What Are The Major Natural Resources Of Serbia?

The economy of Serbia is among the best performing economies in the world and in 2017, Serbia's GDP was the 87th highest in the world at roughly $41.43 billion. On the other hand, the Serbian GDP per capita was the 89th highest in the world at $5,900. Serbia's economy is heavily reliant on the country's natural resources which include arable land, the country's beautiful scenery, oil, and wind, among others.
Wind
One of Serbia's most important natural resources is the wind which is mainly used for the production of energy. Serbia's first wind farm is situated close to the city of Kula and was developed by MK Fintel Wind, one of the leading renewable energy companies in Serbia. Private companies such as Green Star Alternative Energy and MK Fintel Wind are at the forefront of developing Serbia's wind reserves. One of the leading wind energy projects in Serbia is the Belo Blato Project which is owned and operated by Green Star. The Belo Blato project is divided into two stages the first of which was completed in 2009 and has the potential to generate 20 MW of energy. The second phase of the project is expected to increase its energy generation capacity by roughly 300 MW.
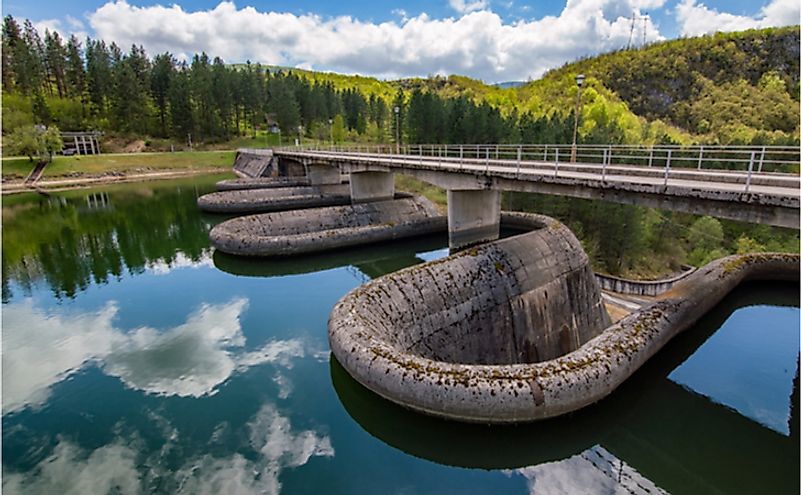
Water
Serbia has several rivers and lakes that supply the country with one of its most important natural resources, water. Some of Serbia's most important rivers include the Danube, the Tisa, and the Sava while some of its most essential lakes include the Đerdap Lake and Vlasina Lake. According to hydrologists, approximately 92% of Serbia's territory is situated within the Danube drainage basin. The Aegean drainage basin encompasses roughly 3% of Serbia's region. Water in Serbia is used for a variety of purposes with some of the most important ones being irrigation and the generation of hydroelectricity. In 2017, the Serbian government estimated that in 2017, close to 90% of the water used for irrigation came from rivers. Hydropower is one of Serbia's most important energy sources. The country has installed capacity of 2.84GW. Some of Serbia's most important hydropower projects include the HE Zvornik Station and the Đerdap I Station, which has the highest installed capacity in the country at 1080 MW. The Serbian government has invested in developing the country's hydropower industry to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels.
Arable Land
In 2015, arable land made up roughly 29.62% of Serbia's total land area and from 2007 to 2015, the size of arable land in Serbia fluctuated considerably reaching its highest point in 2009 and its lowest point in 2013. The most agriculturally productive regions in Serbia are situated in the country's northern and southern sections. In Serbia's northern region, the most fertile areas are located within the Pannonian Plain while in the southern region they are situated around some of the country's major rivers such as the Danube and the Sava. The agricultural sector is one of Serbia's most essential industries as it contributed 6% of the country's GDP in 2017. The Serbian labor department estimated that in 2015, close to 20% of the country's labor force was employed in the agricultural sector. Serbian farmers grow a wide variety of crops such as maize and sugar beets.
Grapes
Serbian farmers grow several varieties of grapes such as the Sauvignon Blanc, Pinot Blanc, and Prokupac. Prokupac is one of Serbia's oldest grape varieties as farmers have been growing it at least since the Middle Ages. Most of Serbia's grapes are used in the production of wines which are mainly consumed locally. Some of Serbia's most important vineyards are situated in the Timok Valley which is located approximately 155 miles east of Belgrade. The Timok Valley is famous for the quality of its red wines. Serbia has a rich winemaking tradition that dates back to the Roman period. The Serbian wine industry developed significantly during the rule of the Nemanjić dynasty. In the modern era, the most common type of wine produced in Serbia is white wine which accounted for up to 64% of the wine produced in the country.
Fruits
Farmers in Serbia also grow a wide array of fruits such as apples, plums, peaches, and pears. The Serbian government estimated that fruit farms in the country covered an area of roughly 1,196 square miles. Most of the fruits in Serbia are grown on small family-owned farms. Plums are some of the most important fruits in Serbia with the government estimating that there were more than 42 million plum trees in the country with each tree believed to produce 29.1 pounds of plums. In 2012, Serbian farmers produced approximately 392,000 tons of plums. Peaches are also popular in Serbia with the government estimating that there were at least 4 million peach trees in the country. Several peach varieties are grown in Serbia such as the Serbian Vineyard Peach, Spring Lady, Spring Gold, and Red Heaven. In 2012, the country produced approximately 53,894 tons of peaches.
Beautiful Scenery
Serbia has been blessed with several beautiful sites that attract large numbers of tourists to the country. Some of Serbia's most beautiful areas include the Fruška Gora Mountain and Mokra Gora. The tourism sector is one of the essential industries in Serbia as it contributed significantly to the country’s GDP. The Serbian labor department estimated that 3% of the country's labor force was employed in the tourism industry. The government of Serbia has urged private companies to invest in the country's tourism industry to increase its contribution to the economy.
Oil And Gas
In 2016, Serbia was believed to have 77.5 million barrels of crude oil reserves as well as significant reserves of natural gas. The only company in Serbia that deals with the exploitation of the country's crude oil and natural gas is Naftna Industrija Srbije. Some of Serbia's most important oil fields are located in the Banat Region.
The Growth Of The Serbian Economy
The government of Serbia has put in place several measures to expand the country's economy such as encouraging foreign companies to invest in the country and improving the country's education system. The measures that the government put in place have been relatively successful as the Serbian economy experienced growth from 2015 to 2017.