How Many Types Of Pollution Are There?
Pollution refers to the addition of contaminating substances to the natural environment resulting in an adverse impact on the environment. Pollution is human-made and the level of pollution of the environment has increased with the rise in human population and developments made by the human civilization. Pollution can be of different types depending on the part of the environment that is getting polluted or the type of pollutants/contaminants causing the pollution. Air, water, and soil pollution are the major types of pollution. However, given the wide range of ways in which our species have managed to contaminate the environment, we also have noise, light, radioactive, thermal, and plastic pollution. The different types of pollution have been discussed in greater details below.
- Air Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Soil Contamination
- Noise Pollution
- Plastic Pollution
- Radioactive Contamination
- Light Pollution
- Thermal Pollution
- Visual Pollution
- Littering
Air Pollution
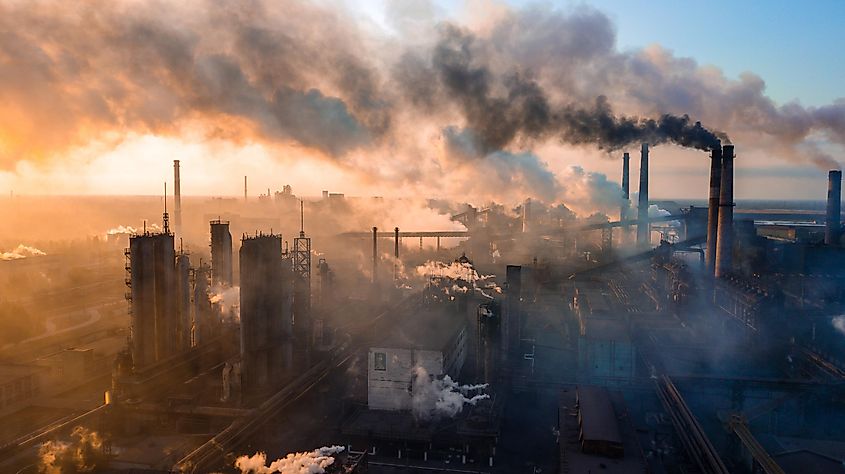

Air Pollution refers to the addition of harmful contaminants, such as toxic gases, particulate matter, chemicals, biological molecules, etc., that modify the natural characteristics of the Earth’s atmosphere. Some common sources of air pollution include wildfires, volcanic eruptions, burning of fossil fuels, mining operations, household combustion devices, motor vehicles, and exhaust gases from industrial facilities.
Various gases like carbon monoxide, nitrous oxide, ammonia, chlorofluorocarbons, and sulfur dioxide are some examples of air pollutants. Air pollution poses a significant threat to the health and well-being of all living beings on our planet, resulting in acute and chronic respiratory diseases, lung cancer, cardiovascular problems, as well as acid rain, and ozone depletion. It is estimated that about 2.4 billion people worldwide are exposed to extreme levels of household air pollution. Approximately 7 million premature deaths yearly are attributed to the combined effects of household and ambient air pollution.
Water Pollution
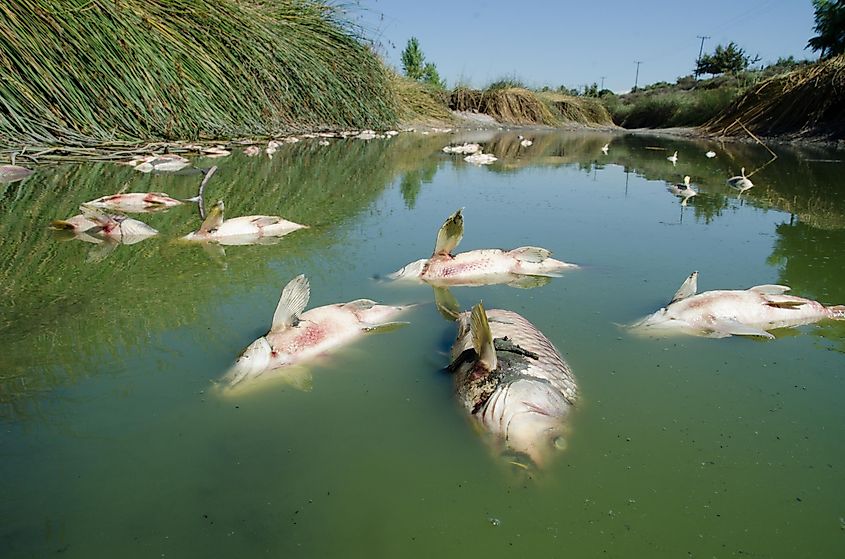

Also referred to as Aquatic Pollution, Water Pollution refers to the contamination of water bodies like lakes, rivers, aquifers, groundwater, and oceans by various toxic pollutants and particulate matter. These harmful pollutants are usually introduced to the water bodies by careless anthropogenic activities, leading to the degradation of the water quality and rendering it toxic for humans as well as several aquatic flora and fauna that are entirely dependent on the water bodies for their survival.
Some chief causes of water pollution include the release of untreated industrial sewage, the dumping of solid wastes, plastic litter, oil spills, drought, and agricultural runoff containing harmful pesticides and nitrogen-rich fertilizers. The increased concentration of harmful chemicals in the water bodies leads to eutrophication, further triggering algal bloom and explosive growth of other life-threatening microorganisms. Furthermore, these toxic chemicals can bioaccumulate in living beings and make their way up the food chain, adversely affecting human health.
Soil Contamination
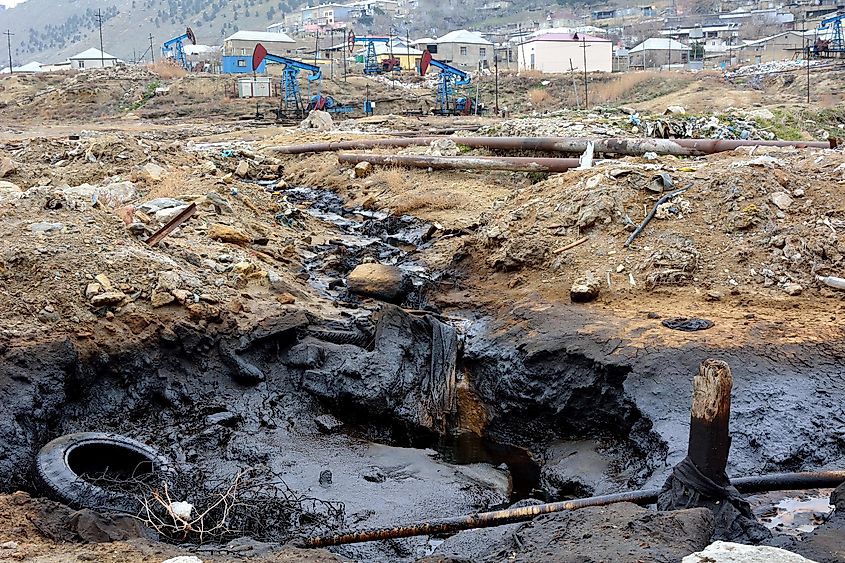

Soil Pollution or land degradation refers to the alteration in the natural soil environment of an area by harmful xenobiotic chemicals. Soil Pollution is mainly caused by agrochemicals, industrial chemicals, solid waste disposal, landfill, and petrochemicals. Soil is essential for the growth of plants, including important crops. Therefore, the degradation of soil results in the reduction of crop yields and poor crop health. Soil Pollution also directly impacts human health when humans ingest vegetables grown in contaminated soil.
Noise Pollution
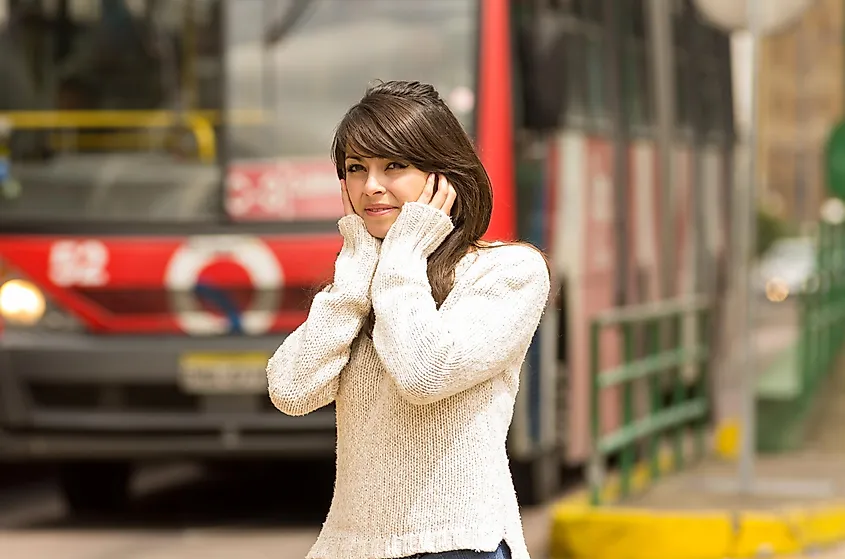

Also referred to as sound pollution, Noise Pollution refers to the extreme amount of noise in the surrounding that disrupts the natural balance, affecting human and animal life. There are several contributors to noise pollution, such as construction noises, transportation noises, industrial noises, household noises, and noise from social events. Due to rapid industrialization and dense urbanization, noise pollution has become very common. Some of noise pollution's adverse effects include hearing loss, sleep disorders, increased occurrence of coronary artery disease, and cardiovascular effects in humans. The unpleasant noise also affects the psychological health of human beings.
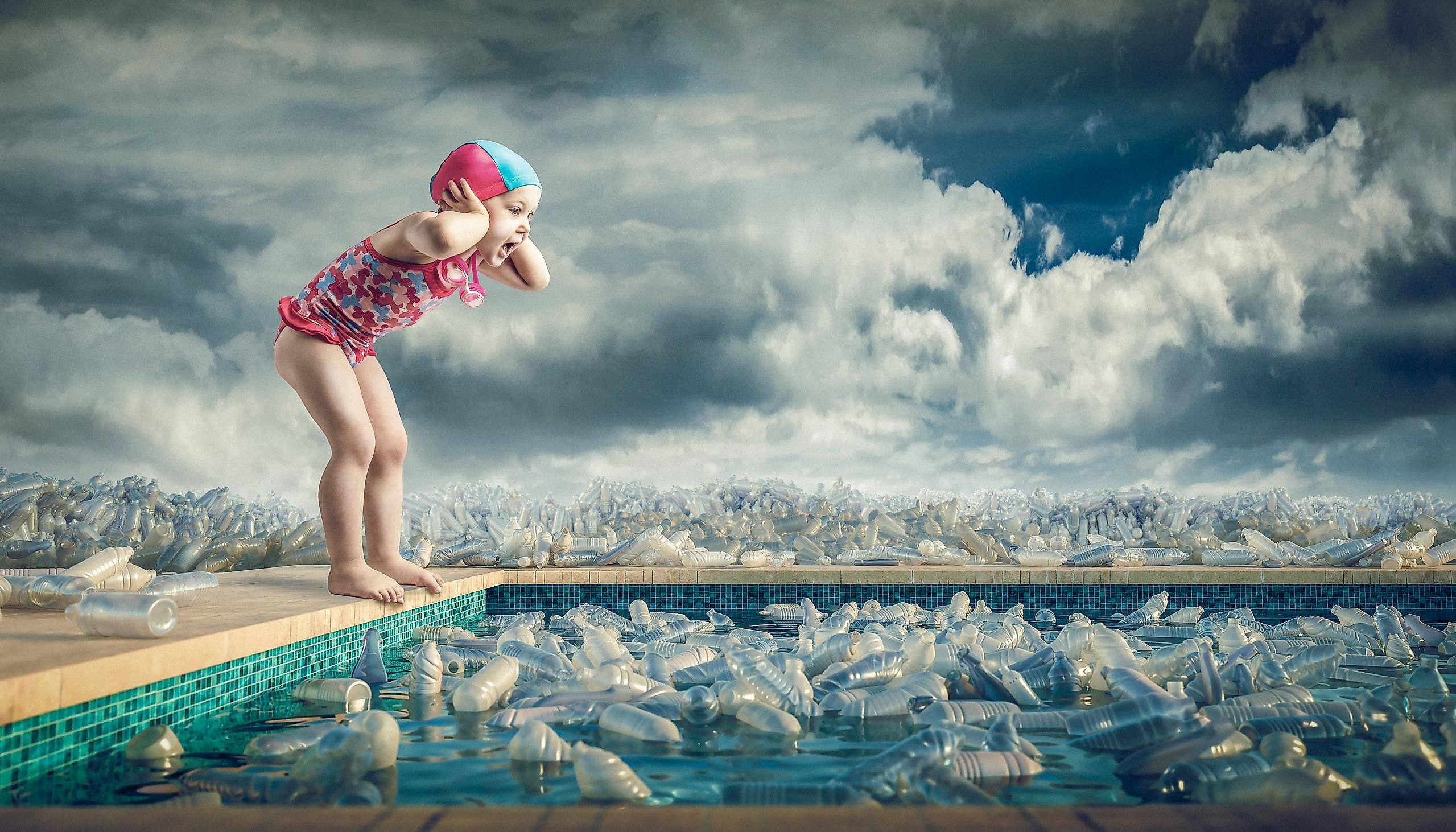
Plastic Pollution
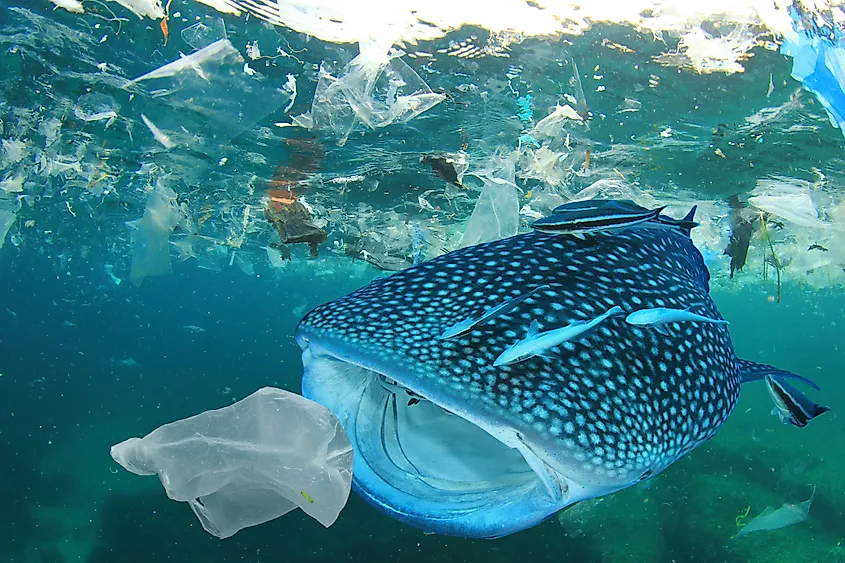

The accumulation of plastic objects and materials in the Earth’s environment is referred to as Plastic Pollution. The chemical structure of plastics makes them resistant to natural degradation processes resulting in immense pollution of oceans, waterways, and land areas. It is estimated that about 80% of the 8.3 million metric tons of plastic produced over the past 70 years has made its way into landfills and oceans.
Moreover, nearly 700 wildlife species have been affected by the high concentration of single-use plastics in the environment. These single-use plastics have resulted in deaths due to ingestion, entanglement, and blocking of breathing passages and stomachs of these wild species. Plastics also have a wide-scale impact on the marine environment, with plastic debris choking marine life and gradually transforming some marine areas into a ‘plastic soup.’
Radioactive Contamination

Also referred to as Radiological Pollution, Radioactive Contamination is caused by the presence of radioactive materials where their presence is most undesirable. The common causes of radioactive contamination are radioactive disasters and irresponsible management of radioactive wastes. Ionizing radiations are produced by the radioactive decay of such contaminants leading to a hazard. Therefore, exposure of human beings to these radioactive substances via inhalation, ingestion, or absorption adversely affects human health.
Light Pollution
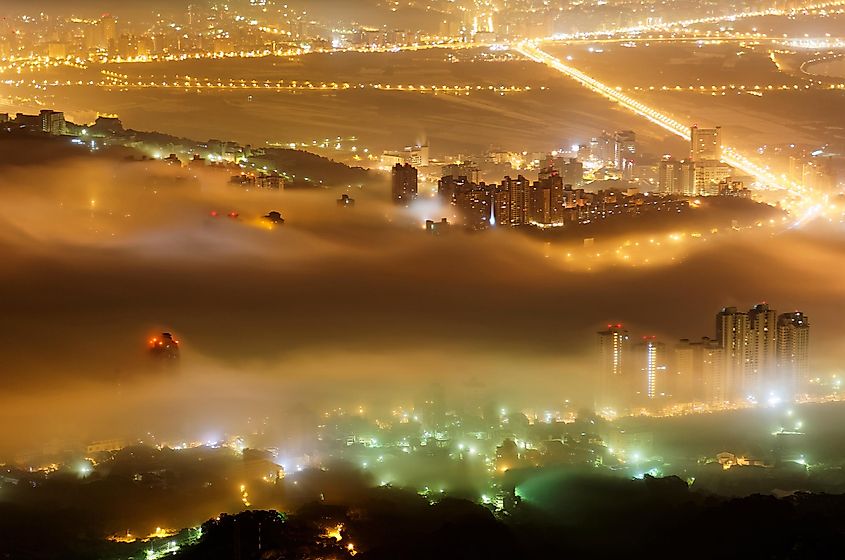

Light Pollution refers to the pollution of the night environment by excessive anthropogenic light. This type of pollution is usually caused by too much use of artificial light to illuminate streets, buildings, advertisement hoardings, industrial areas, sporting venues, etc. Light Pollution is most severe in the industrialized and densely populated regions of Asia, Europe, and North America and some of the major cities like Cairo and Tehran in the Middle East and North Africa. This unwanted or excessive light use causes changes in the visibility of natural features during the night, a decline in insect populations, changes in the behavioral patterns of humans and wild animals, disorientation of migratory species, and collisions of birds with illuminated buildings.
Thermal Pollution
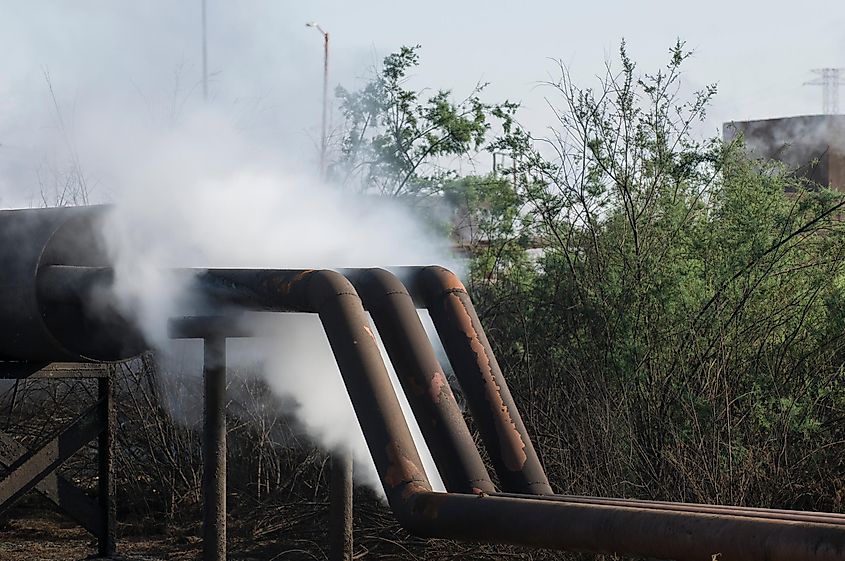

Often known as “thermal enrichment,” Thermal Pollution refers to the degradation of water quality by processes that induce a change in ambient water temperature. It is mainly caused by the water used as a coolant in power plants and manufacturing units that becomes heated during the process. This heated water (about 15°C hotter than a lake or stream water), when released into the natural environment, mixes with the water of lakes and streams to raise the overall temperature of the water bodies. Higher water temperatures reduce the amount of dissolved oxygen a water body can hold and increases metabolic rates in fishes. It also results in the death of aquatic flora and fauna, which experience a “thermal shock” due to this sudden change in water temperature.
Visual Pollution
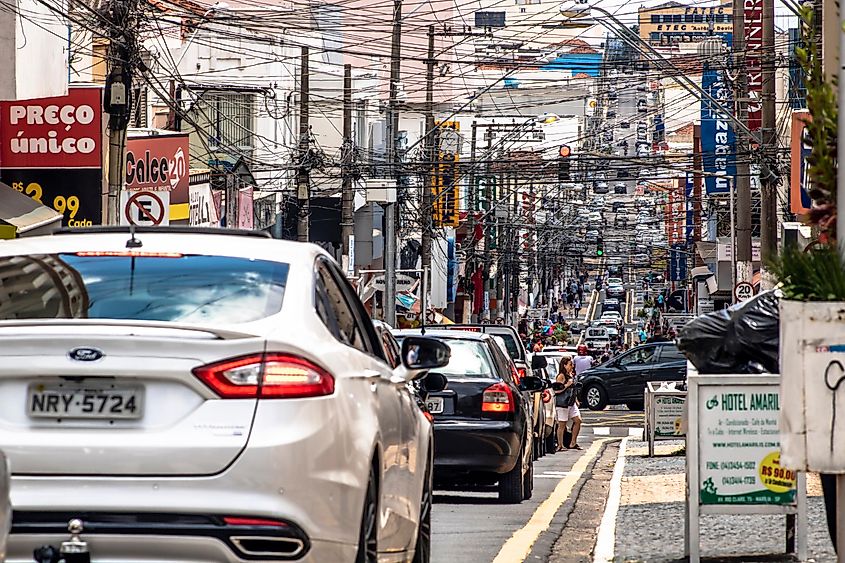

Visual Pollution refers to the installation of ugly physical barriers by human activities that affects one’s ability to enjoy and appreciate the clear vision of natural and manmade landscapes. Visual pollution is created by the open disposal of garbage in different places, installation of billboards, several electric wires crisscrossing each other in urban areas, old dilapidated buildings, dumping of construction materials, etc. The various effects of visual pollution include eye fatigue, distraction, irritability, psychological disturbances, loss of sense of hygiene and aesthetics, loss of identity, and decreases in opinion diversity.
Littering
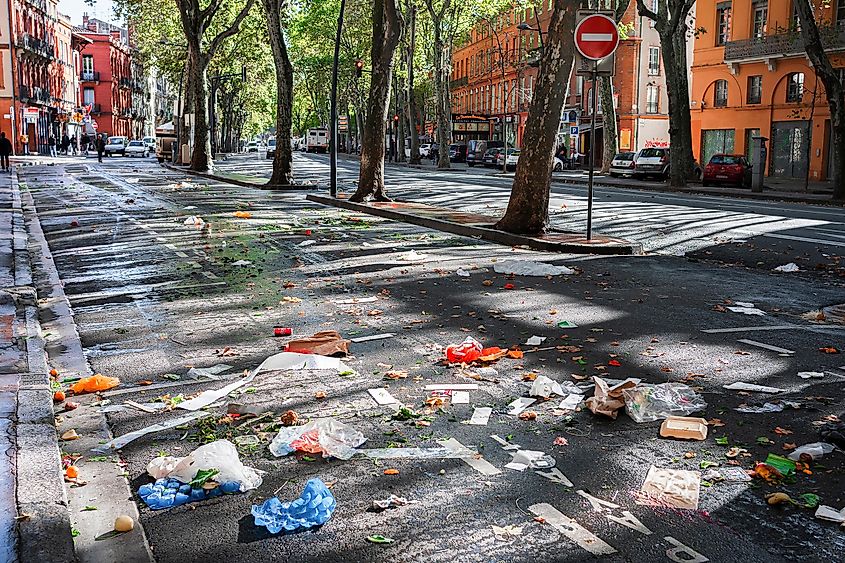

When waste products generated by humans, like food wrappers, plastic bottles, aluminum cans, paper cups, electronic waste, etc., are disposed of in unwanted locations improperly, it leads to littering. In many countries, littering is a serious environmental problem, as these wastes can exist for long periods before their eventual degradation. It is estimated that about 18% of the litter travels through stormwater systems into local water bodies causing water pollution. Litter burning also releases high volumes of particulate matter into the atmosphere leading to air pollution. Different items of litter, such as discarded vehicle tires when filled with water, serve as breeding grounds for mosquitos leading to the further spread of vector-borne diseases.
The above discussion points out the different types of pollution, their sources, and their effects on the health and well-being of all living beings. Environmental pollution is one of the most hazardous threats faced by Planet Earth. Various measures must be adopted to control the release of harmful pollutants damaging our environment. Therefore, every citizen must generate awareness and take necessary action to save our environment from getting further polluted.
How Many Types Of Pollution Are There?
| Type Of Pollution | Definition |
|---|---|
| Air Pollution | Air Pollution refers to the addition of harmful contaminants, such as toxic gases, particulate matter, chemicals, biological molecules, etc., that modify the natural characteristics of the Earth’s atmosphere. |
| Water Pollution | Water Pollution refers to the contamination of water bodies like lakes, rivers, aquifers, groundwater, and oceans by various toxic pollutants and particulate matter. |
| Soil Contamination | Soil Pollution or land degradation refers to the alteration in the natural soil environment of an area by harmful xenobiotic chemicals. |
| Noise Pollution | Noise Pollution refers to the extreme amount of noise in the surrounding that disrupts the natural balance, affecting human and animal life. |
| Plastic Pollution | The accumulation of plastic objects and materials in the Earth’s environment is referred to as Plastic Pollution. |
| Radioactive Contamination | Radioactive Contamination is caused by the presence of radioactive materials where their presence is most undesirable. |
| Light Pollution | Light Pollution refers to the pollution of the night environment by excessive anthropogenic light. |
| Thermal Pollution | Thermal Pollution refers to the degradation of water quality by processes that induce a change in ambient water temperature. |
| Visual Pollution | Visual Pollution refers to the installation of ugly physical barriers by human activities that affects one’s ability to enjoy and appreciate the clear vision of natural and manmade landscapes. |
| Littering | When waste products generated by humans, like food wrappers, plastic bottles, aluminum cans, paper cups, electronic waste, etc., are disposed of in unwanted locations improperly, it leads to littering. |