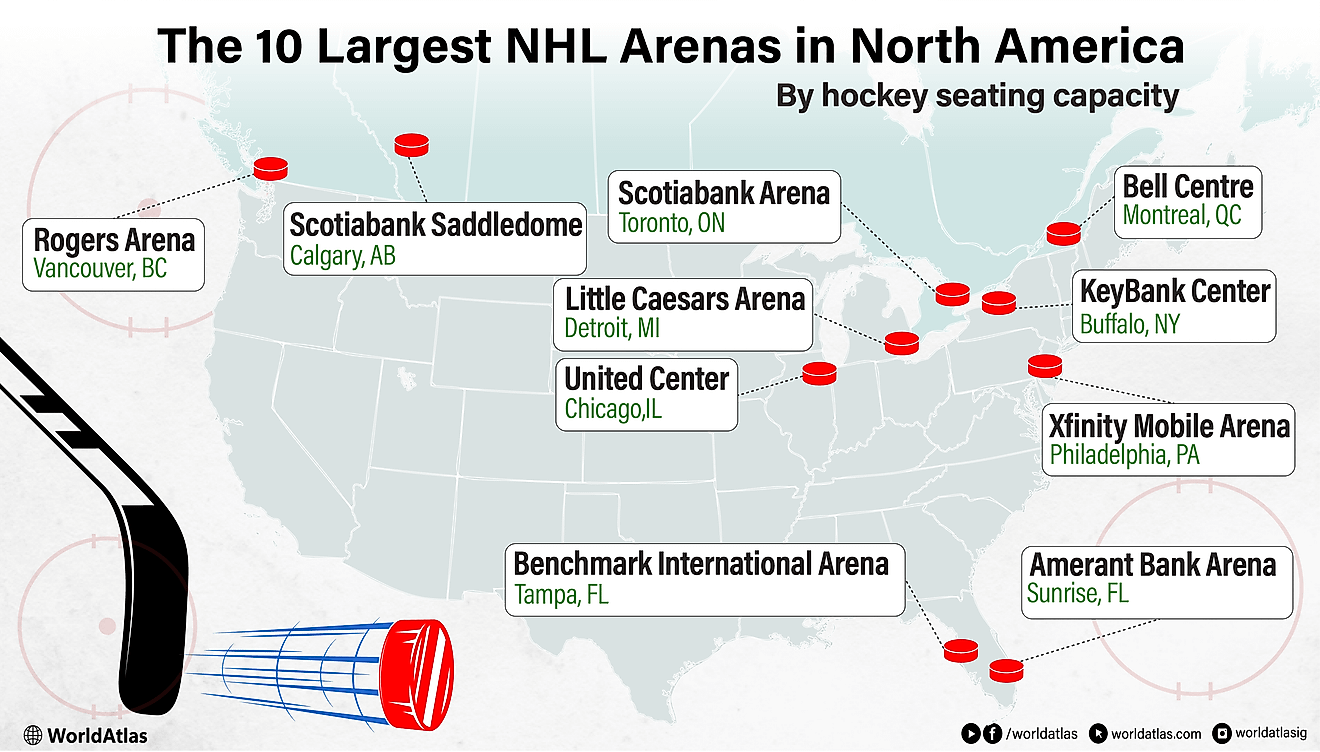
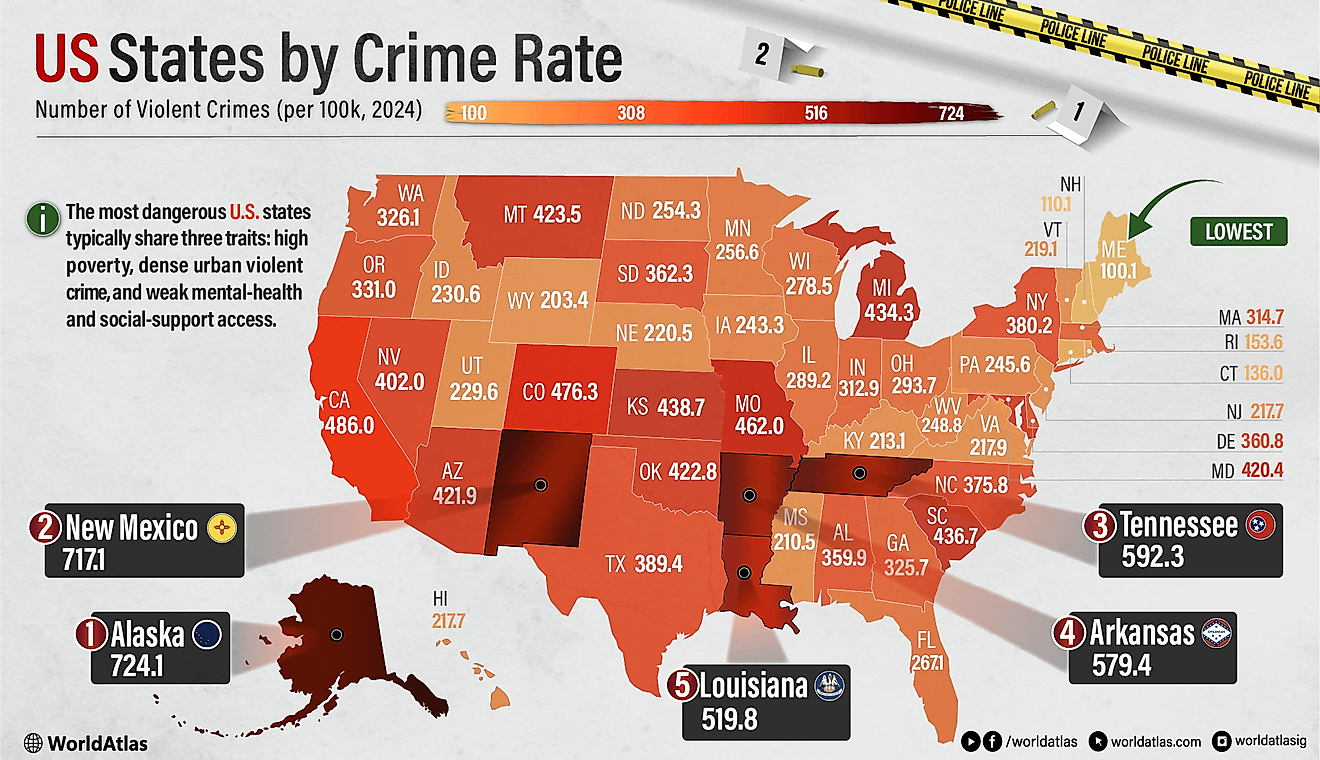
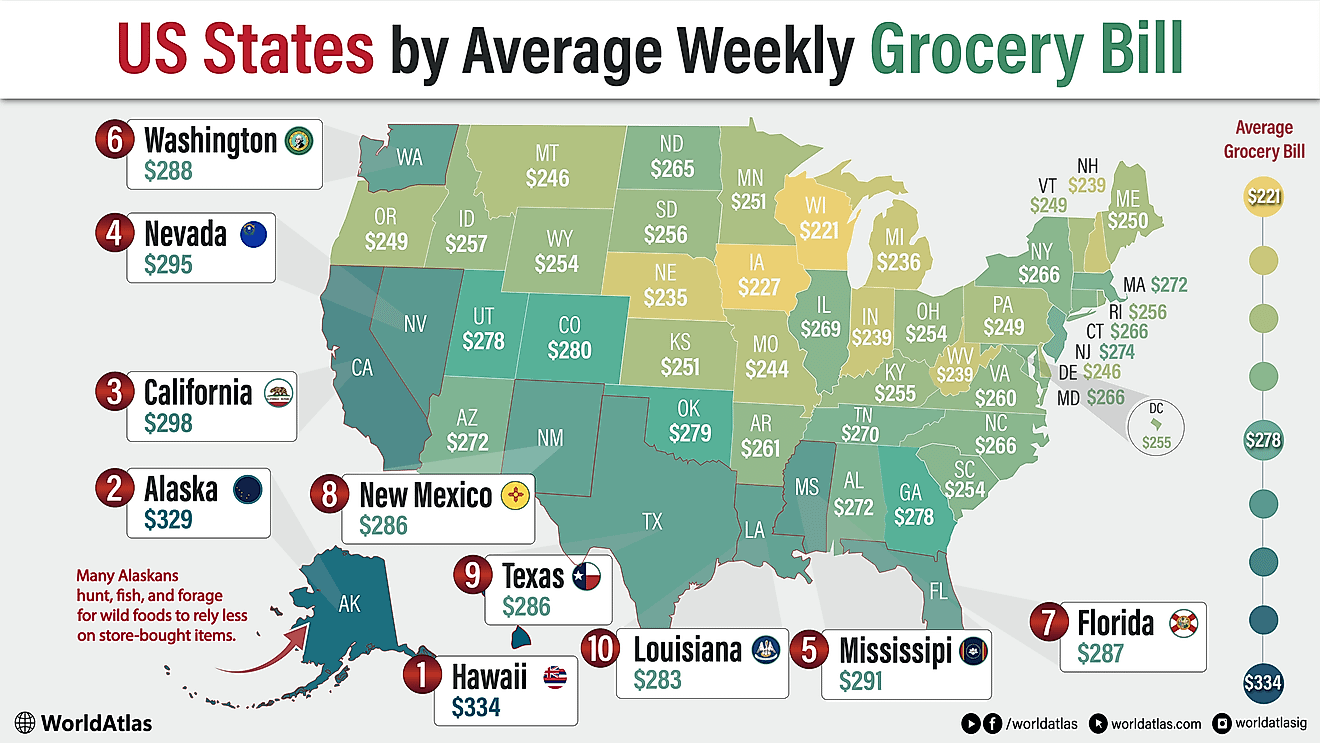
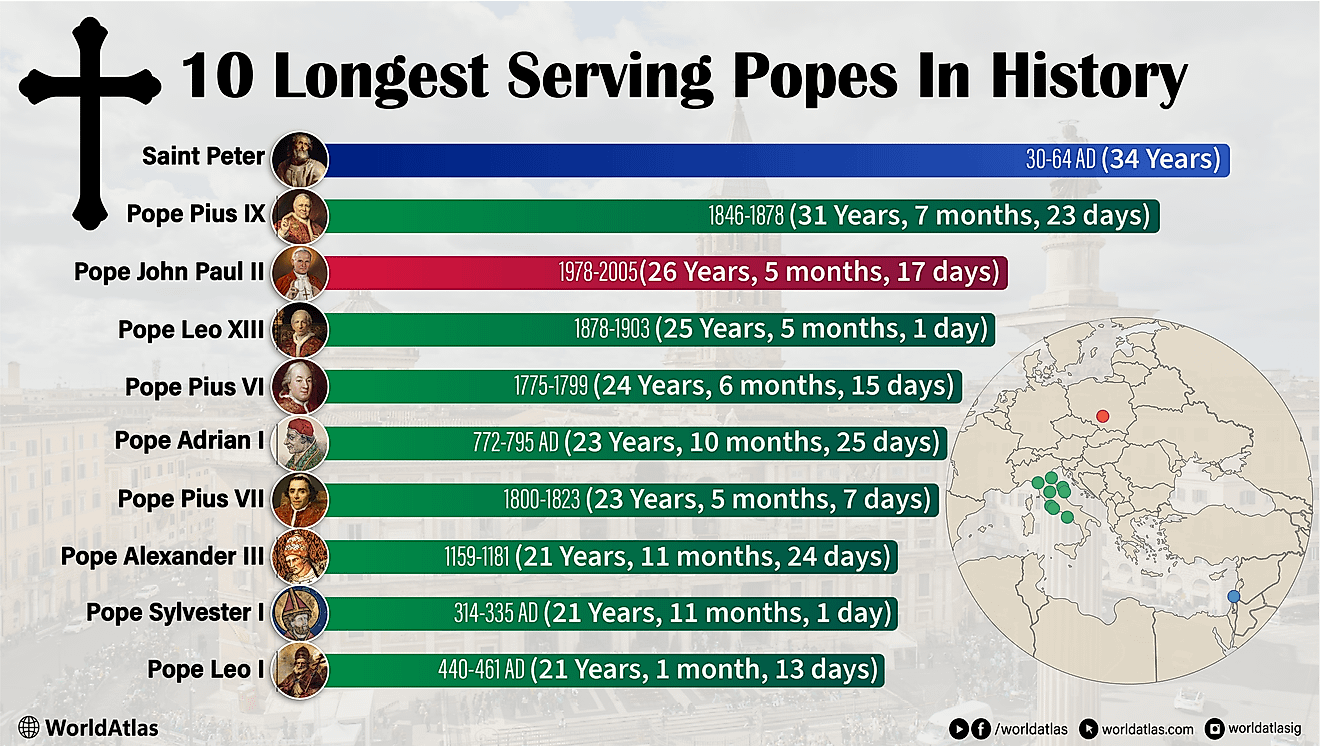
Endangered Indigenous Languages Of The United States

What Is An Endangered Language?
Around the world, many languages are becoming less common as other commonly used languages replace them. In many cases, the progeny of certain language speakers never learns their native family language. This trend is resulting in endangered languages, languages that will likely become extinct in the future. This article takes a look at the endangered languages of the US.
The Decline Of Native American Languages
In the US, native languages spoken by Indigenous peoples have been declining since European colonization began. Before colonialism, approximately 300 languages were used throughout the country. Today, there are around 167 languages, and estimates suggest that only 20 of these Indigenous languages will remain by 2050.
What happened to the original 300 languages? European settlers oppressed the Indigenous population, pushing them off their land, and eventually giving them tracts of land nowhere near their traditional homes. From the late 19th to the early 20th centuries, the government initiated assimilation programs to eradicate Indigenous cultures, including their languages. As part of these programs, the government ran boarding schools for Indigenous children, which removed them from their families for significant periods of time. The curriculum was designed to force the students to learn English. Not only were they punished for using their languages, but their traditional names were also replaced with European-American names. The goal was to create a homogeneous culture within the US.
The federal government did not change these policies until 1972 when Congress passed the Indian Education Act. This act made it legal to teach Indigenous children in their own languages and gave tribes the authority to control schools. This was reinforced in the 1990s when the US government passed the Native American Languages Act, which recognized the importance of preserving Indigenous languages. In 2006, Congress approved funding for tribes that want to establish language programs in local schools.
The Importance Of Preserving Language
Put simply, language is culture. Preserving a language allows its users to maintain a cultural identity, which allows the culture to survive. Researchers suggest that language preservation leads to empowerment within a community. It improves community relationships, enhances self-esteem, and increases cultural wellbeing. The United Nations (UN) also recognizes the importance of preserving native languages. The UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples sets forth the right of indigenous people to develop, use, and share their native languages.
How To Protect And Promote Endangered Languages
The first step toward promoting endangered languages is to make them available to interested learners. One of the most effective ways to accomplish this is by offering language classes to school children. Offering language courses and working to record the language, its vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar and making it available to a wide audience are excellent approaches to preventing language extinction. Any technique that may lead to increased use and exposure, particularly for children, is likely to preserve the language. The biggest challenge in protecting language use is keeping younger generations interested in their language heritage. This interest can be difficult to establish when youth are expected to use English in nearly every facet of their lives. Many tribes have made progress, however. The Navajo and Miami tribes, in particular, have established language immersion programs that have preserved and renewed use within their communities.
Endangered Languages Of The United States
| Language | Status |
|---|---|
| Achumawi language | Critically endangered |
| Acoma-Laguna language | Definitely endangered |
| Ahtna language | Critically endangered |
| Alabama language | Definitely endangered |
| Aleut language (Eastern) | Critically endangered |
| Aleut language (Western) | Severely endangered |
| Arapaho language (Wyoming) | Vulnerable |
| Arikara language | Critically endangered |
| Assiniboine language (United States) | Critically endangered |
| Blackfoot language (United States) | Vulnerable |
| Caddo language | Critically endangered |
| Cahuilla language | Critically endangered |
| Central Alaskan Yup'ik language | Vulnerable |
| Central Pomo language | Critically endangered |
| Central Siberian Yupik language (St. Lawrence Island) | Vulnerable |
| Central Sierra Miwok language | Critically endangered |
| Chemehuevi language | Critically endangered |
| Cherokee language (North Carolina) | Vulnerable |
| Cherokee language (Oklahoma) | Vulnerable |
| Cheyenne language (Montana) | Vulnerable |
| Cheyenne language (Oklahoma) | Vulnerable |
| Chickasaw language | Severely endangered |
| Chinook Jargon language | Critically endangered |
| Choctaw language (Louisiana) | Vulnerable |
| Choctaw language (Mississippi) | Vulnerable |
| Choctaw language (Oklahoma) | Vulnerable |
| Cocopa language (Arizona) | Severely endangered |
| Coeur d'Alene language | Critically endangered |
| Columbia-Moses language | Critically endangered |
| Comanche language | Severely endangered |
| Creek language | Vulnerable |
| Crow language | Vulnerable |
| Gros Ventre language | Critically endangered |
| Gwich'in language (United States) | Severely endangered |
| Halkomelem language | Severely endangered |
| Hän language (United States) | Critically endangered |
| Havasupai language | Definitely endangered |
| Hawaiian language | Vulnerable |
| Hawai'i Sign Language | Critically endangered |
| Hidatsa language | Vulnerable |
| Holikachuk language | Critically endangered |
| Hopi language | Vulnerable |
| Hualapai language | Vulnerable |
| Hupa language | Critically endangered |
| Ingalik language | Critically endangered |
| Ipai language | Critically endangered |
| Jemez language | Vulnerable |
| Jicarilla Apache language | Severely endangered |
| Kalispel-Pend d'Oreille | Critically endangered |
| Karuk language | Severely endangered |
| Kashaya language | Critically endangered |
| Kawaiisu language | Critically endangered |
| Kickapoo language (Kansas) | Vulnerable |
| Kickapoo language (Oklahoma) | Vulnerable |
| Kickapoo language (Texas) | Vulnerable |
| Kiksht language | Critically endangered |
| Kings River Yokuts | Critically endangered |
| Kiowa language | Severely endangered |
| Kiowa Apache language | Critically endangered |
| Klallam language | Critically endangered |
| Koasati language (Louisiana) | Definitely endangered |
| Koasati language (Texas) | Definitely endangered |
| Konkow language | Critically endangered |
| Koyukon language | Critically endangered |
| Kutenai language | Severely endangered |
| Kwak'wala language | Critically endangered |
| Lake Miwok language | Critically endangered |
| Luiseño language | Critically endangered |
| Lushootseed language | Critically endangered |
| Maidu language | Critically endangered |
| Makah language | Critically endangered |
| Malecite-Passamaquoddy language | Definitely endangered |
| Maliseet-Passamaquoddy language | Severely endangered |
| Mandan language | Critically endangered |
| Maricopa language | Severely endangered |
| Massachusett language | Vulnerable |
| Menominee language | Critically endangered |
| Mescalero-Chiricahua Apache language (New Mexico) | Definitely endangered |
| Mescalero-Chiricahua Apache language (Oklahoma) | Critically endangered |
| Micmac language (Massachusetts) | Vulnerable |
| Mikasuki language | Vulnerable |
| Mohave language (Arizona) | Severely endangered |
| Mohave language (California) | Severely endangered |
| Mohawk language (Akwesasne, St. Regis) | Vulnerable |
| Mohawk language (Ganienkeh) | Vulnerable |
| Mohawk language (Kanatsiohareke) | Vulnerable |
| Mono language (Eastern) | Critically endangered |
| Mono language (Western) | Critically endangered |
| Montana Salish language | Critically endangered |
| Munsee language (United States) | Critically endangered |
| Navajo language | Vulnerable |
| Nez Perce language | Critically endangered |
| Inupiat language | Severely endangered |
| Northern Haida language | Critically endangered |
| Northern Paiute language (Idaho) | Critically endangered |
| Northern Paiute language (Nevada) | Definitely endangered |
| Northern Paiute language (Oregon) | Critically endangered |
| Northern Pomo language | Critically endangered |
| Northern Sierra Miwok language | Critically endangered |
| Northern Straits Salish language | Critically endangered |
| O'odham language (Akimel) | Vulnerable |
| O'odham language (Tohono) | Vulnerable |
| Ojibwe language | Vulnerable |
| Okanagan language | Definitely endangered |
| Omaha-Ponca language | Critically endangered |
| Oneida language (New York) | Critically endangered |
| Oneida language (Wisconsin) | Critically endangered |
| Onondaga language (New York) | Critically endangered |
| Osage language | Vulnerable |
| Ottawa language (Michigan) | Critically endangered |
| Pacific Gulf Yupik language | Severely endangered |
| Panamint language | Critically endangered |
| Patwin language | Critically endangered |
| Pawnee language | Critically endangered |
| Picuris language | Vulnerable |
| Plains Sign Talk | Critically endangered |
| Potawatomi language (Kansas) | Critically endangered |
| Potawatomi language (Michigan) | Critically endangered |
| Potawatomi language (Oklahoma) | Critically endangered |
| Potawatomi language (Wisconsin) | Critically endangered |
| Quechan language | Definitely endangered |
| Rio Grande Keresan language | Definitely endangered |
| Sahaptin language | Severely endangered |
| Sauk-Fox language | Critically endangered |
| Seneca language (United States) | Severely endangered |
| Seward Peninsula Inupiaq language (King Island) | Critically endangered |
| Seward Peninsula Inupiaq language (Little Diomede Island) | Critically endangered |
| Seward Peninsula Inupiaq language (Norton Sound) | Critically endangered |
| Shawnee language | Vulnerable |
| Shoshoni language (Idaho) | Vulnerable |
| Shoshoni language (Nevada) | Vulnerable |
| Shoshoni language (Wyoming) | Vulnerable |
| Sioux language | Vulnerable |
| Southern Paiute language | Severely endangered |
| Southern Pomo language | Critically endangered |
| Southern Sierra Miwok language | Critically endangered |
| Southern Tiwa language (Isleta Pueblo) | Definitely endangered |
| Southern Tiwa language (Sandia Pueblo) | Definitely endangered |
| Spokane language | Critically endangered |
| Straits Salish language | Severely endangered |
| Tanacross language | Critically endangered |
| Tanaina language | Severely endangered |
| Tanana language | Critically endangered |
| Taos language | Definitely endangered |
| Tewa language (Arizona) | Definitely endangered |
| Tewa language (New Mexico) | Severely endangered |
| Tipai language (United States) | Severely endangered |
| Tlingit language (United States) | Critically endangered |
| Tolowa language | Critically endangered |
| Tubatulabal language | Critically endangered |
| Tule-Kaweah Yokuts | Critically endangered |
| Tuscarora language (United States) | Critically endangered |
| Upland Yuman language | Vulnerable |
| Upper Kuskokwim language | Critically endangered |
| Upper Tanana language (United States) | Critically endangered |
| Ute language (Colorado, Southern Ute) | Vulnerable |
| Ute language (Colorado, Ute Mountain) | Vulnerable |
| Ute language (Utah) | Vulnerable |
| Valley Yokuts | Severely endangered |
| Washo language | Severely endangered |
| Western Apache language | Vulnerable |
| Winnebago language (Nebraska) | Severely endangered |
| Winnebago language (Wisconsin) | Severely endangered |
| Wintu-Nomlaki language, Wintu language | Critically endangered |
| Yaqui language (United States) | Definitely endangered |
| Yavapai language | Severely endangered |
| Yuchi language | Critically endangered |
| Yurok language | Critically endangered |
| Zuni language | Vulnerable |