What Is The Indian Subcontinent?
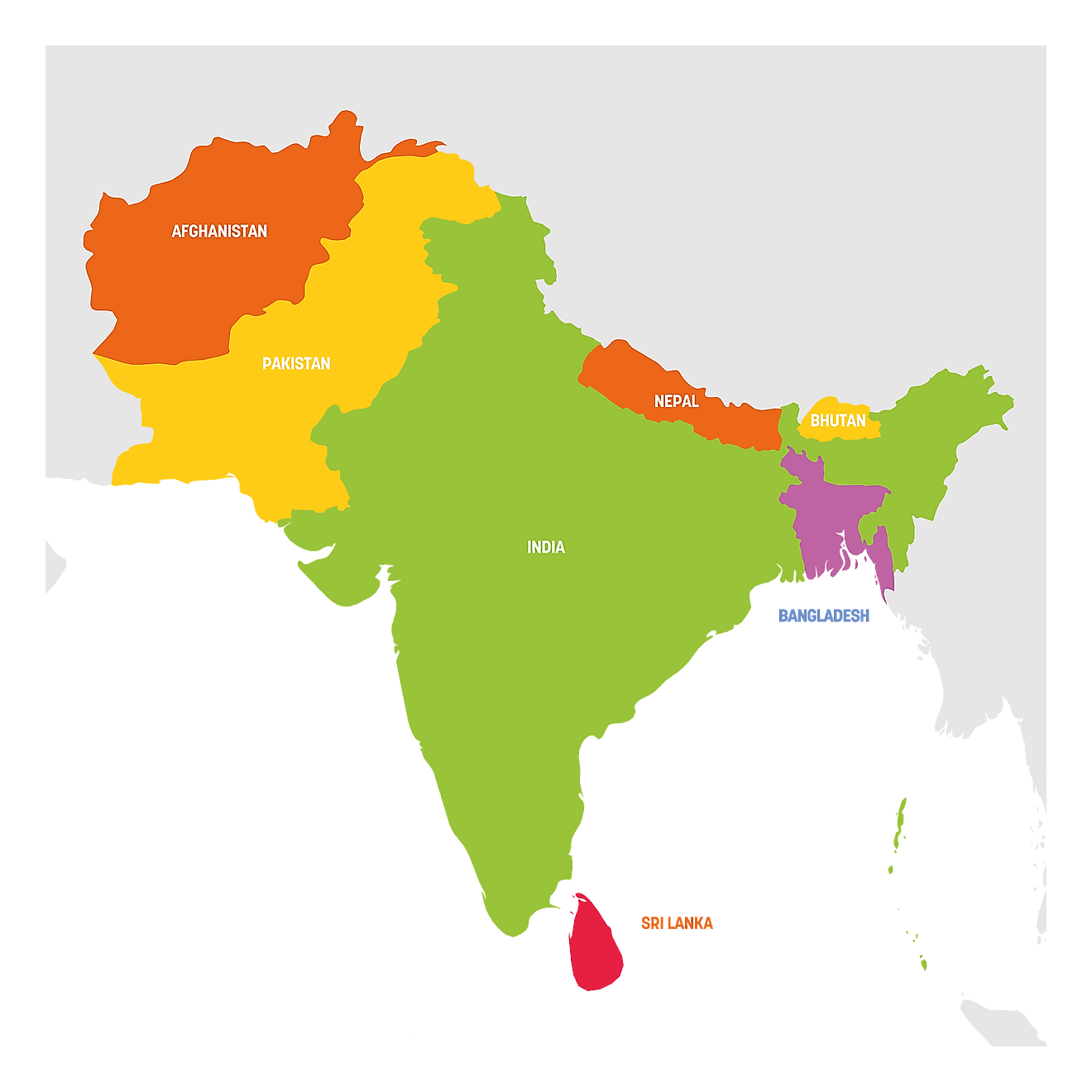
- A subcontinent is a part of a continent that is politically and/or geographically separate from the rest of the continent.
- Geographically, the Indian Subcontinent consists of the peninsular part of present-day India, south of the Himalayas, on the Indian tectonic plate.
- From a political perspective, the Indian subcontinent consists of at least 7 countries: India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives.
- Some consider Afghanistan to be part of the Indian Subcontinent.
- The people of the Indian Subcontinent have shared ethnic, linguistic, cultural, and historical ties.
A subcontinent is a part of a continent that is politically and/or geographically separate from the rest of the continent. The Indian Subcontinent is a subcontinent for both political and geographical reasons. The countries of the Indian Subcontinent have strong political and cultural ties. It is also a subcontinent from a geographical perspective, since it is territory that is geographically separate from the rest of Asia. It should be noted that the term Indian subcontinent is often used interchangeably with the terms South Asia and Southern Asia. In international discourse, these three terms usually denote the same part of the world.
What Constitutes The Indian Subcontinent?
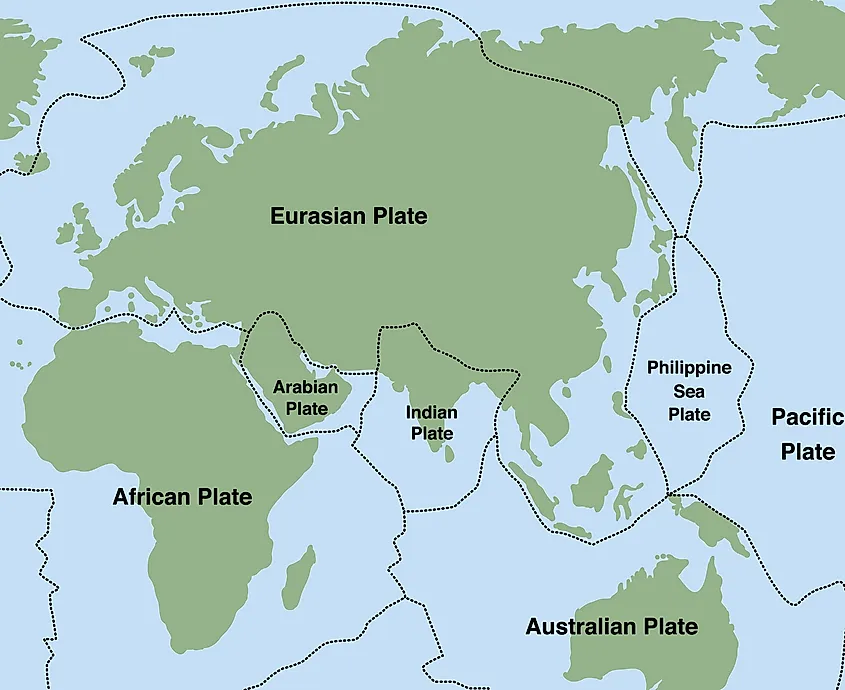
From a geographical perspective, there is a general understanding that the Indian Subcontinent consists of the peninsular part of present-day India, south of the Himalayas, on the Indian tectonic plate that is separate from the rest of Asia. Note, however, that the Indian plate also includes some of southern China and eastern Indonesia, which are not considered part of the Indian Subcontinent. Thus, the geographical definition of the Indian Subcontinent is somewhat arbitrary. But of course, the Indian subcontinent is not defined exclusively from a geographic point of view.
Politics, culture, and history also help define what constitutes the Indian Subcontinent. For example, nearly all of the current countries of the Indian Subcontinent were formerly possessions of the British Empire. This includes the present-day states of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. Myanmar (Burma) was also a British possession, but since it is ethnically, linguistically, and culturally tied more to East Asia, it is generally not considered part of the Indian Subcontinent.

Two countries that were not possessions of the British Empire, however, namely Nepal and Bhutan, are considered part of the subcontinent, mostly for cultural, religious, and political regions. For instance, Nepal shares a common religion with India, Hinduism. Hinduism is the religions professed by most of the people in both India and Nepal. Both Nepal and Bhutan are also considered part of the Indian Subcontinent for historical and political reasons. Both countries historically maintained close relations with India when it was under British control, and still maintain strong ties today.

India, Bhutan, and Sri Lanka also have some religious ties. India was the cradle of the Buddhist religion. Today, although most of India’s population is not Buddhist, there is still a sizeable Buddhist population there. Buddhism is also the most prevalent religion in both Bhutan and Sri Lanka. One could argue that Tibet is part of the Indian Subcontinent because it is linguistically and culturally closer to Bhutan and India rather than China. But since Tibet is controlled by China, it is not considered part of the Indian Subcontinent.
Some consider Afghanistan to be part of the Indian Subcontinent. Indeed, from a political standpoint, Afghanistan is strongly tied to Pakistan, which is universally considered to be part of the Indian Subcontinent. The politics and events that occur in Afghanistan are often intertwined with what happens in Pakistan, especially in regards to the events preceding and following the 9/11 terrorist attacks. There are also ethnic and religious ties between Afghanistan and Pakistan. The Pashtun people, for example, though mostly found in Afghanistan, are also prevalent in southern Pakistan. Many Afghans in general have found refuge in Pakistan, fleeing decades of war in their own country. Both Pakistan and Afghanistan also share Islam as a common religion. From a geographical perspective, however, Afghanistan is generally not thought of as being part of the Indian Subcontinent.
The Indian Subcontinent As A Political And Cultural Community
Politically and culturally, the countries of the Indian Subcontinent are very much one community. For example, relations between India and Pakistan often dominate discussions of international relations in the region. Indeed, the two countries have locked horns with each other on numerous occasions. Armed conflict between the two countries is not uncommon. In fact, the two countries have fought several wars with each other.
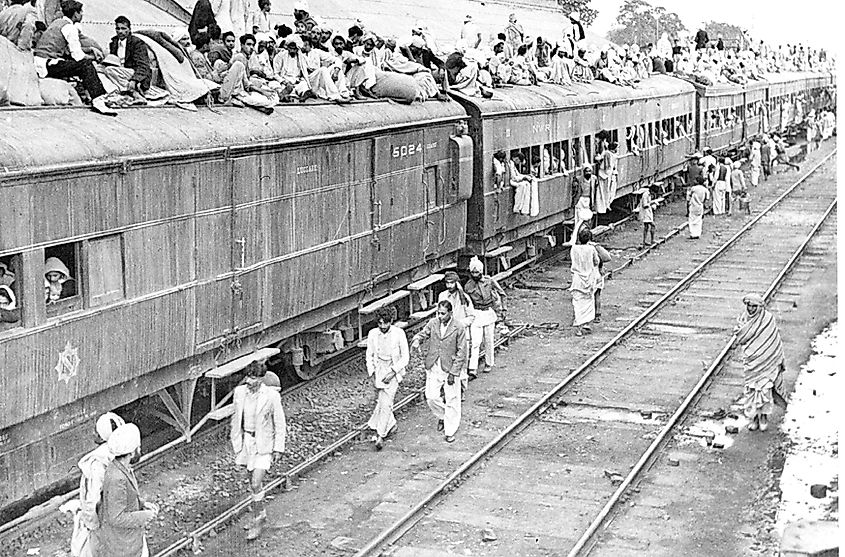

Tensions between the two countries go back to the time of British India and the struggle for Indian independence, though it should be noted that religious tensions between the Muslim and Hindu communities go back centuries. Mahatma Gandhi, long regarded as the lead figure in the Indian independence movement, wanted British India to remain united as an independent country. But many Muslim leaders rejected this, as they did not want to be part of a country in which Hindus were the majority. Instead, they wanted a separate Muslim country. Thus, when the British granted independence to India, the former British possession was partitioned into two countries, India and Pakistan. At that time, Pakistan included what was once called East Pakistan, though this part of Pakistan would later break away and become the independent country of Bangladesh.
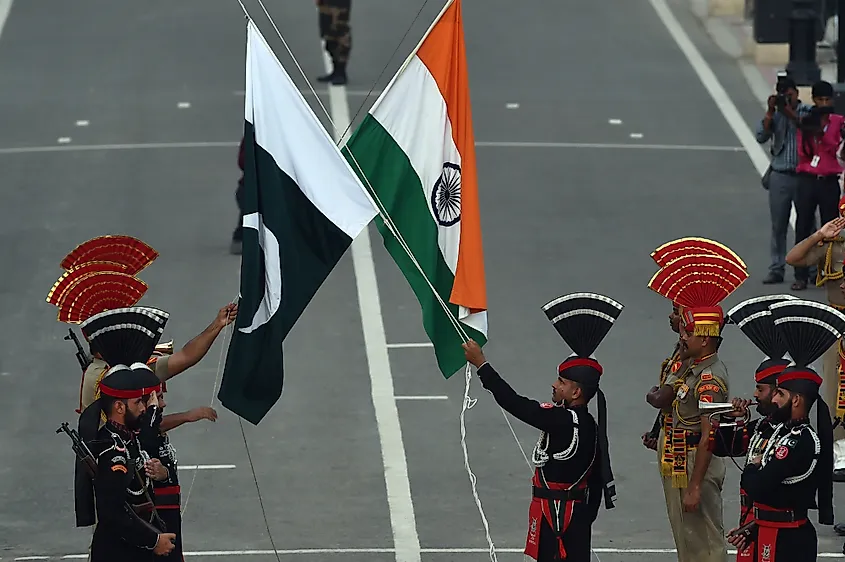

Since the partition, relations between India and Pakistan have been tense. The wars fought between the two countries have usually revolved around a dispute over the territory known as Kashmir. Both countries have control of parts of Kashmir, though they both claim the entire territory as their own. In the 1990s, the Indo-Pakistani conflict reached a new, dangerous level, as both countries had developed nuclear weapons. Thus, people on the Indian Subcontinent, not to mention the rest of the world, fear the outbreak of nuclear war in the region.
There are, however, things that bind the people of India, Pakistan, and the rest of the Indian Subcontinent together. Many of the people in the region have shared ethnic and linguistic ties. Some languages, for example, traverse international borders. Bengali, for instance, is spoken in both India and Bangladesh. Punjabi is spoken in both India and Pakistan. In addition, Urdu and Hindi, the official languages of Pakistan and India respectively, are quite similar, almost to the extent that some consider them the same language, distinguished only by how they are written. Urdu uses an Arabic script, while Hindi uses a script related to Sanskrit. These linguistic similarities allow people in different countries that are part of the Indian Subcontinent to enjoy elements of each other’s culture, such as music and movies.
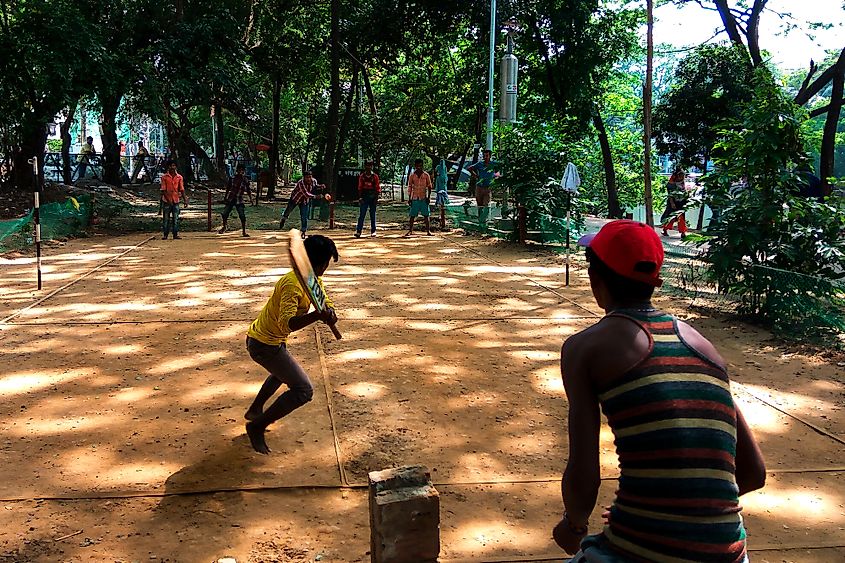

There is also one thing that many if not most people who live in the Indian Subcontinent agree on. That is, the love of one particular sport, cricket. The British left a lasting legacy in the part of the Indian Subcontinent that they once controlled, and part of that legacy is the sport of cricket. People in the Indian subcontinent follow cricket with an almost religious fervor. In fact, the current Prime Minister of Pakistan, Imran Khan, was a star cricket player before he went into politics.