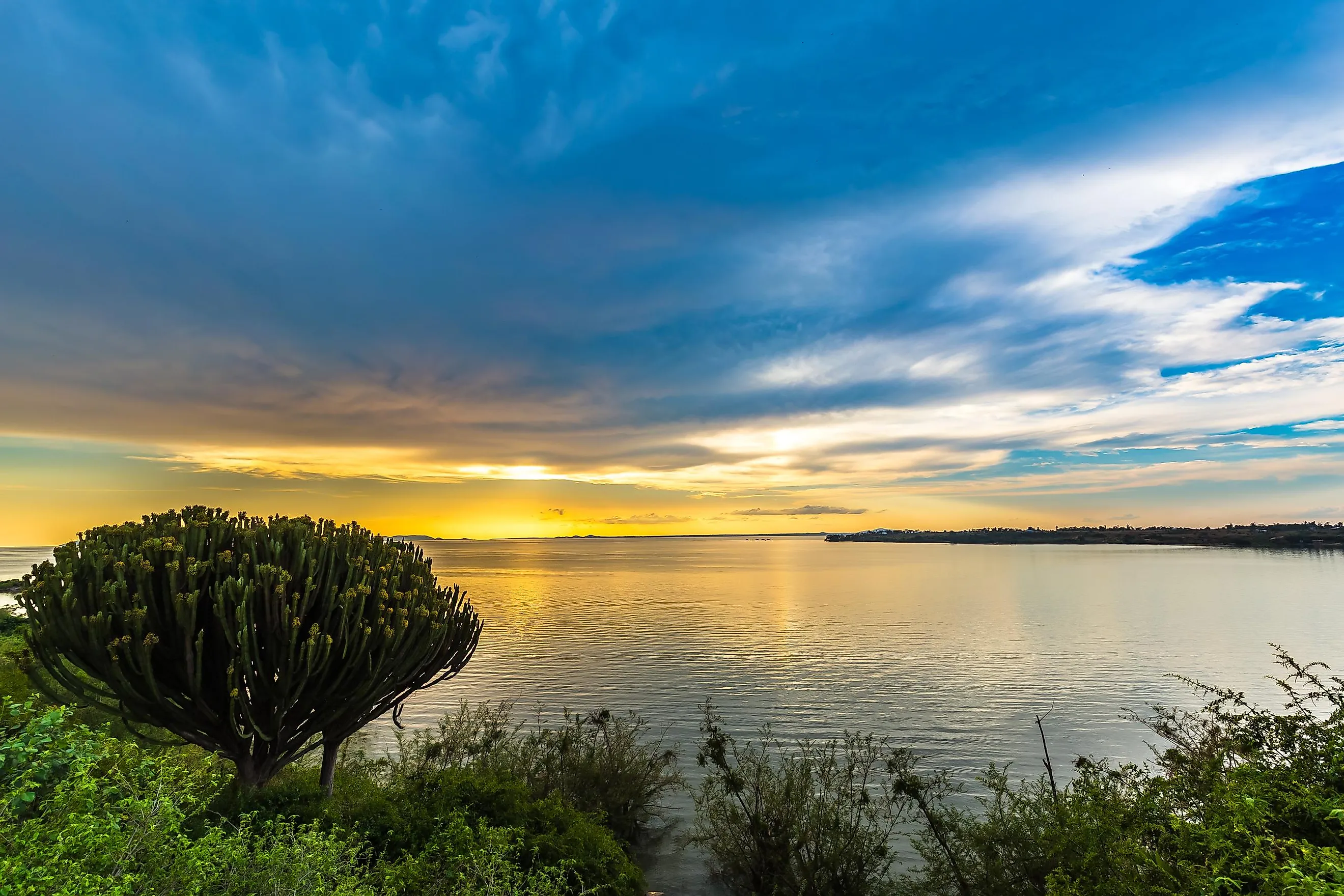
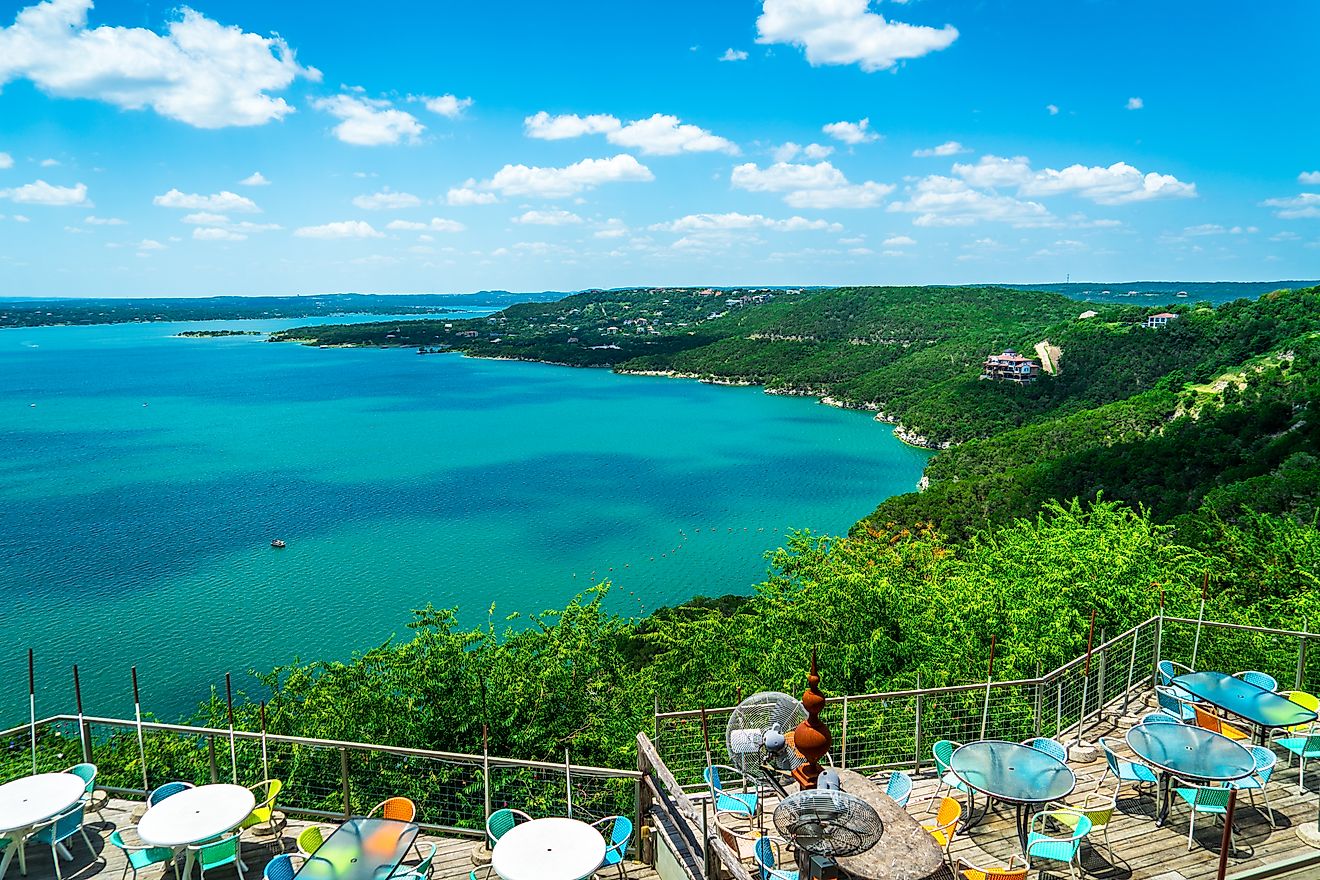
Lake Victoria
A lake is defined as a large water body that is surrounded by land except for the rivers and streams that feed or drain the lake. Varying greatly in size and depths, lakes are found in a wide variety of habitats and are situated at different elevations. Most of the Earth’s freshwater lakes are located at higher altitudes in the Northern Hemisphere.
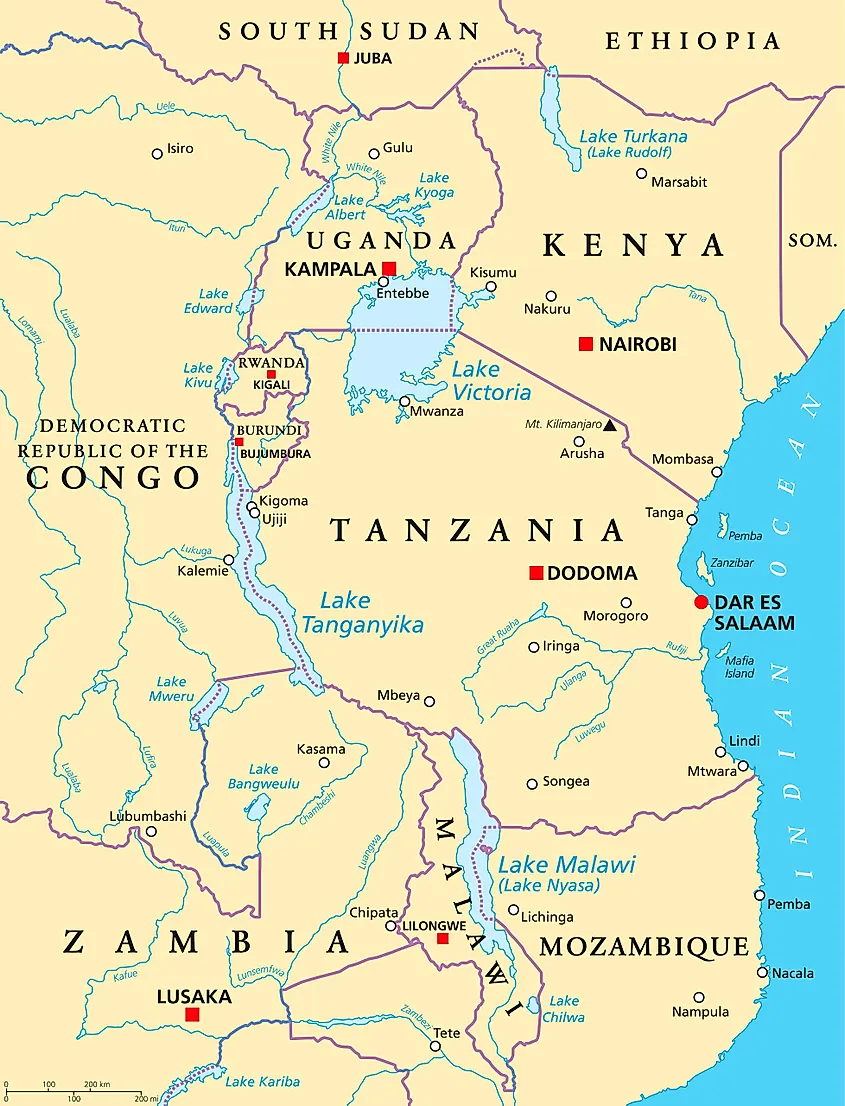
Covering a huge area of about 59,947 km2, Lake Victoria is the largest lake on the African continent and is also the biggest tropical lake in the world. It is one of the African Great Lakes and after Lake Superior in North America, it is the second-largest freshwater lake on Earth. The waters of Lake Victoria occupy a shallow depression and are centered around the East African Rift System.
Where Is Lake Victoria?
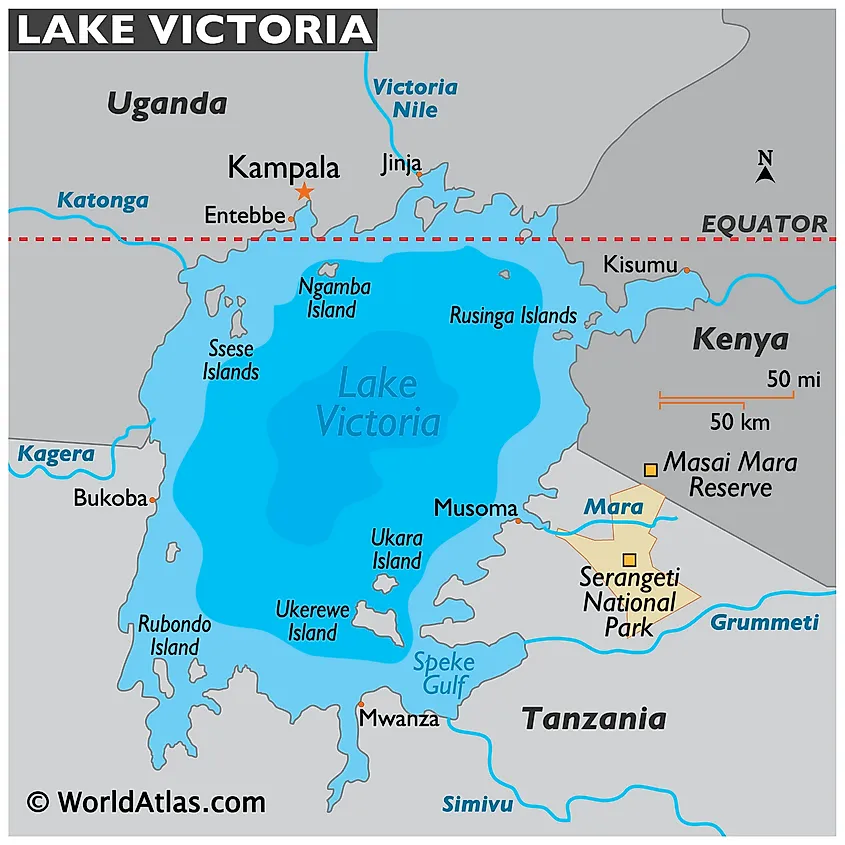
The area of Lake Victoria is shared by the African countries of Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. About 49% of the lake falls under Tanzania, followed by 45% in Uganda and about 6% in Kenya. The lake has a catchment area of about 169,858 km2 and is the chief reservoir of the Nile River.
Geography

This large irregular-shaped lake has a maximum length of 359 km (north-to-south) and a maximum width of 337 km. It is relatively shallow and has a maximum depth of 81 m and an average depth of 41 m. The length of the lake’s shoreline is about 7,142 km and it is the ninth-largest continental lake in the world, contains approximately 2,424 km3 volume of water. Lake Victoria is situated at about 1,135 m above sea level.
Lake Victoria receives about 80% of its water from direct precipitation and about 20% of the water from the numerous rivers and small streams that drain into the lake. The Kagera River is the major river that empties into the lake. Some of the other smaller rivers that flow into the lake include the Katonga, Migori, Mogusi, Nzoia, Yala, Nyando, Sio, and Sondu Miriu Rivers. The only river to exit the lake is the Victoria Nile, which leaves the lake at its northern shore near Jinja town in Uganda.
Several islands are located in Lake Victoria. Some of these islands are the Rusinga and Mfangano islands in Kenya; the Rubondo and Ukerewe islands in Tanzania; and the Ssese and Ngamba islands in Uganda. Located in Tanzania’s Ukerewe District, the Island of Ukerewe is Lake Victoria’s largest island and is also the world’s fifth-largest lake island. The Speke Gulf is located in the lake’s southeastern part while the Emin Pasha Gulf is situated in the southwestern part of the lake.
Brief History

The lake is referred to as Nam Lolwe by the Indigenous Luo people of Kenya and Tanzania and as 'Nnalubaale in Uganda. The British Indian Army officer and explorer John Hanning Speke was the first European to discover the lake in 1858. The lake was named by him in the honor of the British monarch, Queen Victoria. Speke also proclaimed this large lake to be the source of the Nile River and his claim was verified by the American explorer Henry Morton Stanley, after he successfully circumnavigated the lake on an expedition in 1875. Sir William Garstin made a detailed survey of the lake in 1901.
About 30 million people reside in the Lake Victoria region and depend on the lake waters for their sustenance. Fishing is a major economic activity of the people who reside along the shores of the lake. Some of the major towns and port-cities that are located along Lake Victoria are Jinja, Entebbe, and Kampala on the Ugandan side; Musoma, Mwanza, and Bukoba in Tanzania; and Kisumu, Kendu Bay, and Homa Bay on the lake’s Kenyan side. The Nalubaale Dam was constructed in 1952 on the Victoria Nile in Uganda for the generation of hydroelectric power. The Kiira Hydroelectric Power Station was constructed in 2002.
Wildlife
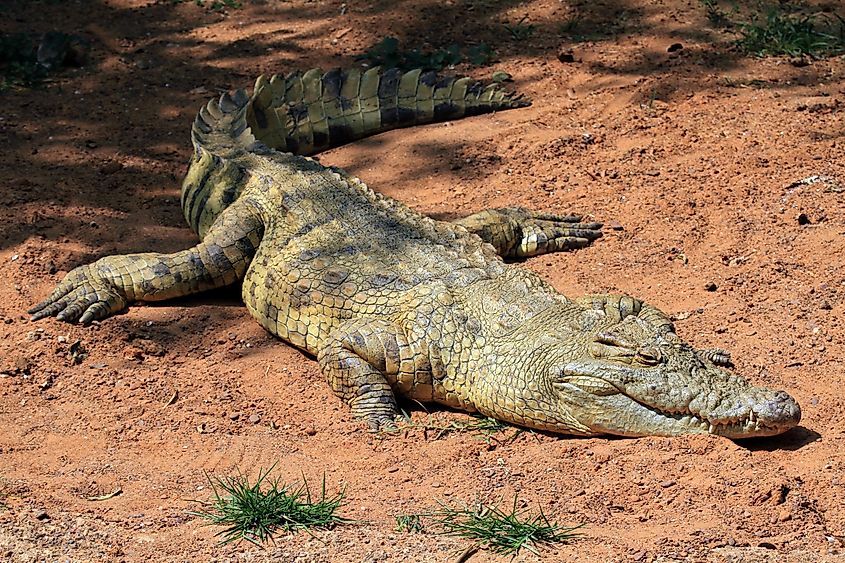

Before the introduction of invasive species like the Nile perch and various Nile tilapias into the waters of the lake, Lake Victoria hosted an immense array of endemic fish species. Many have since gone extinct in the last 50 years. The most dominant fish species in the lake belong to the groups of Victorian haplochromines and lake tilapias. Some of the fish found in the lake include cyprinids, catfish, African tetras, the spiny eel, elephant fish, marbled lungfish, and climbing gourami. Freshwater crab species can also be found here. About 28 species of freshwater snails, 17 species of bivalves are also found in the lake. Evarcha culicivora which feeds on mosquitoes is the only jumping spider species that is found in the Lake Victoria region. The waters of the lake and its surrounding wetlands provide habitats for Nile crocodiles, Williams’ mud turtle, and the African helmeted turtle. Several mammals like the marsh mongoose, spotted-necked otter, African clawless otter, hippopotamus, sitatunga, and bohor reedbuck are found in the lake’s basin.
Environmental Threats
The excessive accumulation of nitrogen and phosphorus due to the discharge of agricultural sewage and untreated industrial effluents into the waters of Lake Victoria has led to eutrophication and massive growth of water hyacinth. This invasive plant species has created anoxic conditions in the lake and has also interfered with boat movements, fishing, and hydroelectric power generation. The introduction of invasive fish species like Nile perch, Nile tilapia, and blue-spotted tilapias has led to the complete extinction of many endemic fish species in the lake.