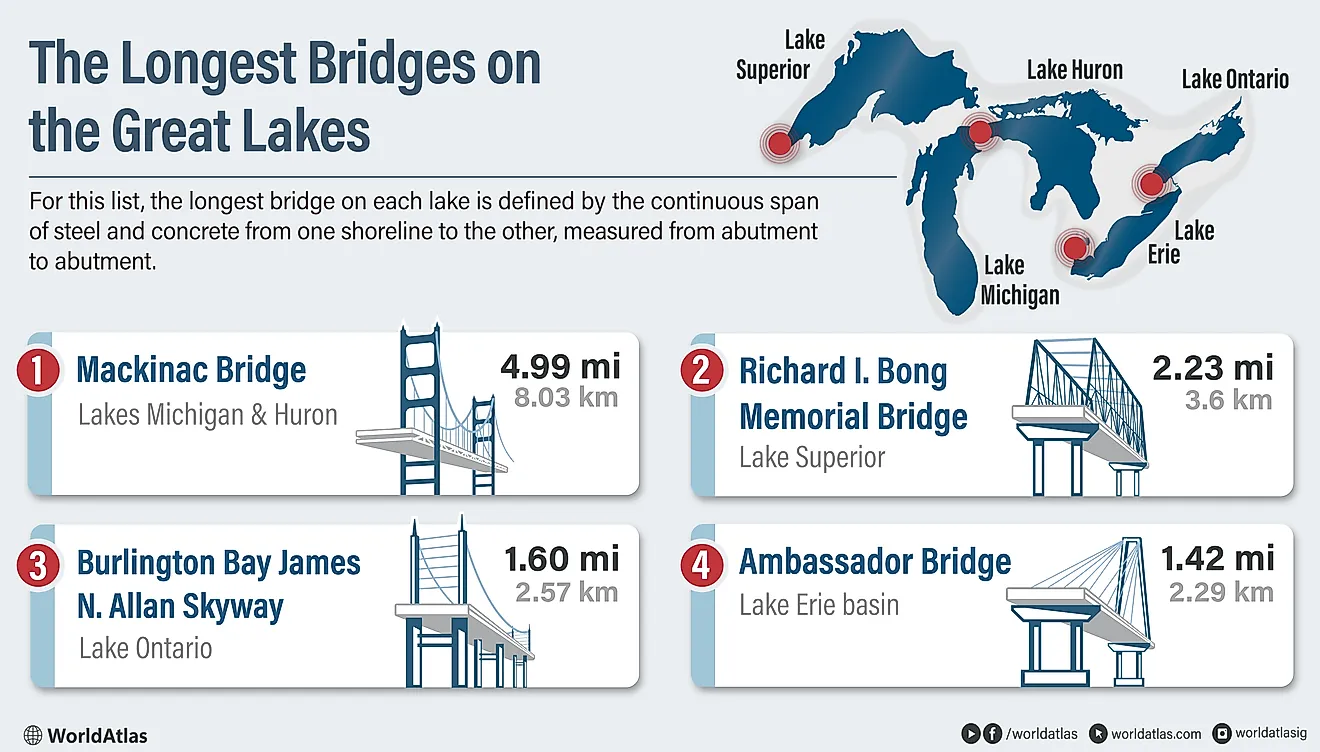
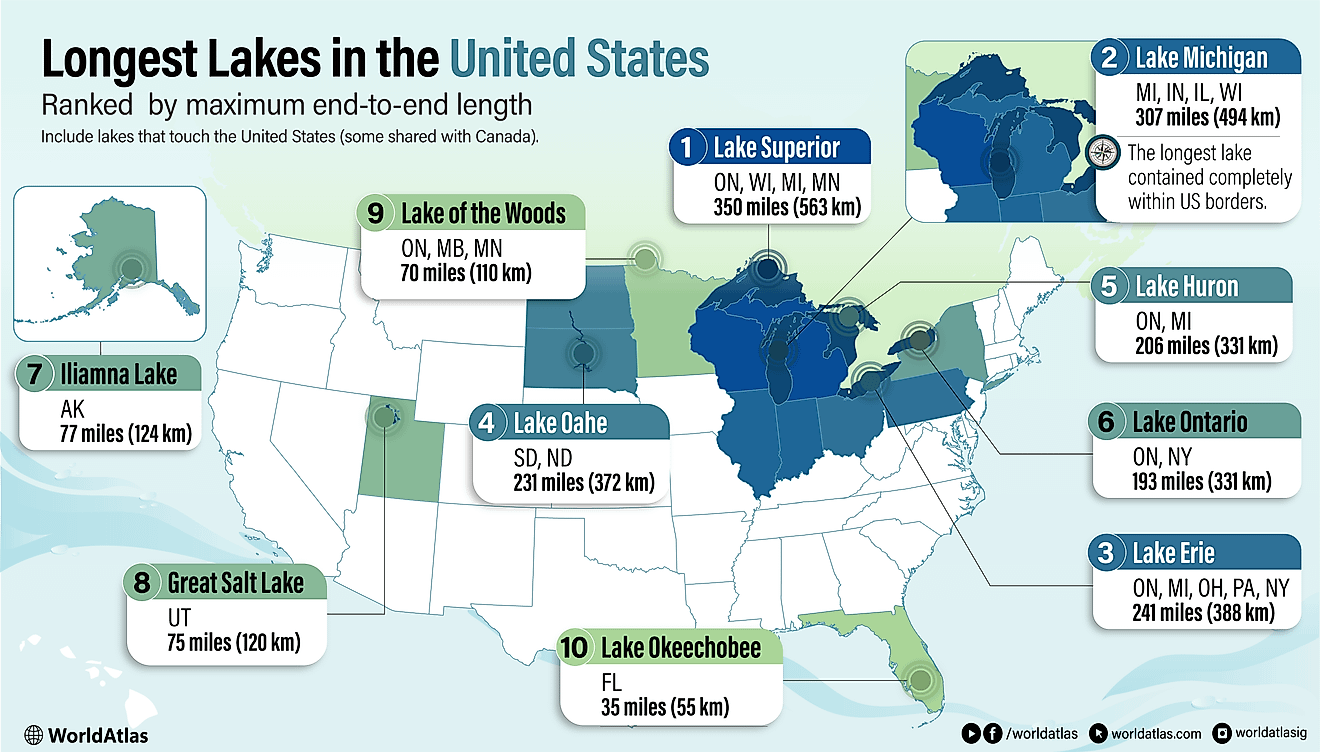
Bothnian Sea
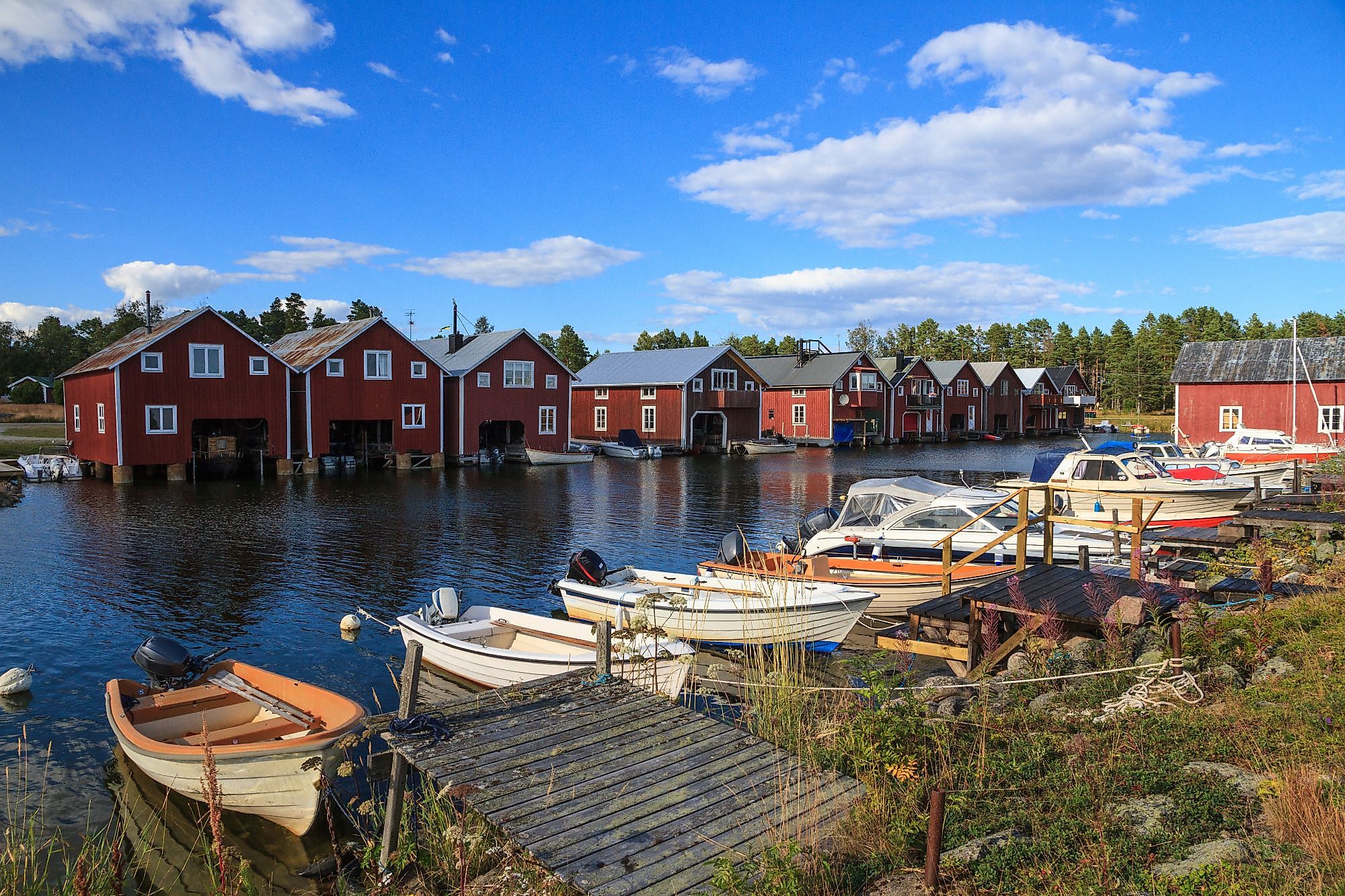
The Bothnian Sea, known in Finland as Selkämeri and in Sweden as Bottenhavet, is a sub-basin of the Baltic Sea and a sea in the Gulf of Bothnia, located between Finland and Sweden. In Swedish, the sea’s name is derived from two words, “botten,” meaning “bay” and “hav,” for “sea,” combined to form bay-sea. The sea’s Finnish name translates to “open stretch of water.” The Bothnian Sea links the Bothnian Bay to the Baltic Proper and is home to the Bothnian National Park. It is an important source of livelihood for the people living in the cities along its coast and a prime location for swimming, hiking, scuba diving, snorkeling, and birdwatching.
Location Of The Bothnian Sea
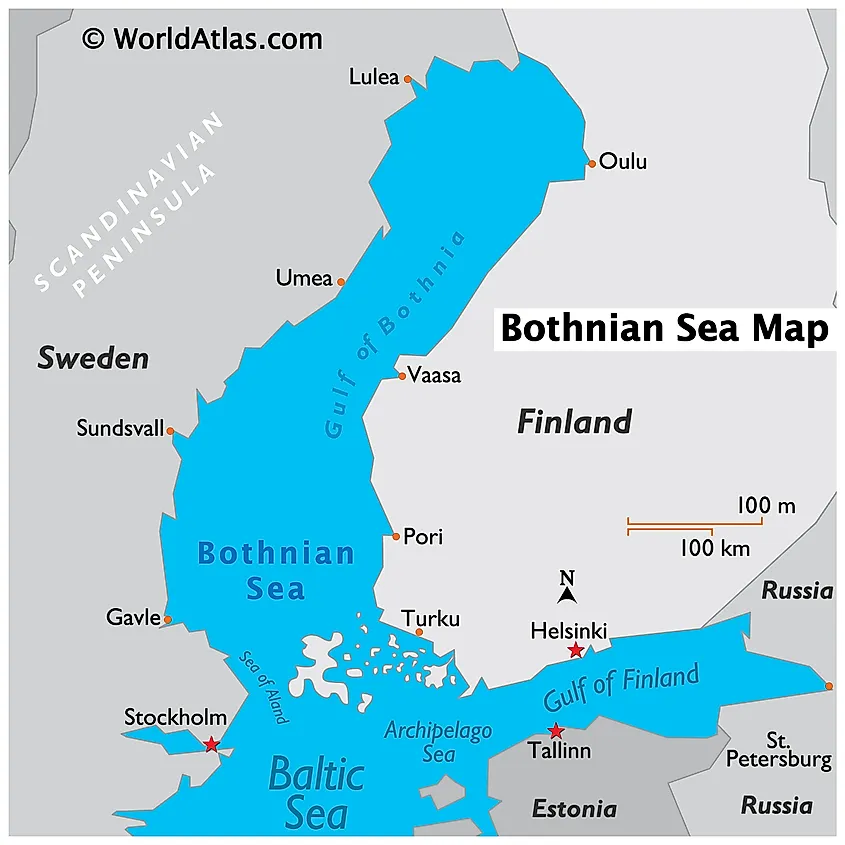
The Bothnian Sea is the southern portion of the Gulf of Bothnia, the Baltic Sea’s northern arm. The gulf is located between Sweden’s eastern coast and Finland’s western coast. It is divided into several water bodies, including the Sea of Aland, Kvarken, Bothnian Bay, and the Bothnian Sea. The Kvarken separates the Bothnian Sea and the Bothnian Bay, while the Sea of Aland connects the sea to the Baltic Proper. The Archipelago Sea, with a coastline on Finland, borders the Bothnian Sea to the south. Major cities along the sea’s coast include Pori and Rauma in Finland and Sundsvall and Gavle in Sweden. Aland, Finland’s autonomous region, is located on the sea’s southern end.
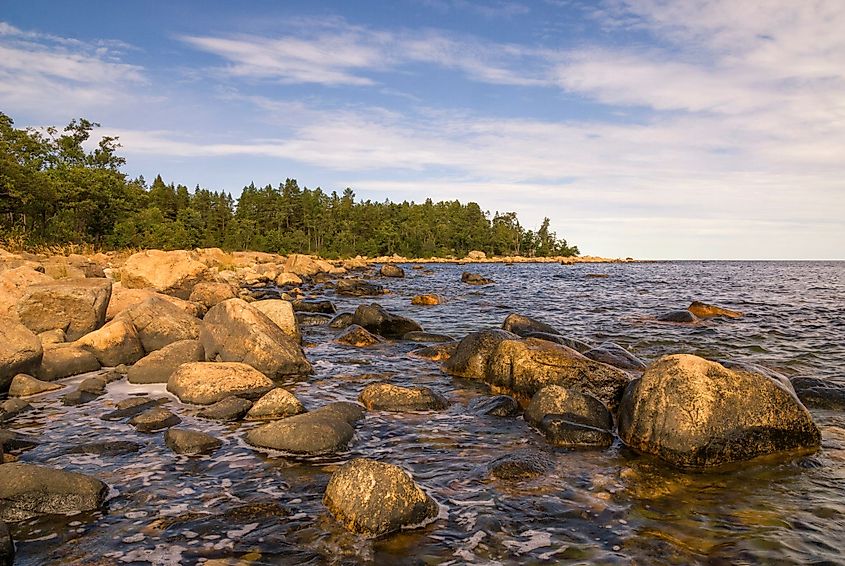

The Bothnian Sea is a sub-basin of the larger Baltic Sea, a portion of the Atlantic Ocean bordering Finland, Poland, Sweden, Estonia, Denmark, Russia, Lithuania, Germany, and Latvia. The sea has a surface area of 79,000 square kilometers, making it the largest section of the Gulf of Bothnia. Several large rivers drain into the Bothnian Sea, including the Angermannalven River originating in Sweden and Kokemaenjoki in Finland.
The sea has normal brackish water and a lower saline level compared to other seas. Besides the freshwater rivers draining into the sea, the water current and winds also affect the sea’s salinity level. The sea freezes for up to five months every year.
Brief History
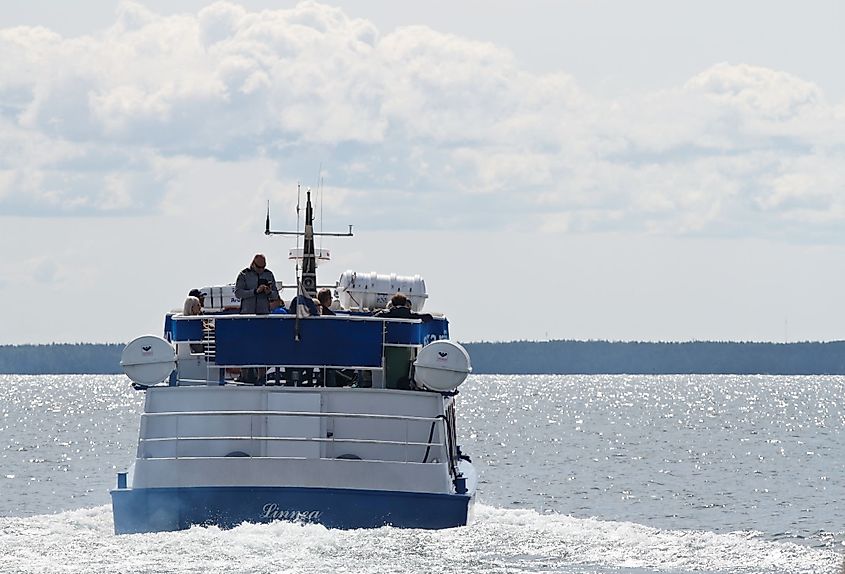

The Gulf of Bothnia, including the Bothnian Sea, was covered by ice for about 100,000 years during the last ice age. People began settling on the sea’s coast as the ice sheet melted away around the 8th millennium BC. Since then, the Gulf of Bothnia and its water bodies have been an essential natural resource for Sweden and Finland. For years, the Bothnia Sea supported agriculture in areas along its coast. It was (and still is) an important transit route for vessels to the coastal cities. The vessels transport mainly oil and ore to coastal cities like Rauma, Turku, and Sundsvall.