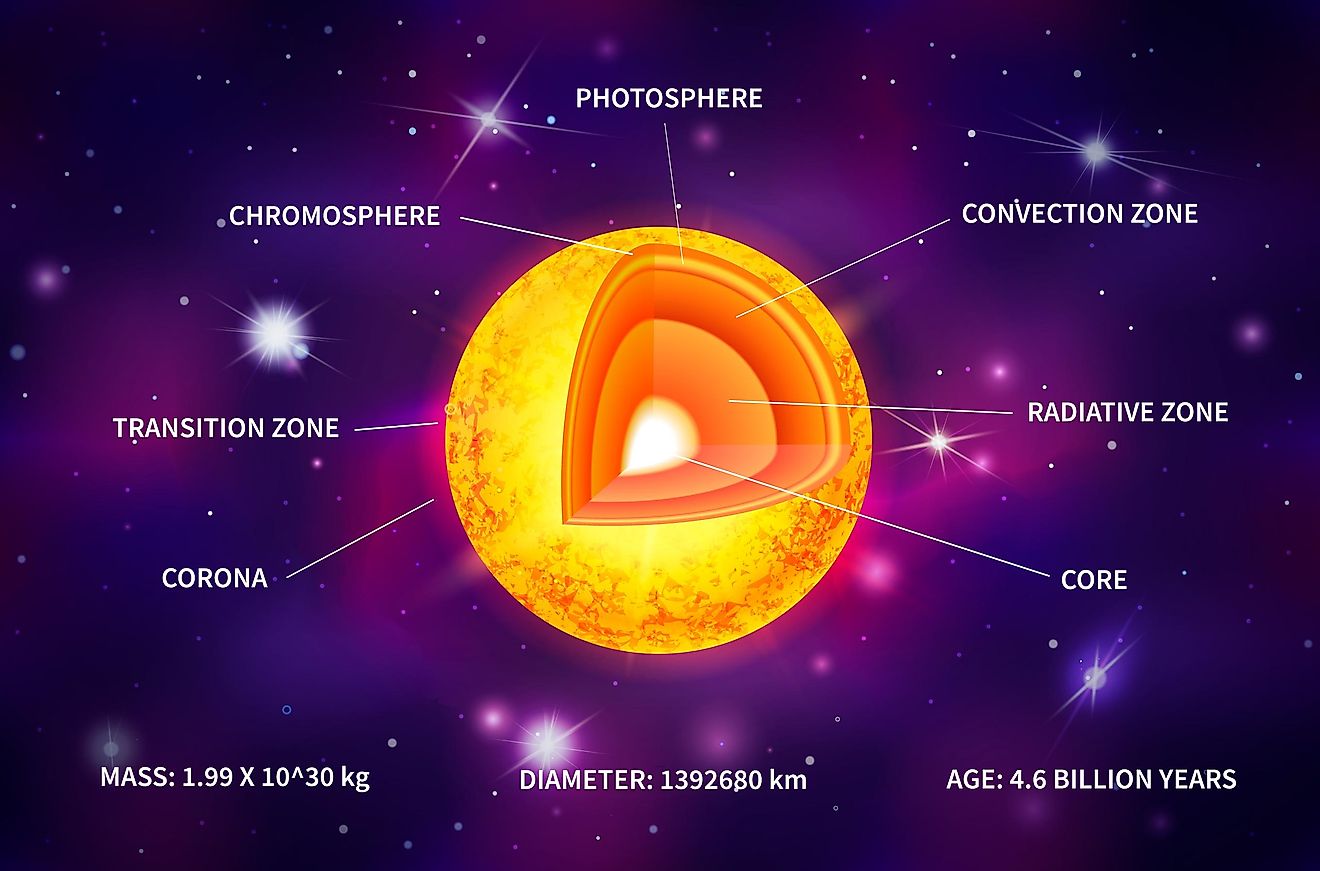
Why Is Space Dark?
When we look out into space, we see a universe that is saturated by darkness. Despite the fact that there are billions of stars in just our galaxy alone, the night sky is mostly dark, with the faint stars providing only slivers of light. Why isn’t the combined light from all the stars in our galaxy and beyond lighting up our night sky? In other words, why is space so dark?
Olbers’ Paradox
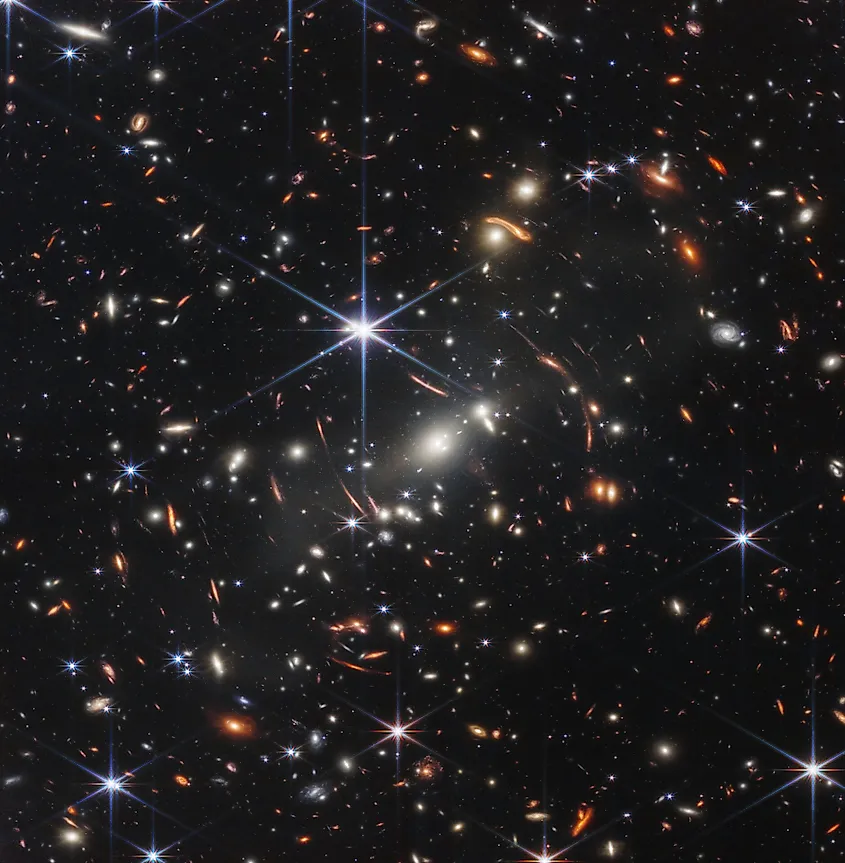

Although asking why space is dark may seem like a strange question, there was a time when the darkness of space posed a serious problem towards our understanding of the universe. Up until the 1920s, the prevailing model of our universe was that it was static and eternal. However, some astronomers pointed out that if the universe was static and eternal, then the light from every star in the universe would have reached the Earth, causing the night sky to experience a uniform luminosity. The night sky would be as bright as the sun due to the combined light of every star in the universe. This became known as Olbers’ Paradox, after the German astronomer Heinrich Olbers in 1823. Although the paradox is named after Olbers, he was not the first astronomer to notice issues with the model of an eternal universe. Many scientists had identified this issue, and so for decades, the fact that space was dark directly contradicted what humanity thought was true about our universe.
The Expansion Of Space

In the 1920s, the model of a static and eternal universe was largely dispelled when the astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe is expanding. The universe was no longer seen as an eternal, unchanging void. Rather, the universe was now understood to be finite and dynamic. Edwin Hubble had uncovered the expansion of space by observing the red-shift of distant galaxies. Hubble had noticed that the vast majority of galaxies were red-shifted, meaning that they are moving away from us at tremendous speeds, causing their light to become stretched and red-shifted. The red-shift of distant galaxies became one factor that explained why space is so dark. As light becomes red-shifted, it becomes either microwave radiation or radio waves, two wavelengths of light that are invisible to our eyes. If our eyes could see in these wavelengths, the night sky would appear brighter than it does.
The Big Bang
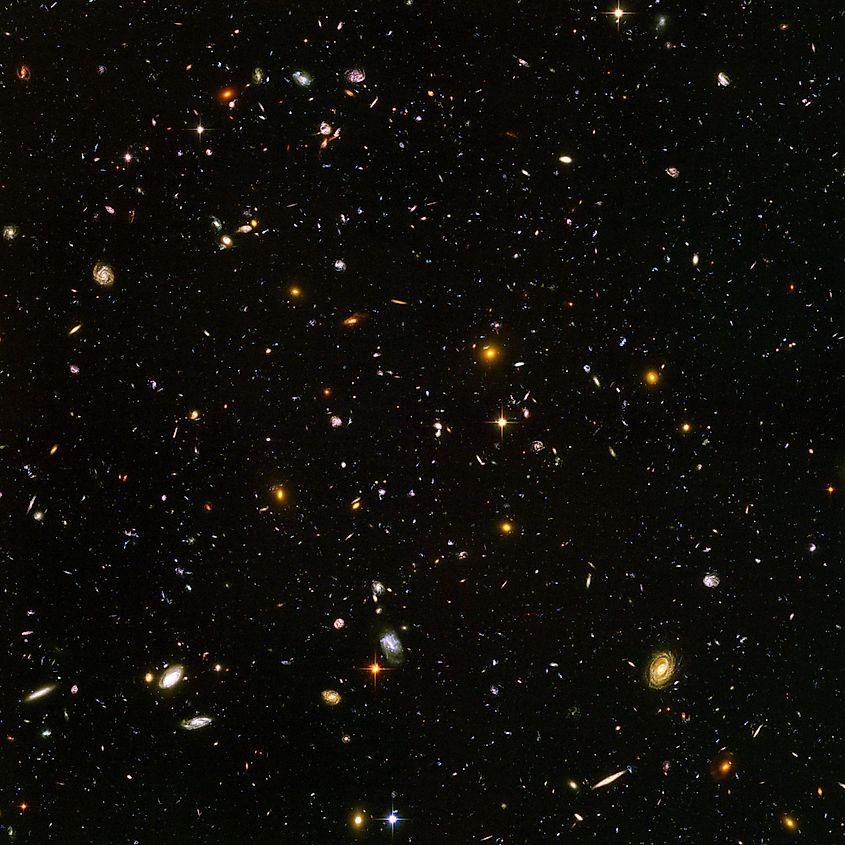

The red-shift of distant galaxies was one factor in explaining why space is dark, yet another would soon be uncovered. Hubble’s discovery that space is expanding soon led to the realization that if you simply run the universe in reverse, everything ends up at a single point. Thus, all the matter and energy contained within the cosmos originated from a single point. This model became known as the Big Bang, and it has since become the most widely accepted model for the earliest moments of the universe. The Big Bang occurred around 13.8 billion years ago, which although seems like a tremendous amount of time, it is nowhere near being an infinite amount of time. Since the universe has only existed for a finite amount of time, stars have only been emitting light for so long. Some stars are so far away that their light has not yet reached us. Space is dark because there is a vast number of stars that are simply too far away to be seen.