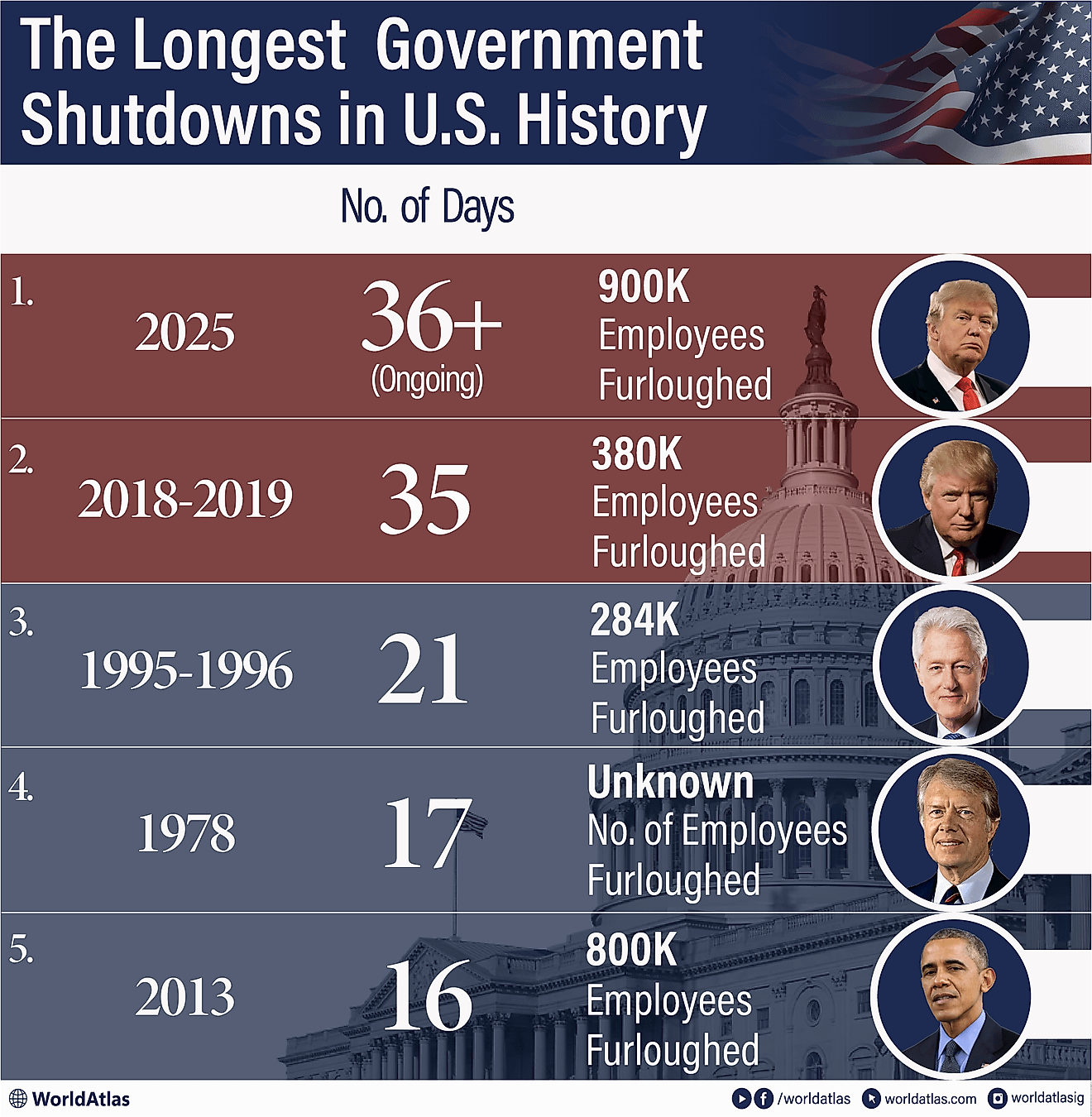
Countries With Open Borders

An open border refers to a border that allows the free movement of people between jurisdictions with few conditions or restrictions. A border may be open due to the absence of legal controls or a lack of adequate supervision or enforcement along the border. A border may also be open as a result of international legislation that allows people to move across freely. Additionally, an open border usually refers only to the free movement of people, but does not include goods and services, and also includes only political jurisdictions and not private property.
Federations and confederations may have a common external border control through a system of collective border control, and may occasionally have open borders with non-member countries, especially enclaves, such as the European Union and Switzerland, which have a special international agreement. International border controls are a relatively new phenomenon, and historically several countries maintained open international borders. It was only after the First World War that border controls became a widespread practice.
Schengen Agreement
The Schengen Agreement is a treaty that established the Schengen Area in Europe, and as a result, abolished most internal checks. The treaty was adopted on June 14, 1985, in Schengen, Luxembourg, by five founding countries that were also among the founding members of the European Economic Community (EEC), which was the predecessor of the European Union (EU). The treaty proposed to abolish border checks within the signatory states, and other measures included allowing vehicles to cross without stopping, allowing residents to move freely, as well as harmonizing visa policies. The Schengen Area functions as a single state for the purposes of international travel, with external border controls for the entire region, but no internal border controls. The Schengen Agreement currently has 26 member states and covers a combined area of 1.665 million sq mi and an estimated population of 400 million.
Common Travel Area (CTA)
The Common Travel Area (CTA) is an open border area between the United Kingdom (UK), Channel Islands, Isle of Man, and Ireland. However, British Overseas Territories (BOT) are not signatories to CTA. The agreement allows member citizens to move freely within the area without restrictions, with the exception of identity documents required for air travel. Controls for entry to the area are carried out by the country of the first entry. The Common Travel Area was first adopted in 1923 between the UK and Ireland.
Union State
The Union State is an agreement between Belarus and Russia designed to create social, economic, and political integration. First established in 1996, with further agreements signed in 1997 and 1998, the Union State allows citizens of the two countries to move freely across the borders without restrictions such as border checks. While the nature of the political entity remains vague, the intention of the treaty was to create a federation, like the former Soviet Union, with a common flag, head of state, legislature, citizenship, and constitution. The Russian State Duma ratified the Union State on December 22, 1999, while it was ratified by the national assembly of Belarus on January 26, 2000. However, after its inauguration, both countries seemed to lose their initial enthusiasm. Russia and Belarus restored customs controls along the border in 2001, meaning that the customs union was suspended until it was adopted once again in 2010.
Treaty of Peace and Friendship
The governments of India and Nepal signed the Treaty of Peace and Friendship in 1950, which is a bilateral agreement between the two states that established close strategic ties. The treaty was adopted on July 31, 1950, after it was signed in Kathmandu by the Prime Minister of Nepal and India's Ambassador of Nepal. The treaty came into effect immediately and allowed the free movement of citizens of Nepal and India across the shared border.
CA4 Border Control Agreement
The Central America-4 Free Mobility Agreement is a treaty adopted on June 2016 by Nicaragua, Honduras, Guatemala, and El Salvador that allows free border crossings for citizens of the four signatory states without any checks or restrictions. Any foreign national entering one of the four signatory states can travel freely to the other member states without obtaining additional permits when traveling by land, but not by air. Foreign travelers moving within the area by air must obtain all required permits and undergo checks. The CA4 treaty is similar to the European Schengen Agreement, which has established a harmonized visa regime for all foreigners traveling to the area.
Trans-Tasman Travel Arrangement
Australia and New Zealand signed the Trans-Tasman Travel Agreement in 1973, which allowed citizens of the two countries to move freely across the border. The agreement also allowed citizens to reside and work in either of the two countries with minimal restrictions. However, new requirements have been introduced since the agreement was first created. For example, beginning July 1, 1981, any foreign national entering Australia, including New Zealanders, must carry a passport.
Arguments for Open Borders
Proponents of open borders argue that free migration of people is the most effective method of reducing poverty in the world. When migrants move from less developed countries to highly developed ones, they can earn higher incomes, therefore uplifting them from poverty. Additionally, migrants can also increase remittances sent to their home countries, which is significant, as estimates suggest that remittances by migrants total about three times the amount of global aid provided by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). According to economists, open borders could increase the overall gross world product (GWP) by between 67% and 147%, with the potential of doubling the world's gross domestic product (GDP).
Countries With Open Borders
| Rank | Agreement | States |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Schengen Agreement (and microstates with open borders) | Austria, Belgium, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Monaco, Norway, Poland, Portugal, San Marino, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and Vatican City |
| 2 | Common Travel Area | Ireland, United Kingdom |
| 3 | Union State | Belarus, Russia |
| 4 | Treaty of Peace and Friendship | India, Nepal |
| 5 | Treaty of Friendship | India, Bhutan |
| 6 | CA4 Border Control Agreement | El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua |
| 7 | Trans-Tasman Travel Arrangement | Australia, New Zealand |
| 8 | Andean Community | Bolivia, Columbia, Ecuador, and Peru |
| 9 | CARICOM Single Market and Economy | Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, and Trinidad and Tobago |
| 10 | Gulf Cooperation Council | Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman, United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Bahrain |
| 11 | East African Community | Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, South Sudan, Rwanda, and Burundi |