What is the Blob?
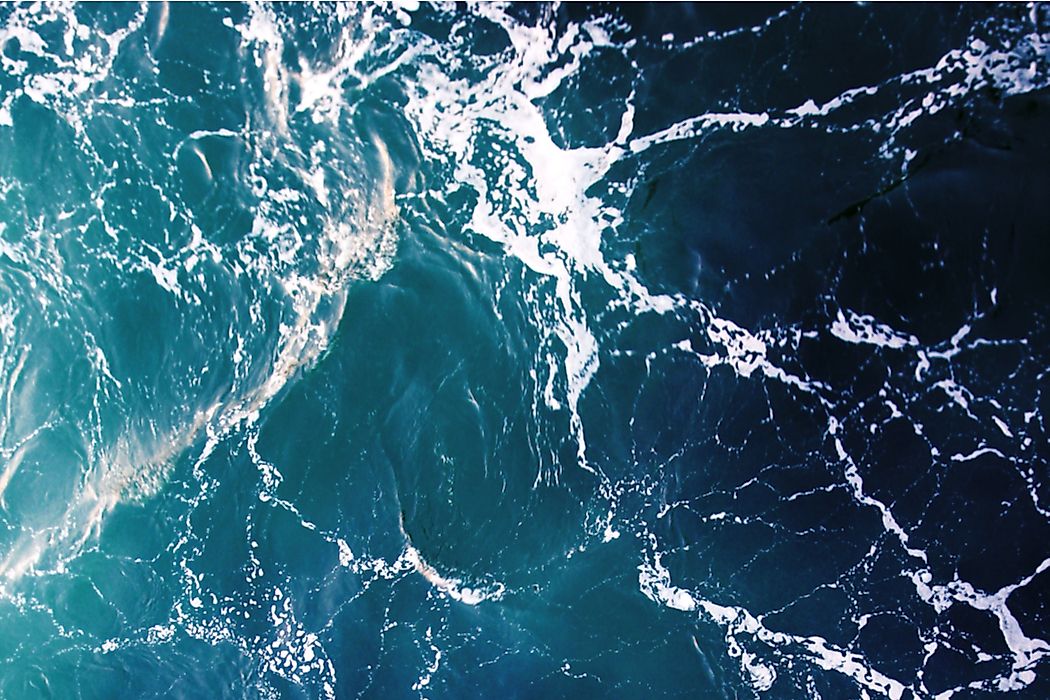

The Blob refers to a place in North America’s coast, off the Pacific, that experiences warm temperatures. The spot was first discovered in 2013, and it has continued to expand throughout the years. The blob was present in 2016, but it seems to have disappeared that year then it reappeared in September 2016. This patch of warm water is an unusual occurrence in the ocean, and it is thought to influence the bizarre weather experienced in the coast of Pacific in North America. The waters in the patch lack nutrients.
When Was the Blob Discovered?
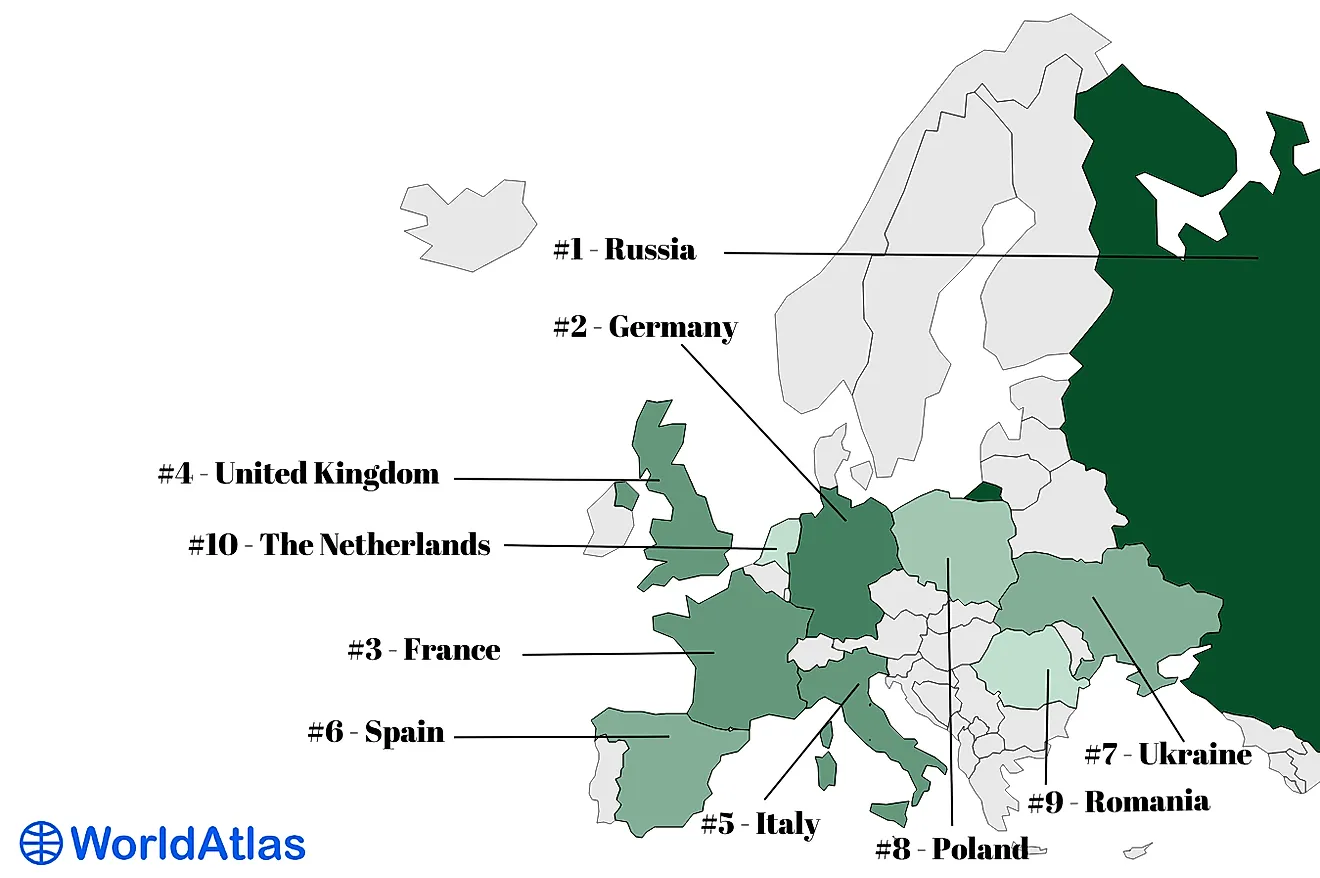
Nicholas Bond and his colleagues from the University of Washington discovered the blob when the patch of water in the location could not cool down like other places as expected, but remained warm. Nicholas referred to the spot as the blob and the name was adopted. On discovery, it was said to have a width of 500 miles and a depth of 300 feet. It expanded with time, and in June 2014 it had gotten to a length and width of 1,000 miles with a depth of 300 feet. Presently, the blob touches the North American coast, stretching from Mexico to Alaska stretching to about 2,000 miles. The blob has three different patches, which include the coastal parts of Canada, Washington, California, and Oregon and it is known as Coastal Upwelling Domain by the Oceanographers. The second is located off the Bering Sea and Alaska, the last one is the smallest and is located off Mexico and Southern California. In 2014, the blob had a temperature of 4.5 °F warmer compared to the usual temperatures experienced at that time of the year.
Factors That May Have Led to the Blob
Several scientists have been trying to find what causes the blob, and they came up with several probable causes. Some experts figured the blob could be attributed to the loss of heat to the atmosphere from the sea being lower than the typical temperature and the water circulation also being lower leading to a constant upper water layer. The two causes are said to be as a result of a fixed region of high atmospheric pressure named the Ridiculously Resilient Ridge that has been in existence since 2014. Other experts believed that the blob is a result of cyclical changes with the surface of water in the mid-latitude of the Pacific Ocean changing from cold temperatures to stage in what is named the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. The cycle happens intermittently over the years and is known to affect the climate.
Effects in the Pacific
The blob has had several impacts on the environment. The first is marine life; the water in the blob lacks nutrients thus it is not conducive for marine life. The patch has upset the food chain in the Northeast Pacific with fish migrating in search of places with many zooplanktons to feed on and sea lions starving. The sea animals favoring warmer waters have also moved to the areas covered by the blob. In 2014, for the first time, mass coral bleaching in Hawaii was noted by biologists from the University of Queensland, the bleaching is thought to have been caused by the blob.