What Are The Commonwealth Countries?

The Commonwealth of Nations arose from the slow decolonization of the British Empire in which territories under this rule sought independence to self-govern and later gained sovereignty. These former dependents of the Empire came together as equals. With no constitution or by-laws, members of the Commonwealth are under no obligation. Together they share common interests and goals, such as democracy, world peace, equality, and free trade.
History
The Balfour Declaration established the British Commonwealth of Nations at the 1926 Imperial Conference. It was formalized through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. Its initial members were the United Kingdom, Canada, the Irish Free State, Newfoundland, and the Union of South Africa. It was later revised to include independent nations. Today 56 countries are members of the world's oldest political association.
The first Head of the Commonwealth was King George VI but was taken over by Queen Elizabeth II after his death.
Leaders of the Commonwealth nations gather every two years for the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM) where they collaborate on primary decision-making.
Purpose

People of different nationalities.Friendship, communication, teamwork. Image credit franz12 via shutterstock
The Commonwealth's objective is to ensure that the members experience ongoing prosperity. It offers every nation equal standing in contributing to the policies and priorities of the Commonwealth. States that join the Commonwealth must embrace equality, free trade, world peace, liberty, and human rights. Membership in the Commonwealth is voluntary, and member states are at liberty to exit at any time without any consequences.
Besides the governing aspect of the Commonwealth of Nations, the countries also have other relations such as the Association of Commonwealth Universities and the Commonwealth of Learning for academic purposes and the Commonwealth Games for sports purposes.
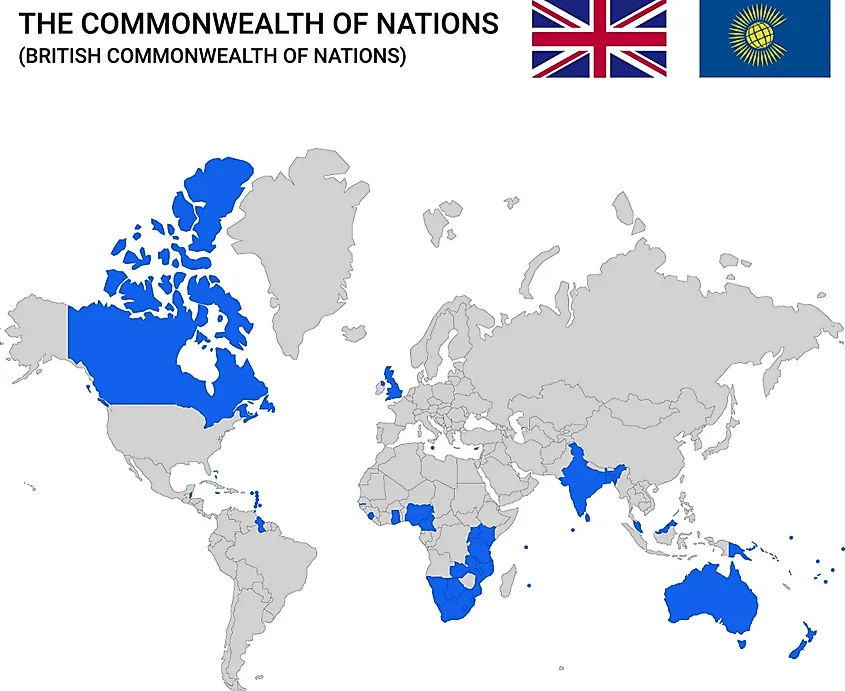
Member Countries By Region

Africa
- Botswana
- Cameroon
- Ghana
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Malawi
- Mauritius
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- South Africa
- Swaziland
- Uganda
- United Republic of Tanania
- Zambia
Americas
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Canada
- Dominica
- Grenada
- Guyana
- Jamaica
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- St. Kitts and Nevis
- Trinidad and Tobago
Asia
- Bangladesh
- Brunei Darussalam
- India
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Pakistan
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
Europe
- Cyprus
- Malta
- United Kingdom
Pacific
- Australia
- Fiji
- Kiribati
- Nauru
- New Zealand
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu











