What Is A Blizzard?
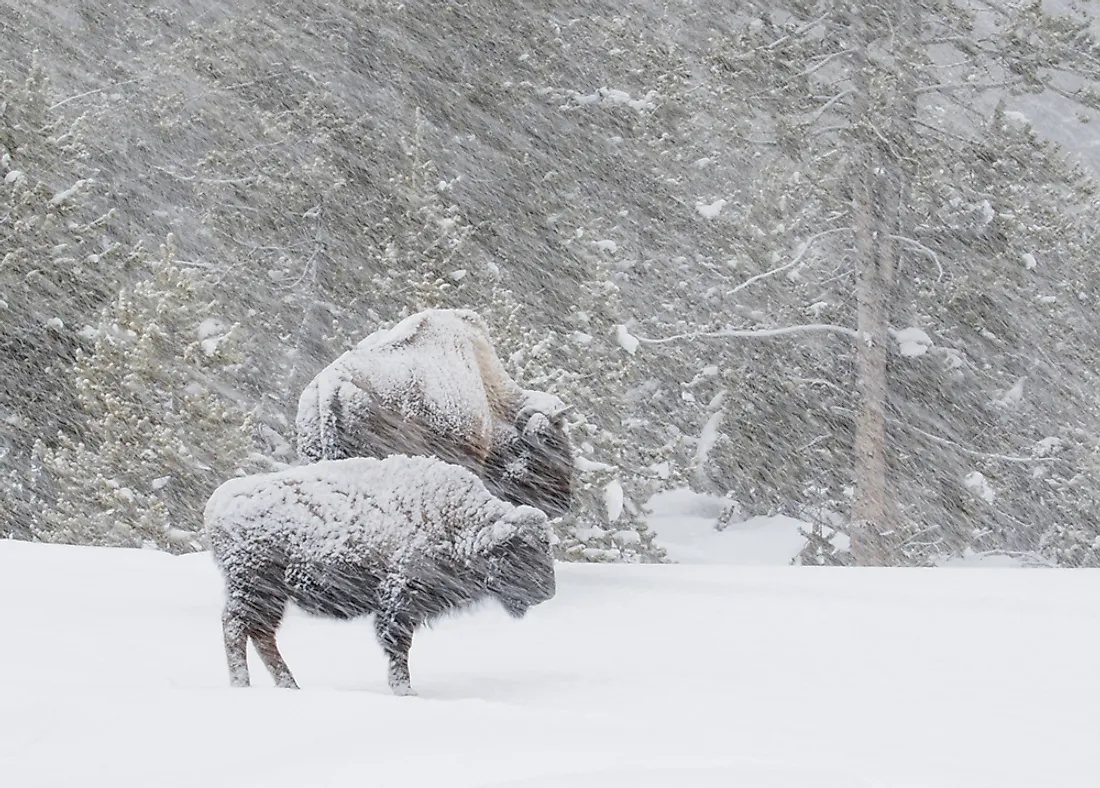

A blizzard is an intense weather condition characterized by extremely low temperatures and strong winds at speeds that exceed 35 miles per hour, accompanied by vast quantities of blowing or falling snow for a minimum of three hours. Although often mistaken for a snowstorm, a blizzard has stronger and more powerful winds than a snowstorm. Blizzards limit visibility to a quarter of a mile or less as a result of the blowing snow. Extreme blizzards have wind speeds exceeding 45 miles per hour, temperatures of 70°F or lower, and visibility near zero. Ground blizzards have no falling snow, but instead exhibit snow blowing near the ground.
Causes of Blizzards
Blizzards are formed when a warm moist wind traveling from the equator towards the poles rises above a cold dry wind with temperatures below the freezing point traveling from the poles towards the equator. A field is formed between the two air masses, where snow is formed and falls to the ground. The combination of snowfall and strong wind creates a snowstorm. When wind speeds exceed 35 miles per hour, the windy snowstorm becomes a blizzard. In the US, blizzards are caused by northwesterly winds trailing winter depressions and low-pressure systems. However, a special case is experienced in Antarctica, where winds spin over the edge of an ice plateau at approximately 100 miles per hour.
Places in the US Most Susceptible to Blizzards
Blizzards are primarily fueled by high-speed winds during winter rather than by the quantity of snow-fall. This helps understand the geographical susceptibility to blizzards within the continental US. Flat terrain provides the perfect conditions for a wind to reach blizzard speed. The Midwest and the Great Plains both feature this type of landscape, which explains why they are frequently hit by blizzards. The Northern Plains may be considered the ideal location for blizzard conditions, which is the result of flat terrain that enables blizzard speed winds, coupled with loose light snow from the extremely low temperatures. The Alberta clipper storm system lasts more than three hours.
Effects of Blizzards
Blizzards are destructive and can be dangerous. Extremely low temperatures can quickly cause hypothermia, frostbite, permanent nerve damage, and in severe conditions, even death. Visibility is substantially limited, a condition that makes travel extremely dangerous. Intense blizzards can easily trap vehicles in snow, damage communication and power lines, and make roads impassable. As a result, towns may reach a state of emergency for as long as several days at a time. The deadliest blizzard recorded in history occurred in Iran during February 1972 and resulted in 4,000 deaths. The blizzard dropped as much as 26 feet of snow in certain areas and two entire towns had no survivors.