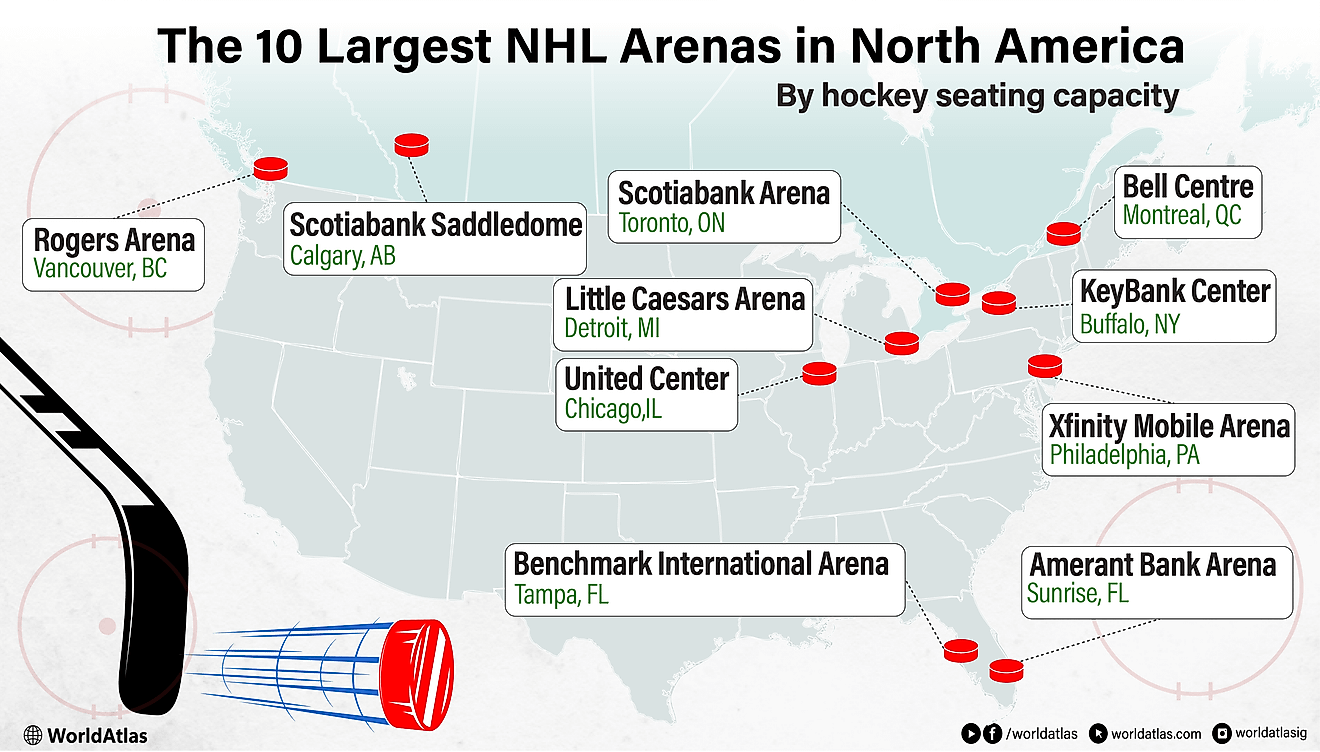
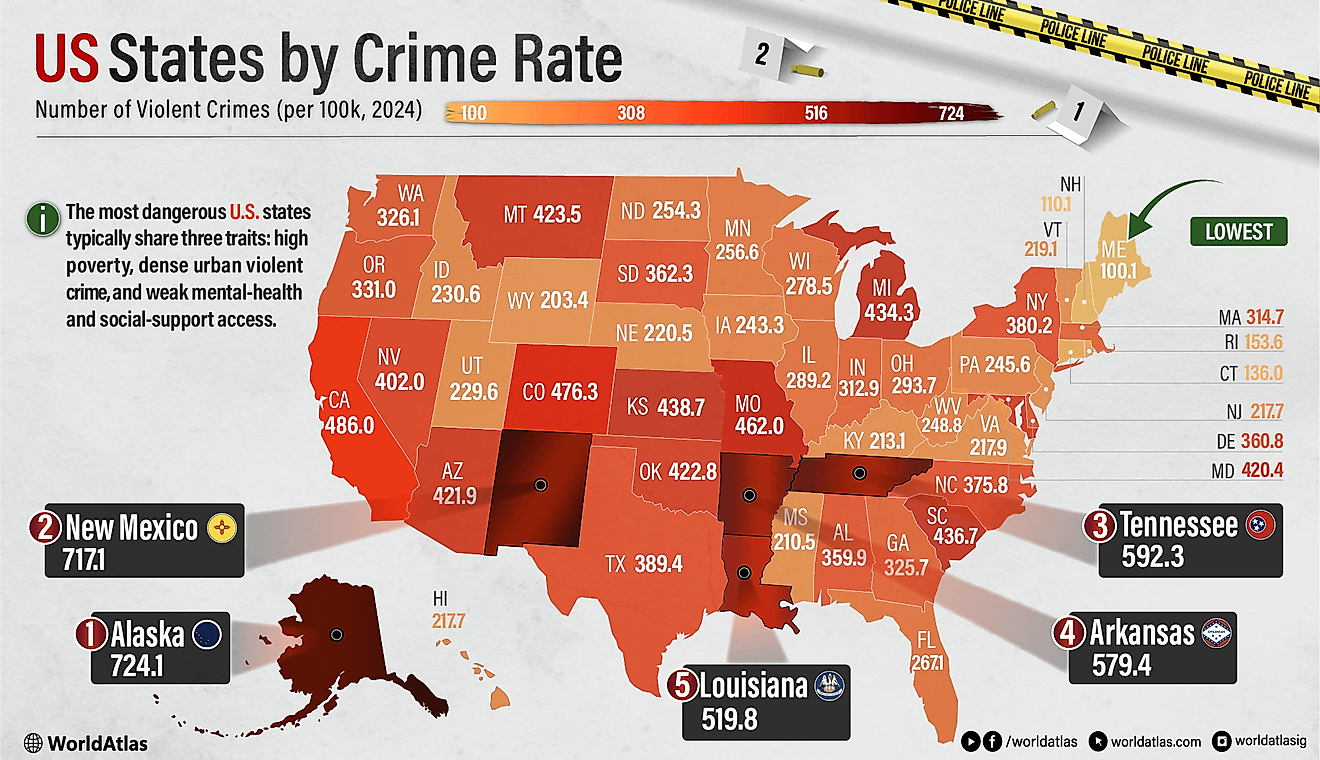
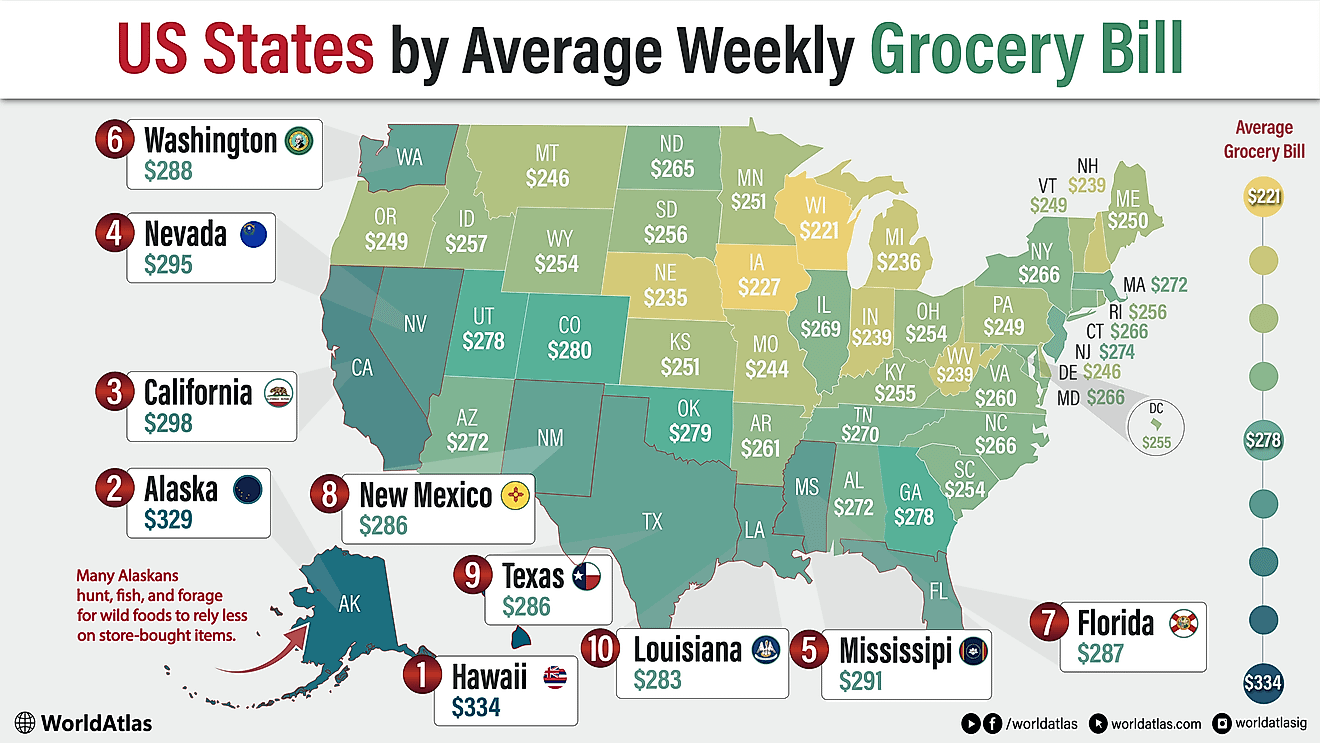
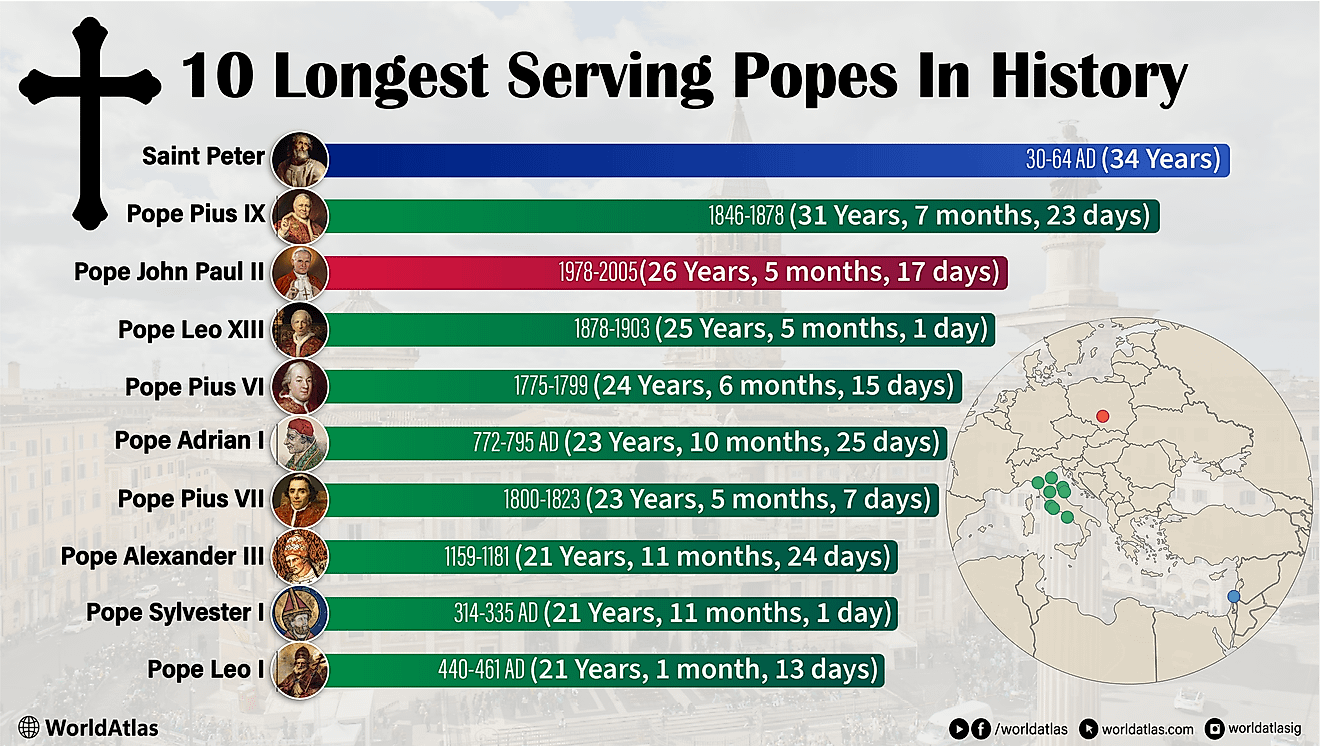
Languages Spoken In Belarus

Belarus is located in the northern region of Eastern Europe. It shares borders with Poland, Lithuania, Russia, Ukraine, and Latvia. The population is 9,498,700 and has high ethnic diversity. The country has spent the majority of its history under the rule of other countries and kingdoms which help explain the languages spoken here today. Belarus has two official languages and several minority languages. This article takes a look at those.
The Official Languages Of Belarus
Belarusian
Researchers have discovered texts written in Old Belarusian, one of the oldest versions of the Belarusian language, from as early as the 13th and 14th centuries. The language belongs to the East Slavic language family and descends from Old East Slavic. At the end of the 18th century, nobility spoke Belarusian. By the 19th century, it was only spoken in some areas and more so by the peasant class. It was at this time that Russia and Poland began laying claim to the country and introducing their official languages, Russian and Polish, to the educational system. It remained a language of the lower classes until the end of the 19th century when a Belarusian revival began, in part to protest the Russian and Polish influences.
In the early 20th century, a movement was made to record and formalize the grammar of the language. In 1924, under Soviet rule, Belarusian became one of four official languages. In Polish-ruled West Belarus, however, the language was further suppressed and banned. After World War II, use of the language once again declined as the region underwent “Soviet unification” that made Russian the principal form of communication. When Belarus became independent in 1991, Belarusian once again became popular and was the only official language for a few years before public protest led to the inclusion of Russian as a state language. Since then, the interest in maintaining and preserving Belarusian has declined.
Its use by families at home has also declined. In 1999, approximately 36.7% of the population spoke Belarusian at home, while a 2009 survey indicates that the number decreased to 11.9%. In total, 29.4% of the population is fluent in Belarusian, and 52.5% can only read and speak it. Some language support groups are attempting to revive literacy in Belarusian.
Russian
The most widely spoken language in Belarus is Russian, one of the two official languages. Russian was reinstated as an official language after the Belarusian referendum of 1995 during which 88.3% of voters supported an equal legal status for both Russian and Belarusian. This referendum resulted in an increased use of Russian throughout the country. In 1999, only 58.6% of the population claimed to speak Russian at home, whereas in 2009, that number increased to 69.8%.
Minority Languages Of Belarus
In addition to the two official languages, several other minority languages are spoken throughout Belarus. Some of the most common of these include Polish, Eastern Yiddish, and Ukrainian. Trasianka is a language phenomenon that can be heard in some places. It is a mix of the structures and vocabulary of Russian and Belarusian that is spoken rapidly. Trasianka is the result of the local language being influenced by the socially dominant language and became particularly common when rural Belarusian-speaking migrants began moving into Russian-speaking cities.