World's Top 5 Diamond-Producing Countries
Diamond is a naturally occurring rare mineral that is composed of pure elemental carbon. Due to the extremely rigid arrangement of the carbon atoms in a crystal structure, diamonds possess the maximum hardness and thermal productivity than any natural material. Diamonds are also in high demand as gemstones and as luxurious commodities. Despite having a reputation for being used in jewelry like rings and necklaces, 80% of mined diamonds are used for research and industrial purposes because of their toughness and shine.
The hardest substance known to man, diamonds, are frequently used to drill, grind, or cut other difficult materials. Initially, its reserves were only discovered in Africa and provided to the rest of the globe, but today, exploration and production of diamonds have also begun on other continents. Currently, Russia produces 30% of the world’s diamonds, and approximately 39.12 million carats of diamonds were produced in Russia in 2021, making it by far the greatest diamond-mining nation in the world. With a production of 22.9 and 17.6 million carats of diamonds, respectively, Botswana and Canada are placed in second and third place, followed by the Democratic Republic of the Congo and South Africa.
1. Russia (39.12 million carats)
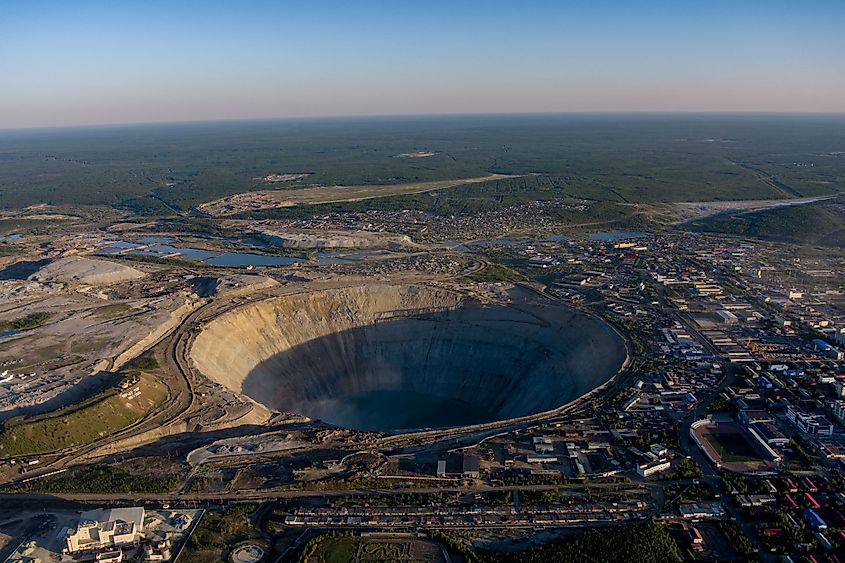

Russia presently leads the world in diamond output after it began mining in 1947. Regarding volume, it is also the top exporter of rough diamonds worldwide. ALROSA is Russia's largest diamond miner, maintaining a virtual monopoly over the sector and producing over 90% of the nation's annual output. Russia houses some of the world's greatest mines and diamond reserves (some of which have not yet been explored), including Udachny, Grib, and Aikhal. It was revealed in 2014 that Alrosa intends to expand the Udachny mine into a 5 million carat per year project, making it the most significant diamond mine in both Russia and the entire globe. Alrosa first used Udachny in 1971, and during the following 43 years, it has helped the company make over $80 billion. Alrosa should be able to keep its position as the world's biggest diamond producer by volume for the foreseeable future due to Udachny's figures.
2. Botswana (22.88 million carats)
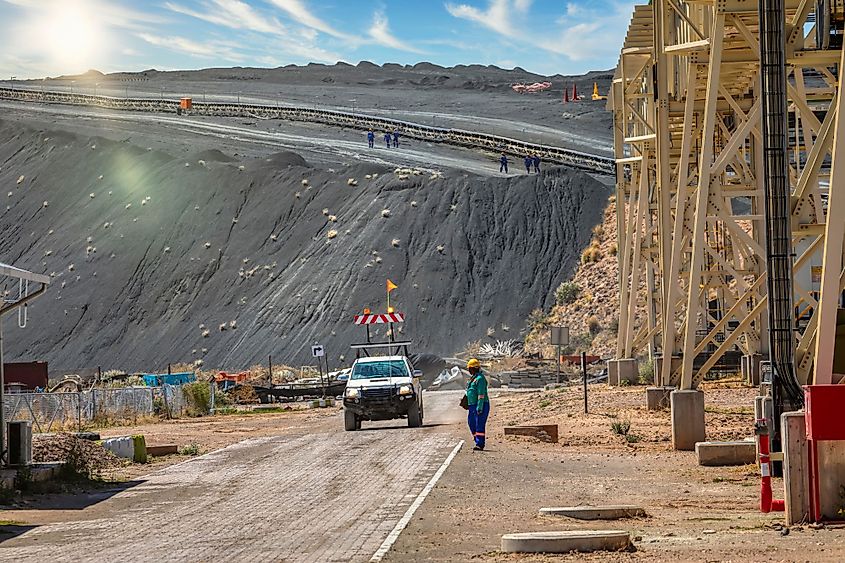

A significant diamond mine was found in 1966, the year Botswana declared its independence from Britain, in a rural region called Orapa, about 250 miles from the nation's capital of Gaborone. De Beers, the firm that discovered the mine, was and still is the world's largest supplier of "rough stones." The two most significant of the seven mines in the country are Orapa and Jwaneng. Despite ranking second in terms of volume, Botswana tops the list of the world's top producers of diamonds. Botswana, which was one of the world's 25 poorest nations, has achieved upper-middle income status due to the revenue from diamonds. The nation is currently vying for a more significant position in the sector as the No. 1 player Russia faces condemnation from around the world for its invasion of Ukraine.
3. Canada (17.62 million carats)
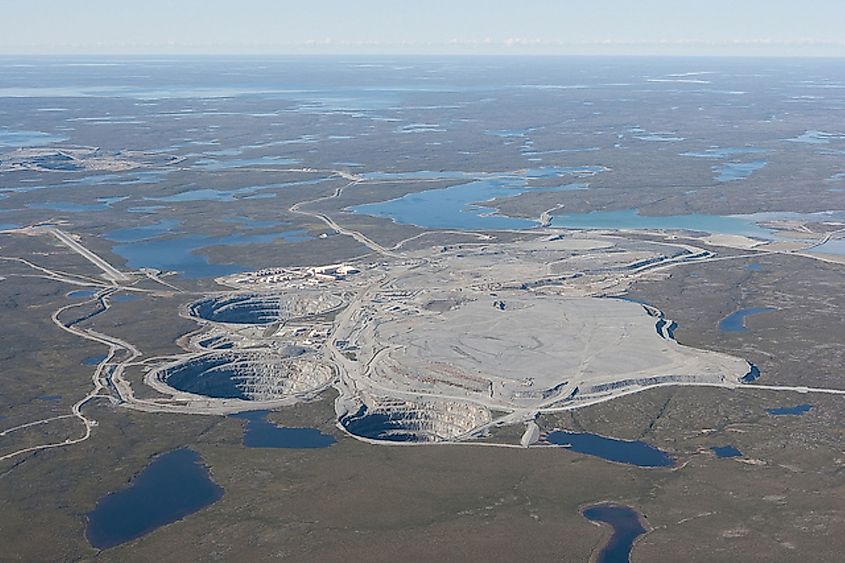

The Northwest Territories, which were once used as hunting grounds, are now used mainly for large-scale resource extraction, including diamond mining. Diamonds weren't found by non-natives until 1991, specifically by two geologists named Chuck Fipke and Stewart Blusson. The first diamond mine in the Northwest Territories, known as Ekati, opened in 1998 because of this finding. The Arctic Canadian Diamond Company presently oversees the operation of Ekati, which is a responsible steward of the environment and a significant source of high-quality employment and money for the area. Most of Canada's diamonds are mined in the Northwest Territories, which comprise about 40% of the total geographical area. There are currently four working diamond mines in Canada, three in the NWT – the Ekati, Diavik, and Gahcho Kué mines – and the Renard diamond mine in Quebec.
4. Democratic Republic of the Congo (14.09 million carats)
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is the country that turned South Africa's diamond industry profitable. Miniere de Bakwange (MIBA), a joint venture between the Belgian business Sibeka and the DRC government, which controls 80% of the company, is the only commercial diamond producer in the DRC. Although ongoing political unrest has caused production to fall recently, the DRC has the capacity to produce more diamonds. Only a tiny area has been examined, and mining has only ever been done on a small basis. Most of the DRC's output is mined by the informal sector rather than mining companies. De Beers markets about one-third of Sibeka's production and holds a 20% stake in the company.
5. South Africa (9.72 million carats)
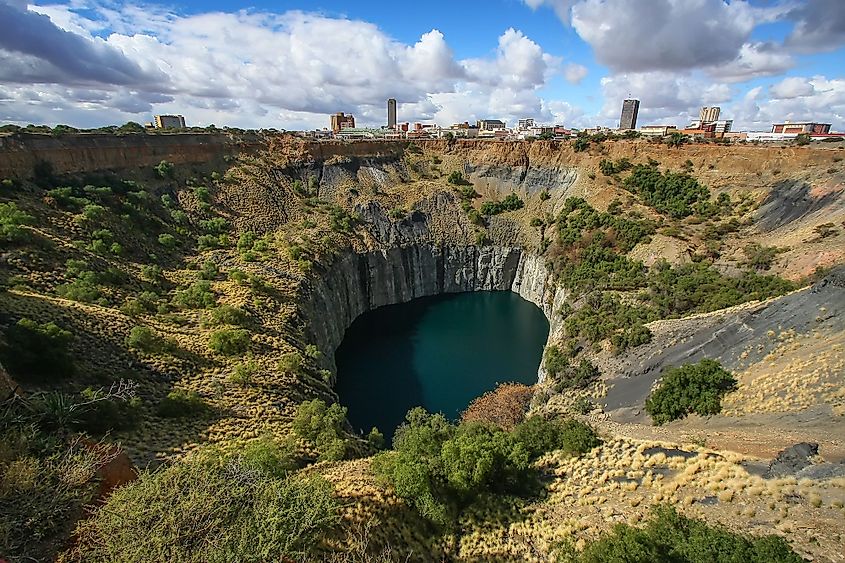

Almost all the modern diamond trade originates in South Africa. The earliest diamonds found in South Africa were alluvial diamonds. Diamonds were initially discovered in yellow earth in 1869, and then later below ground in hard rock called blue ground near and in what would become Kimberley in the Northern Cape, the diamond center of the world. Later, the blue rock was given the mining town's name: kimberlite. One of the country's biggest diamond deposits is located in the South African province of Gauteng. As the government and miners continue to find significant diamond resources and pipelines, the demand for diamonds in South Africa is anticipated to rise.
One can therefore expect the global diamond industry to keep expanding and displaying a bright future as long as economic prosperity continues to improve and as long as there are still diamond reserves that have not yet been mined.