What Are The Major Natural Resources Of Finland?
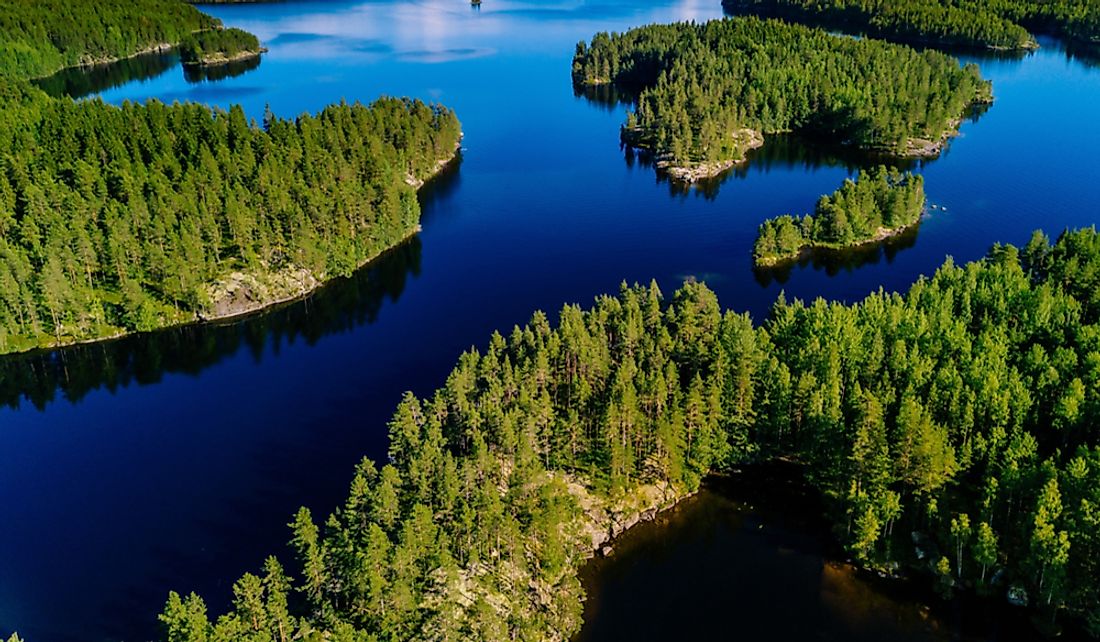

Finland is one of the most stable economies in the world with its $300-billion nominal GDP ranking as the 41st largest in the world. While many of the country’s export items come from its manufacturing industry, the country’s natural resources also feature in its list of export items with some examples being pulp and paper, and sawn timber. Finland is among the European countries which are known for their dense forest covers. These forests are a major natural resource of the country and support one of Finland’s largest industries, its forestry industry. The rivers and lakes are also important natural resources in Finland since they earn the country millions of dollars in fishing, hydroelectric power generation, and tourism.
Finland's Natural Resources
Forests
Finland is situated in a region which is known for thick forests running across most of northern Europe. About 72% of Finland is under forest cover, making it the second most forested country in Europe after Sweden. The thick forests are a major natural resource for the country and a major foreign exchange earner. The country is the leading producer of many forestry products not only in Europe but globally. Finland is among the largest producers of sawn timber in Europe and is one of the leading producers of paper and pulp globally. The prominence of forestry in Finland’s economy can be seen in the dominance of forestry products in the country’s exports where the industry is responsible for an estimated 20% of all exports from Finland. Some economists value the country’s forestry industry at over $20 billion. Some of the major players in the industry include Metsa Board and Stora Enso which are behemoths in the global forestry industry. The forestry industry is also a major employer in the country with more than 15% of all industrial workers in the country or more than 0.16 million people being employed by the industry. Majority of these workers are either indirectly or directly employed in the sawmill sector. The country is also home to the world’s best carpenters who produce some of the finest woodwork in the world. Despite being largely-developed, more than 20% of the country’s inhabitants use wood for energy which normally wastes from the pulp and paper mills found all over the country.
Minerals
Finland is a country which is laden with mineral wealth. Among the minerals found in the country include copper, iron ore, nickel, cobalt, and chromium, all of which are found in commercial quantities. However, the country seems to focus more on imports for its metal requirements despite having immense deposits of different types of metals. The reason behind the surprising preference is because the country concentrates more on adding value to processed metals. Nonetheless, metals are still a significant portion of the country’s export items. Examples of such metals include welded steel pipes, coated sheets, and copper pipes.
Lakes
One of the most important natural resources of Finland is the country’s thousands of lakes. Also known as “the land of a thousand lakes,” Finland has one of the highest concentrations of lakes of any country in the world. The total number of lakes found in the country is estimated to be about 0.187 million. These lakes have innumerable economic benefits to Finland. The lakes support a wide range of aquatic life and are, therefore, crucial in the country’s fishing industry. The nation’s largest lake, Saimaa is important in water transport as it features a series of canals which are used in the transportation of a wide range of cargo. Another huge lake in the country is Paijanne which covers an area of over 413 square miles. The lake injects millions of dollars into the economy of tourist revenue as it attracts thousands of canoe enthusiasts each year.
Rivers
The northern European nation is home to thousands of miles in rivers which are also natural resources for the country. Some of the major rivers in the country include the Tenojoki, Kymijoki, Kitka, Simojoki, and Kemijoki rivers. Similar to the lakes, these rivers are home to many species of fish which are an important source of protein for residents of Finland. The Tenojoki River is notable for being among the best places for salmon fishing in the continent. Grayling and trout are other examples of fish found in the Finnish rivers. Apart from being important sources of fish, the rivers also play a crucial role in the country’s energy industry through the production of hydroelectric power. Having the highest energy consumption per capita in the EU and with the world turning to renewable energy, Finland has invested heavily in renewable energy sources one of which being hydro-electricity projects in the major rivers. The country has over 300 hydroelectric power plants which in total produce more than 3.1 gigawatts.
Agricultural Land
Despite experiencing harsh climatic conditions, Finland’s agricultural industry has grown to make the country self-sufficient. The abundance of agricultural products in the country which experiences harsh winters is made possible through the employment of cutting-edge technology in the industry as well as the practice of large-scale farming. The country also has large tracts of land under irrigation to make them agricultural productive. These technologies enable Finland to be the sole country to practice agriculture at a significant scale in the extreme northern part of the globe. Finland agricultural industry is an important employer in the country, with an estimated 0.12 million people being employed in the industry. However, the importance of agriculture to Finland’s economy has been on a decline with the number of people employed by the sector and the number of farms in the country gradually decreasing in recent years.
The Freezing Temperatures
One of the problems the country is always faced with is the freezing temperatures experienced all over the country. Situated near the earth’s Polar Regions, Finland’s longest season is the winter when temperatures plummet to below zero degrees. The lowest temperature ever recorded in the country measured -60.7° Fahrenheit which was recorded in 1999. The freezing temperatures has pushed up the demand for energy in the country, with Finland currently having one of the highest energy consumption rates per capita of any country in the world and the highest in the EU. About 25% of all the energy consumed in the country is used in heating applications.