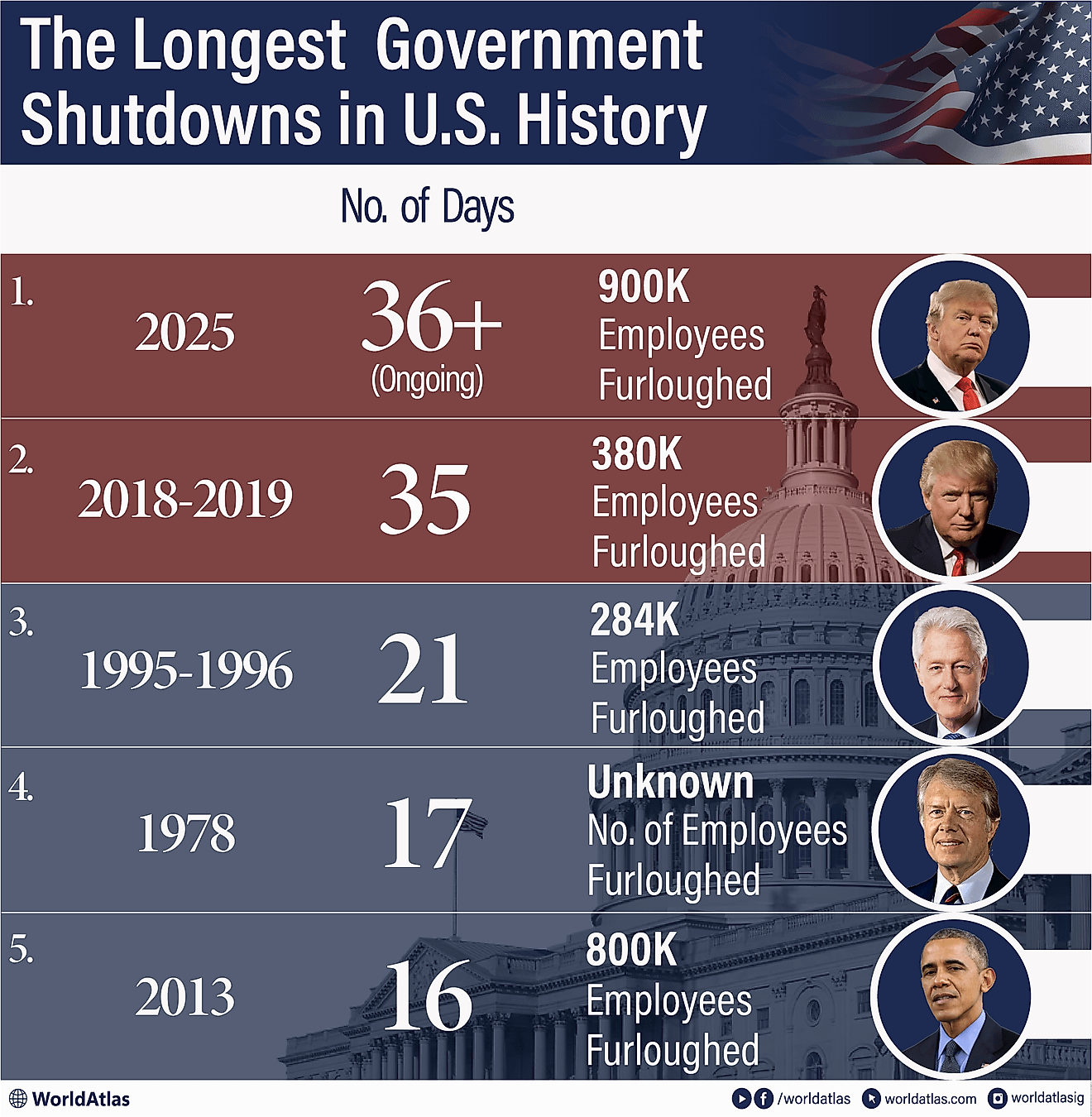
Which Countries Border South Africa?

South Africa is one of the largest countries in Africa, covering an area of 0.471 million square miles. The country has a land border that stretches 3,021 miles in length. The country’s international border was first delineated when the country was still a colony and was established as a result of treaties agreed by the European colonial powers in the late 19th century. Six countries border South Africa, one of which is an enclave. These bordering countries are Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Namibia, Botswana, Lesotho, and Swaziland. Lesotho, which is surrounded by South Africa, is an enclave. The Botswana-South Africa border is the longest of South Africa’s international borders, while the country’s border with Zimbabwe is the shortest.
Botswana
One bordering country of South Africa is Botswana, a country is situated north of South Africa. Natural borders such as rivers largely define the border, and for the most part, the border follows the course of rivers. These rivers that act as natural borders are the Limpopo, Molopo, Nossob, and Marico rivers. The border starts at the tri-point connecting Namibia, South Africa, and Botswana and moves east until it reaches the Zimbabwe-South Africa-Botswana tri-point. The border stretches a total of 1,223 miles in length, making it South Africa’s longest international border it shares with another country. The border was established in the late 19th century as dictated by order of the Council passed in 1895. The two countries retained the colonial border after gaining independence in the 20th century. Numerous border crossings exist along the border, to facilitate cross-border legal movement, which also features border towns found near the border.
Namibia
North-east of South Africa is Namibia, a country with which it shares a 601-mile long land border. The border starts at the Botswana-South Africa-Namibia tri-point and runs east to the Atlantic Ocean. The border was first demarcated during the 1890 Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty signed between the German and the British, to separate Britain’s Cape Colony from German South West Africa. Both countries maintained the border as provided in the 1890 Treaty even after gaining independence. There are a total of seven border crossings found on the Namibia-South Africa border. Two of these border crossings are situated in transfrontier parks and are used by tourists. The two countries have, laid claim to a portion of the border running along the Orange River, with the main contention being the part of the river the border lies, as stipulated by the 1890 treaty. Namibia maintains that the border runs through the middle of the river, a position opposed by South Africa which instead claims that the border runs through the northern bank of the river.
Mozambique
Mozambique is situated northeast of South Africa. The two countries share a land border that is 305 miles in length. The border starts at the tri-point connecting Zimbabwe, Mozambique, and South Africa near the confluence of the Limpopo and Luvuvhu rivers, and moves southeastwards until it reaches the Indian Ocean near the town of Ponta do Ouro. The border is however interrupted by the kingdom of Swaziland, which divides the border into two; the northern and southern segments. The northern segment runs 255 miles while the southern segment is 50 miles in length. Four border crossings are found along the Mozambique-South Africa to facilitate cross-border movement between the two countries. The busiest of the crossings is the Ressano Garcia-Lebombo border post as it lies where the busy Maputo Corridor Highway crosses the international border. Two border crossings are inside the Limpopo Transfrontier Park; the Pafuri and the Giriyondo border posts, with the latter being only used by tourists.
Swaziland
The Kingdom of Swaziland is situated to the northeast of South Africa and is South Africa’s smallest bordering country. Of the country’s bordering countries, Swaziland shares the second-shortest land border with South Africa, with the border between the two countries being 267 miles in length. There are 11 border posts situated along the border between the two countries which include, the Josefsdal-Bulembu border post, Waverley-Lundzi border post, Bothashoop-Gege border post, and the Nerston-Sandlane border post.
Lesotho
Lesotho is an enclave, surrounded entirely by South Africa. The two countries share a land border that is 565 miles in length. The Mont-aux-Sources peak of the Drakensberg Mountains marks the start of the border, from where it runs along the Orange, Tele, and Caledon rivers, and the Drakensberg Mountains’ drainage divide, and back to its starting point, to form a loop. Eastern Cape, Free State, and KwaZulu-Natal are the three South African provinces that touch the border, as well as all of Lesotho’s ten districts. The border was first delineated in 1868 during the formation of the British Protectorate of Basutoland (modern-day Lesotho). The Convention of Aliwal North held in 1869 provided for the establishment of a border dividing Orange Free State in South Africa, and Basutoland, with the description of the border being confirmed later in a government notice of November 1871. According to the colonial border provisions, the border was to follow the St. John, Cornetspruit and Tees rivers, and marked by the Jammerberg and Langeberg mountains. There are numerous border posts found along the South Africa-Lesotho border including the Maseru Bridge and Ficksburg Bridge border crossings, both of which operate 24 hours of the day.
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe borders South Africa to the north, with the two countries sharing a 140-mile long land border, the shortest international border South Africa shares with another country. The tri-point connecting Zimbabwe, South Africa and Botswana near the confluence of the Limpopo and Shashe Rivers marks the start of the border, from where it runs eastwards and ends at the Mozambique-South Africa-Zimbabwe tri-point. The border was first delineated in the 1881 Pretoria Convention and confirmed during the 1884 London Convention that saw the demarcation of the international border of the Transvaal Colony (later South Africa) and that of Southern Rhodesia (modern-day Zimbabwe). The Beit Bridge is the sole border crossing point on the Zimbabwe-South Africa border. The border crossing point doubles up as a border town where Zimbabwe’s A6 Highway joins to the N1 Highway of South Africa that connects Zimbabwe to South Africa’s economic hubs of Johannesburg and Pretoria.