What Are The Major Natural Resources Of The Gambia?

The Gambia is a Western Africa country located on the Atlantic coast and bordered on its other three sides by Senegal. It is a narrow strip of land that surrounds the Gambia River, a navigable river that dominates the country. The Gambia has a peculiar shape and size which is as a result of a territorial compromise made in the 19th century between Great Britain (who was in control of the lower Gambia River), and France (who controlled the colony of Senegal). Periodic negotiations in the 20th century to unite Senegal and The Gambia resulted in the temporary formation of the Senegambia confederation (1982-1989). The Gambia is Africa’s smallest non-island country and one of the most densely populated countries in the continent. The Gambia has limited natural resources and depends mainly on agriculture. Here are some of the natural resources of Gambia.
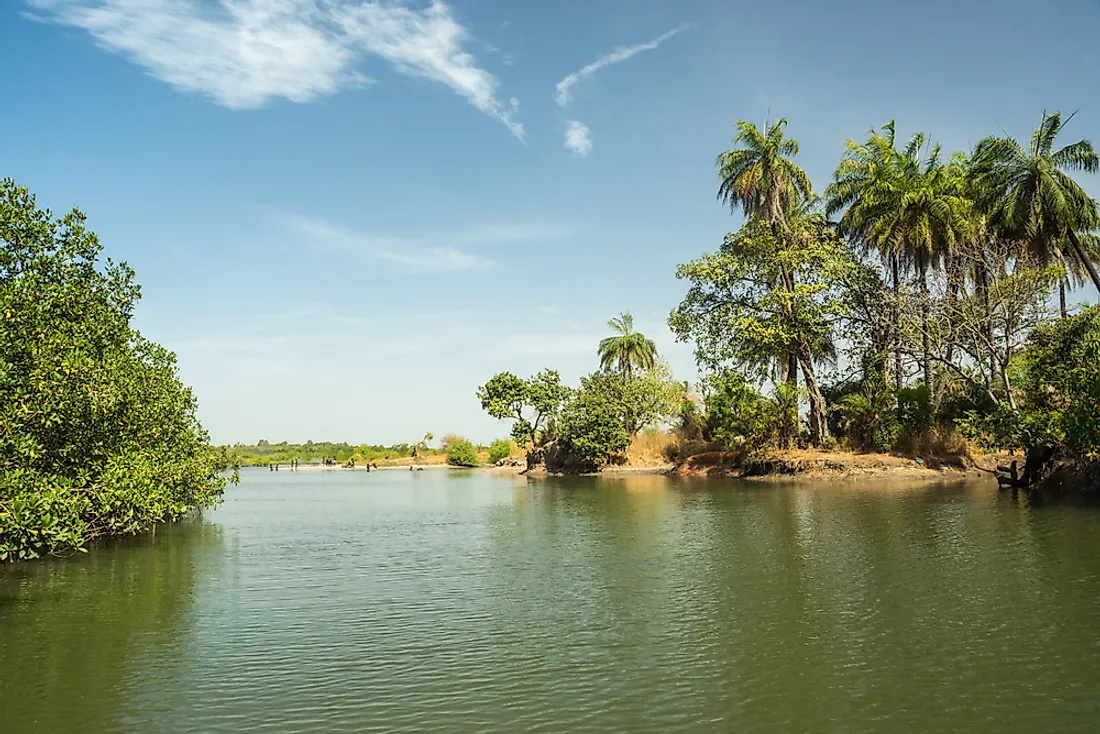
River Gambia
The Gambia River is one of the main resources of The Gambia. The river runs for approximately 700 miles from the Fouta Djallon plateau in Guinea through Senegal and The Gambia before emptying into the Atlantic Ocean. Almost half of the river flows through The Gambia. It is the country’s dominant feature. The River Gambia is one of the most important waterways in Africa. It is the only river in Africa that is navigable by the ocean-going vessels all year round. River Gambia is also an important fishing ground for the people of The Gambia. Oyster harvesting is an important economic activity on River Gambia. Oyster is also an important ingredient for the oyster stew, traditional cuisine in the Gambia.
Fisheries
Apart from livestock and crops, Gambians rely on fisheries to supplement their food deficit. Although the coastline limits marine fishing, the country has a commercial fishing potential offshore and in the river. Fishing activities in the country have been hampered by inadequate fishing equipment. However, the government is determined to ensure that the sector succeeds by granting fishermen loans for the purchase of fishing equipment such as motorized fishing boats and construction of processing plants.
Quartz Sand
The River Gambia flows over a sandstone plateau consisting of compacted sediments of quartz sand formed about 16 million years ago. The large reserves of quartz sand can be found in the Greater Banjul Area. Although the mining industry in the Gambia is very small because the country lacks large mineral reserves, successful mineral operations have been ongoing, especially in areas with glass and quartz sand deposits. The Gambian government continues to seek prospective investors who can effectively help in the mining of the silica sand without exploiting the locals. It is estimated that the existing reserves can yield up to one million tons of quartz sand. River Gambia has the potential to generate hydro-electric power but there are no dams on the river within the country.
Climate
The Gambia experiences a tropical climate characterized by hot and rainy season which lasts from June to November and cool temperatures for the rest of the year. The country’s climate resembles the climate of the neighboring countries such as that of Senegal, northern Benin, and southern Mali. The climate of Gambia is one of the main tourist attractions, with visitors flocking the country for the traditional sun-seeking holiday. The tourist is common along the beaches where they not only get to enjoy the hot climate but also sample the sandy beaches experience. Apart from tourism, the tropical climate also favors agricultural activities in the country.
Agricultural Land
Agriculture accounts for approximately 30% of The Gambia’s GDP and employs about 75% of the labor force. Crop production is the major agricultural activity, accounting for about 13% of the GDP. Livestock accounts for only 4.4%. Although most of Gambia’s soil is poor and sandy, approximately 558,000 hectare is arable land and is able to support a wide range of agricultural activities, accounting for 38% of the total land area. Currently, 200,000 hectare of the arable land is under rain-fed agricultural production. Some of the commonly grown crops include peanuts, millet, rice, beans, corns, sorghum, and fruits such as cashews and mangos.
National Parks And Reserves
The Gambia has a total of seven national parks and nature reserves, covering an area of about 43,727 hectares. They are managed by the Department of Parks and Wildlife. The largest protected area in the Gambia is the Bao Bolong Wetland Reserve which covers an area of about 22,000 hectares. It was the first reserve in the country to be acknowledged as a wetland area under the Ramsar Convention (an international convention for the conservation and sustainable use of wetland areas). Other protected areas include Kiang West National Park, Niumi National Park, Tanbi Wetland Complex, Tanji Bird Reserve, River Gambia National Park, and Abuko Nature Reserve.
Minerals
The Gambia has a significant amount of minerals that have yet to be exploited. The mining industry does not play a major role in the economy as the economy mainly relies on tourism, agriculture, and imports. Some of the minerals locally available in the country include zircon, titanium, laterite, clay, sand, and silica. The Department of Trade, Industry, and Employment are responsible for the administration of mining in the country. However, because of the lack of investors most of these minerals remain largely unexploited. The government of Gambia has instituted some policies such as the issuance of special certificates to attract direct foreign investment. The Gambian deposits with a significant amount of minerals include Batukunku, Kartung, and Sanyanga. These deposits contain mainly the heavy-minerals assemblage such as zircon, ilmenite, and rutile.
Beaches
The Gambia has a coastline of approximately 50 miles on the Atlantic Ocean. The coastline is lined by some of the most beautiful beaches in West Africa. Some of the famous beaches include the Northern Kombo beaches which meander the south bank of River Gambia on a strip of 12.5 kilometers wide and sandy shores Southern Kombo beaches which extend from Brufut Height to Kartong, and Cape Point beach. These beaches are popular destinations for tourists, especially from Europe, who visit the country during the summer. Some of the beaches have world-class facilities such as resorts, hotels, and restaurants where visitors can sample the Gambian cuisine.