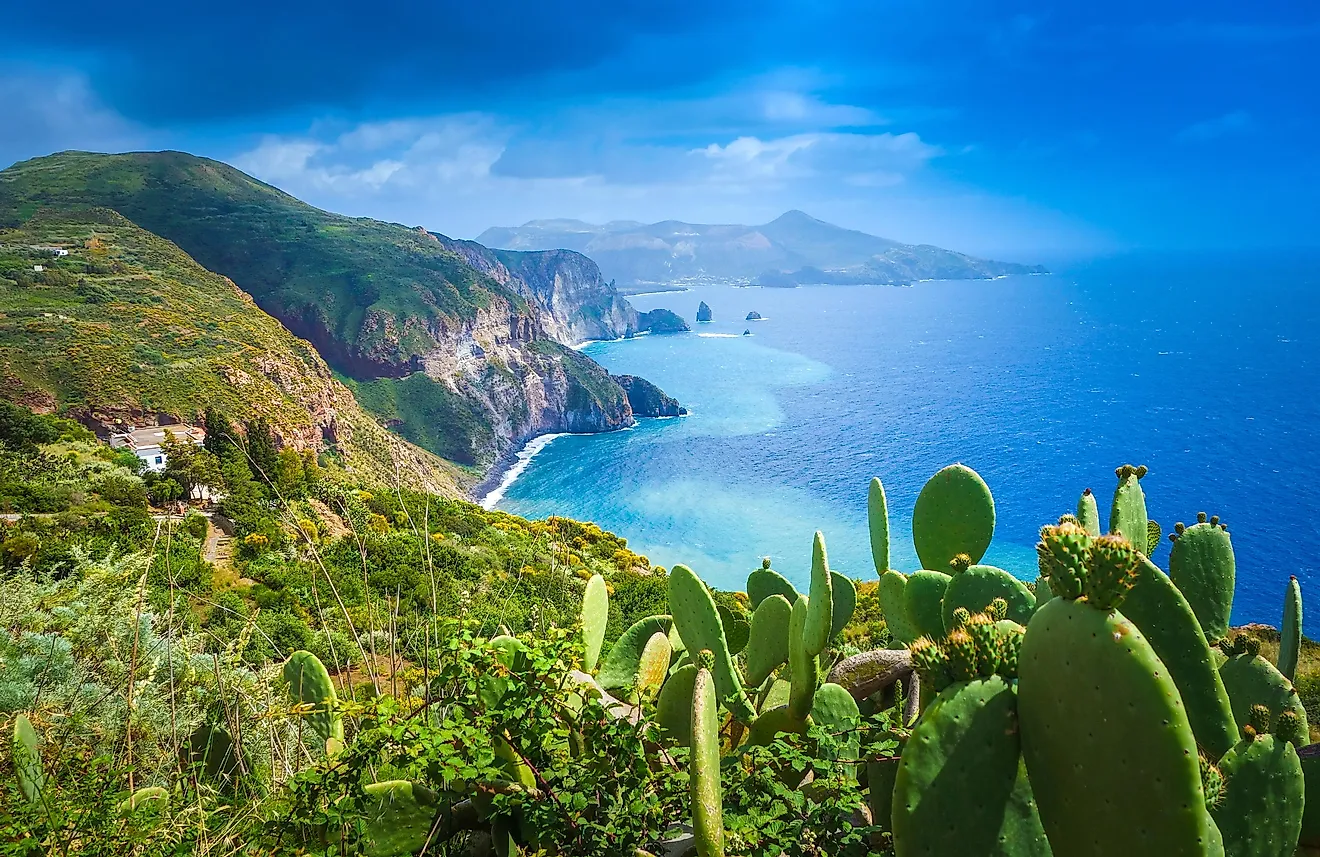
Bali, Indonesia
The archipelagic nation of Indonesia is positioned between the Pacific and the Indian Oceans and comprises over 17,504 islands. Covering a total area of 5,780 km2, the island of Bali is the westernmost island in the Lesser Sunda group and a province of the Republic of Indonesia.
Bali is located about 8° south of the Equator, west of Lombok island, and east of Java Island. The 2.4 km-wide Bali Strait separates Bali from Java, whereas the 60 km-long Lombok Strait separates Lombok from the island of Bali.
Geography
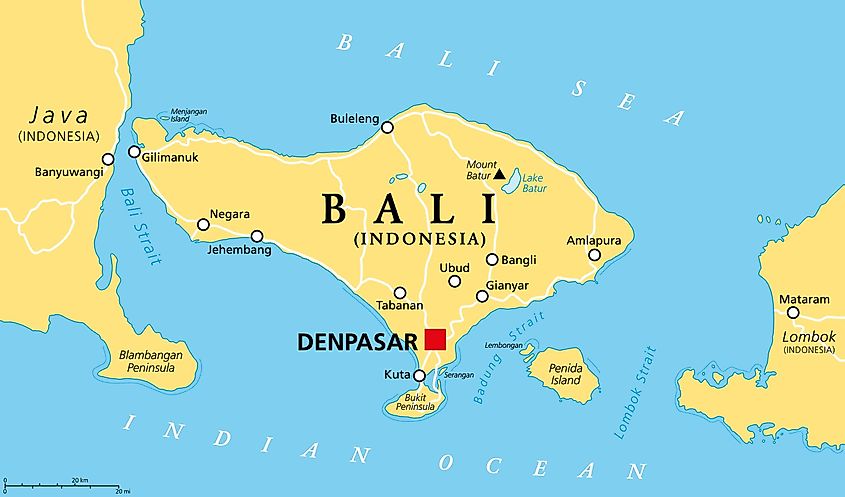
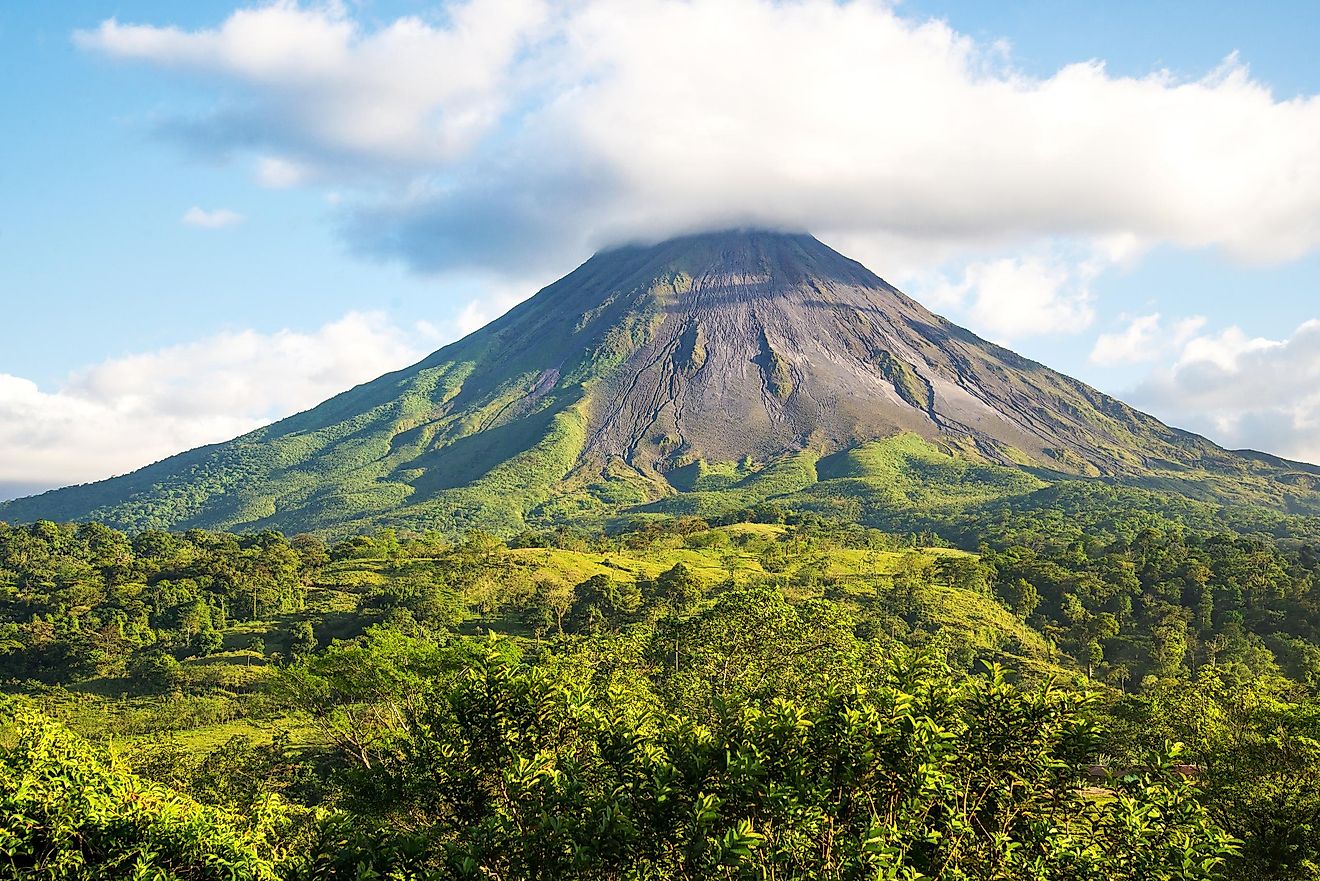
Bali measures approximately 112 km in length and has a maximum width of about 153 km. A major part of Bali is mountainous and the island comprises several peaks that are more than 2,000 m in elevation. Mount Agung (Bali Peak), which rises to an elevation of about 3,142m is the highest point on the Bali island. Also referred to as the “Mother Mountain,” Mount Agung is an active volcano whose last eruption in 1963 devastated several villages and killed more than 1,500 people on the island. There are a few small rivers on the island including the Ayung River, Sungi River, and the Telaga Waja River.
The volcanic nature of Bali has contributed to its exceptional fertility and the island’s tall mountain ranges also cause high rainfall, thereby supporting its highly productive agricultural sector. Located to the south of the central mountains are the main lowlands of the island, where most of the rice cultivation is done. The northern part of the mountain slopes more steeply to the sea and forms the island’s major coffee-producing area where, along with coffee, vegetables, rice, and cattle are also produced. Bali is surrounded by coral reefs. White sand beaches are found in the island’s southern part, whereas black sand beaches are found in the northern and western parts of the island.
Located near the island’s southern coast is Denpasar, the provincial capital and the largest city of Bali. The three small islands of Nusa Ceningan, Nusa Lembongan, and Nusa Penida are under the administration of Bali’s Klungkung regency and are positioned in the southeastern part of the island. The 20 km-wide Badung Strait separates the three islands from Bali.
Due to its proximity to the Equator, Bali experiences a considerably even climate with average daily temperatures ranging between 20 to 33 °C throughout the year. The monsoon season on the island is from December to March.
Wildlife

Drawn by the famous naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace in 1859, the Wallace Line is a biogeographical division between the Australian and the Southeast Asian fauna. The island of Bali is located to the west of the Wallace Line and hence possesses similar faunal characteristics to that of Southeast Asia. More than 280 avian species are found in Bali including the endemic Bali myna and other species like black-naped oriole, barn swallow, crested serpent eagle, Java sparrow, savanna nightjar, yellow-vented bulbul, sacred kingfisher, etc. Various mammalian species like squirrels, Asian palm civets, bats, crab-eating macaque, Javan langur, black giant squirrel, Sunda pangolin, and leopard cat are also found here. More than 500 reef-building coral species have been recorded in the Bali island area.
Many marine animals like barracuda, hawksbill turtle, giant sunfish, giant moray eel, hammerhead shark, and sea snakes have been recorded in the waters around the Bali island.
Brief History

Bali was originally inhabited by the Austronesian people around 2000 BCE, who migrated to the island from Taiwan. The Balinese people were culturally and linguistically related to the inhabitants of Malaysia, Oceania, and the Indonesian archipelago. Most of the island’s inhabitants were followers of Balinese Hinduism and the different Hindu sects of Brahma, Bodha, Bhairawa, Ganapatya, Pasupata, Sora, Siwa Shidanta, Resi and Vaishnava existed in ancient Bali.
In 914 AD, the Balinese people developed Subak, their complex irrigation system for the cultivation of rice in wet fields. In 1512, the Portuguese explorers Antonio Abreu and Francisco Serrão were the first Europeans to visit the island. Cornelis de Houtman, the Dutch explorer, landed in Bali and established the Dutch East India Company. The famous naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace arrived to Bali in June 1860. During the Second World War, the island was occupied by the Japanese forces. In 1946, Bali became a part of the State of East Indonesia. On December 29, 1949, Bali became a part of the Republic of Indonesia.