Zambezi River
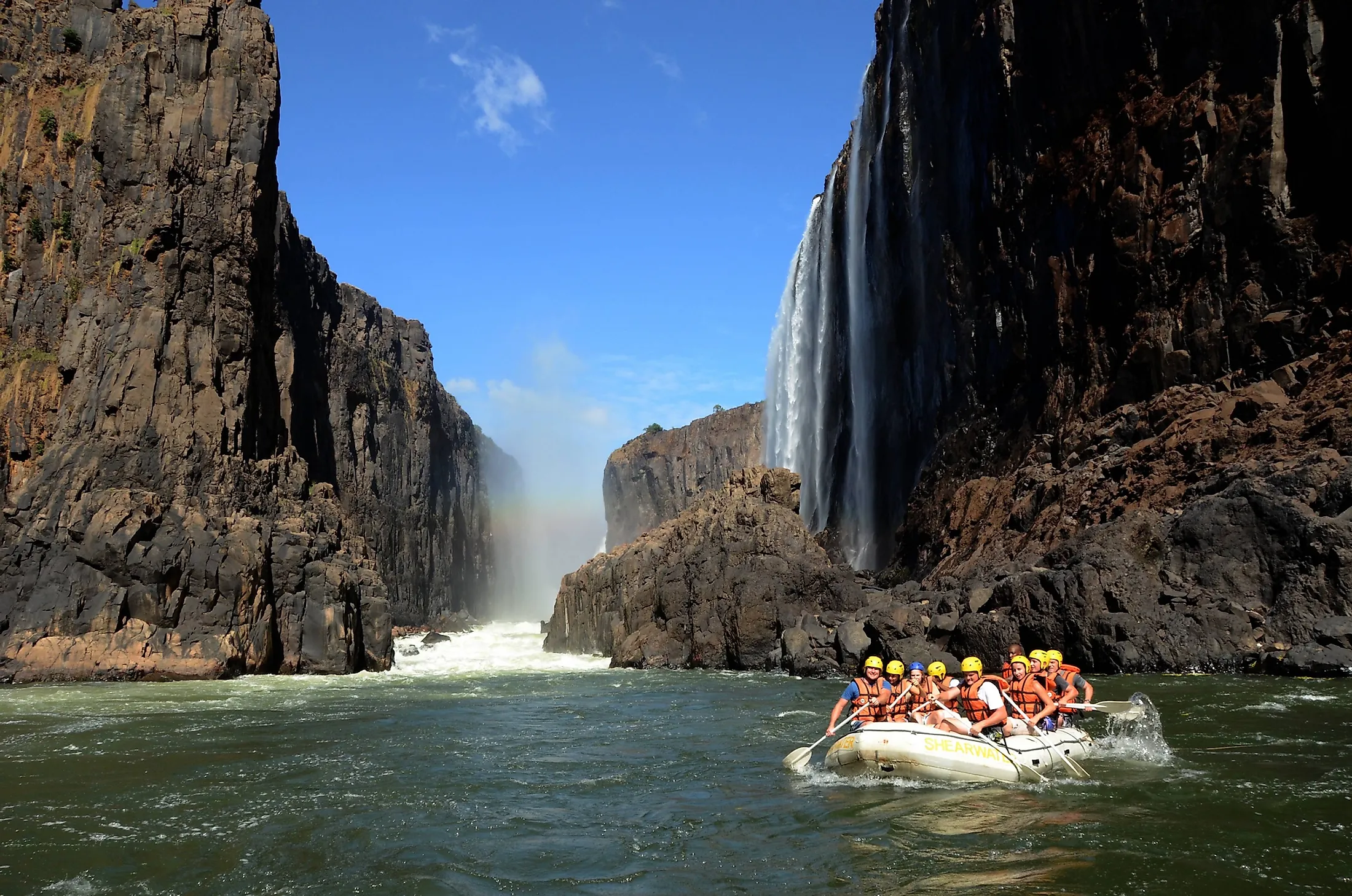
Zambezi River, sometimes spelled as Zambesi or Zambeze, is Africa’s 4th longest river and the continent’s longest east-flowing stream. The river rises from the Central African Plateau in Zambia and flows for about 2,574 kilometers through Angola, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique before emptying into the Indian Ocean. The Zambezi is a Tonga word for “Great River.” The river is known for several notable waterfalls, including Victoria Falls, one of the world’s largest waterfalls, and the Chavuma Falls on the Zambia-Angola border. The Cohara Bassa and Kariba Dams, two of Africa’s major hydroelectric power sources, are located along the Zambezi’s course.

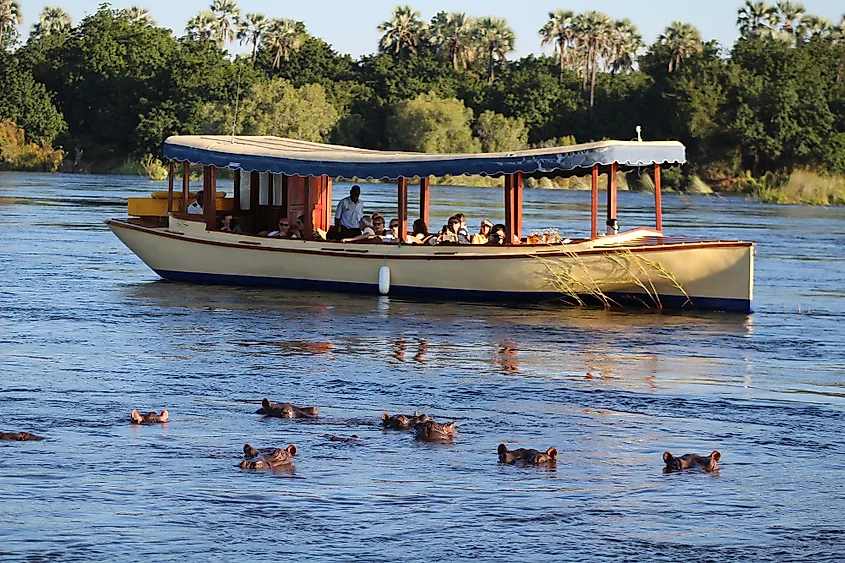
Zambezi River is a major stream in south-central Africa that either forms the boundaries or crosses up to six countries, namely Zambia, Angola, Namibia, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Mozambique. It is Africa’s 4th longest river and the world’s 32nd longest river system. It flows for approximately 2,574 kilometers from its source in Zambia to its mouth in the Indian Ocean. It drains an area of more than 1.39 million square kilometers, with Zambia accounting for the largest drainage area (41.6%). Besides the six countries, the Zambezi Basin also covers Tanzania and Malawi. The river has a mean discharge of 3,400 cubic meters of water per second. The river’s course is divided into three sections: upper, middle, and lower Zambezi River.
Course Of The Zambezi River
Source And Upper Zambezi
Zambezi River Rises in a shallow wetland area (dambo) in Ikelenge District, North-Western Province, Zambia, about 1,500 meters above sea level. The source area is designated as an Important Bird Area, forest reserve, and a national monument and is protected as Zambezi Source National Forest. The Upper Zambezi River flows southwest for about 32 kilometers before entering Angola. In Angola, it flows for over 280 kilometers and receives several tributaries, including Chifumage and Luena. Then the river re-enters Zambia and flows rapidly until it reaches Chavuma Falls.
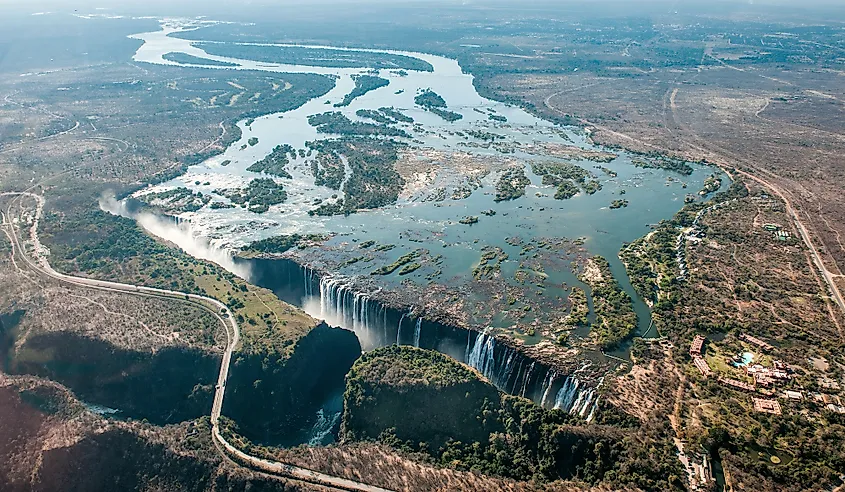

The Zambezi covers approximately 400 kilometers from the source to the falls. In Zambia, the Zambezi is joined by tributaries such as Kabompo, Lugwebungu, and Luanginga Rivers. The Zambezi River receives Luanginga a short distance from Lealui, then turns south-southeast and enters a steep stretch between Ngonye Falls and Katima Mulilo Rapids. Then, the river runs on the Zambia Caprivi Strip (Namibia’s extension) border for about 128 kilometers until its confluence with the Cuando River. It proceeds to Victoria Falls, where the Upper Zambezi ends.
Middle Zambezi
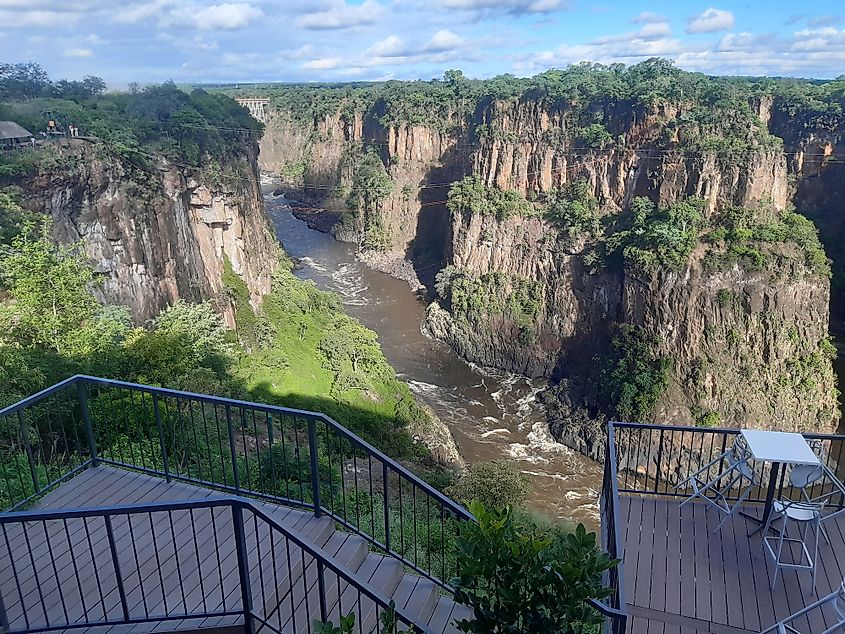

Below the Victoria Falls, the Middle Zambezi continues eastwards for about 200 kilometers, flowing through a basalt wall and Batoka Gorge. After the gorge, the Zambezi flows rapidly in rapids which end about 240 kilometers from Victoria Falls. Then the river enters Lake Kariba, the world’s largest artificial lake by volume, completed in 1959 and formed by the Kariba Dam. The river continues its flow northeastwards, then turns east at the confluence with Kafue River. Then it receives Luanga River as it enters Mozambique. The Middle Zambezi ends as the stream enters Cohara Bassa.
Lower Zambezi
The Lower Zambezi River flows for about 650 kilometers from Cahora Bassa to the Indian Ocean. This section of the river is generally shallow, especially during dry seasons, since it spreads out and flows through a broad valley. It receives Shire River about 160 kilometers from the mouth. The Zambezi River forms a delta as it approaches the Indian Ocean. It splits into four main distributaries, Timbwe, Luabo, Chinde, and Kongone, with sandbars obstructing each of the four branches.
Wildlife In The Zambezi River Region

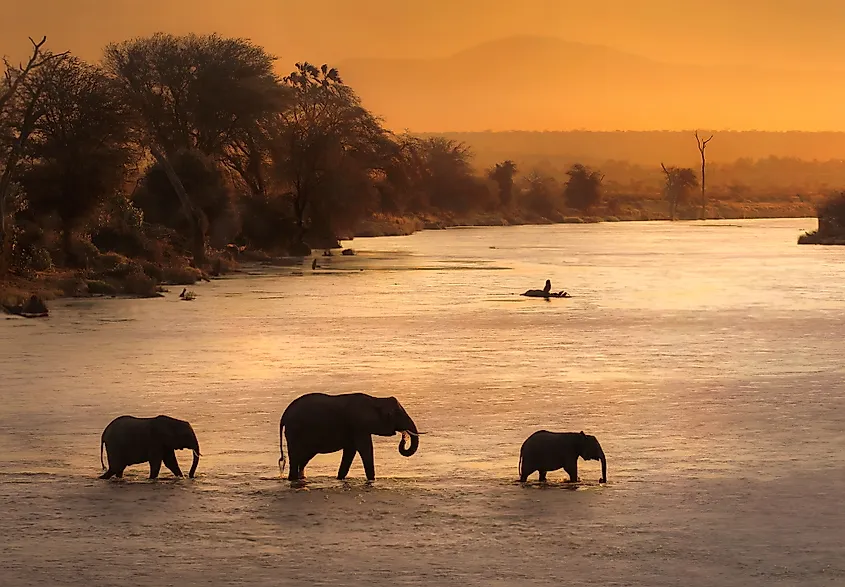
The Zambezi Delta comprises swamp forests, savannas, and grasslands. The delta and the entire river system are home to a large population of eland, reedbuck, cheetahs, leopards, spotted hyena, and lions. Bird species found in the region include saddle-billed stork, African Openbill, garganey, pintail, wattled crane, and white pelican. The river supports reptiles like monitor lizards, and Nile crocodiles. The Zambezi is home to several fish species, including tigerfish, catfish, cichlids, and yellowfish.