The Fastest Things In The Universe
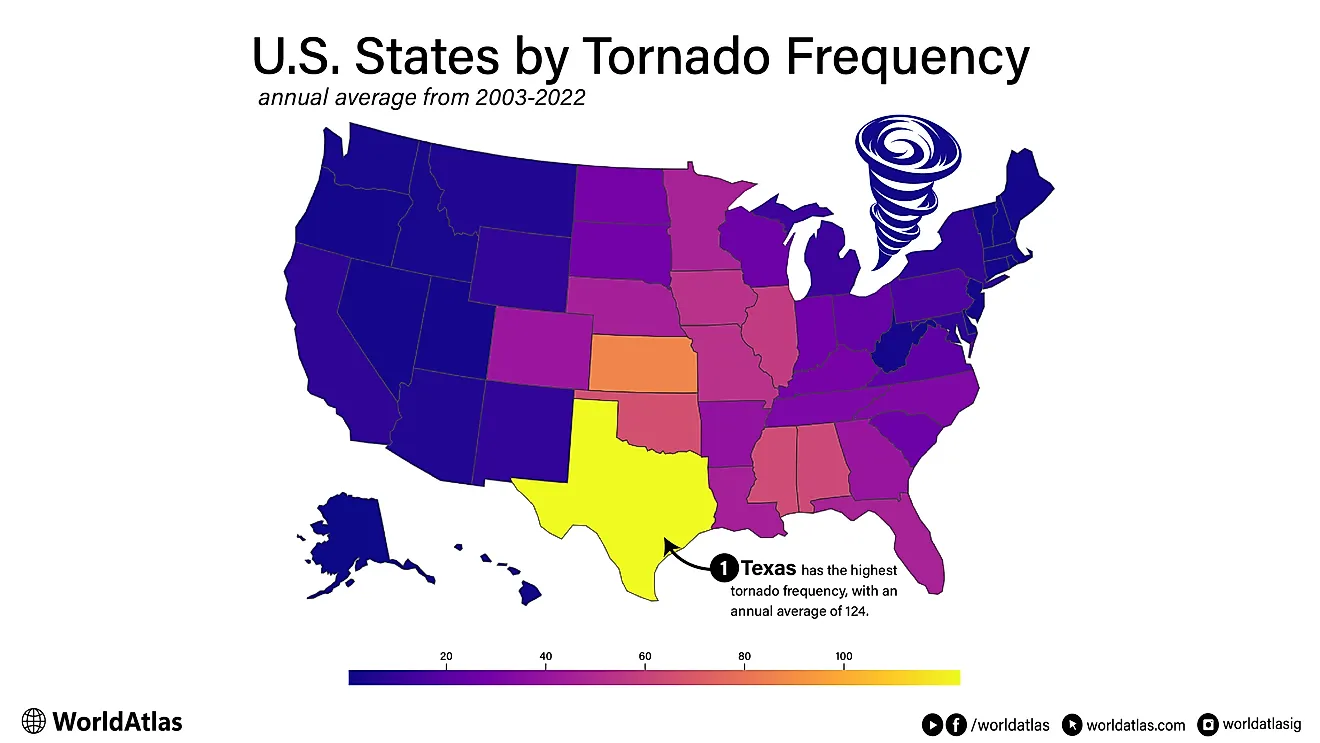
Speed shapes cosmic structure and human ambition alike. The Universe imposes an ultimate ceiling, the speed of light, 299,792,458 m/s, yet within that bound, nature and technology produce remarkable record-holders.
Photons traverse interstellar voids almost instantaneously, defining timing for every larger system. Among macroscopic bodies, exoplanet Kepler-78b loops its star in 8.5 hours, racing six times faster than Mercury. Near the Galactic Centre, hyper-velocity star US-708 streaks away at 1,200 km/s, expelled by a thermonuclear supernova. Even humanity competes: NASA’s Parker Solar Probe, slingshot by Venus, now skims the Sun at 147 km/s, the fastest machine ever built.
Cosmic rays and matter blasted from black holes speed close to light itself, testing the reach of our instruments and ideas. Drawing on fresh observations and the basics of relativity, this article explains how gravity, intense light, and advanced engines can hurl objects to extreme velocities, why some speed limits can never be broken, and how new telescopes and probes may soon reveal even faster motion.
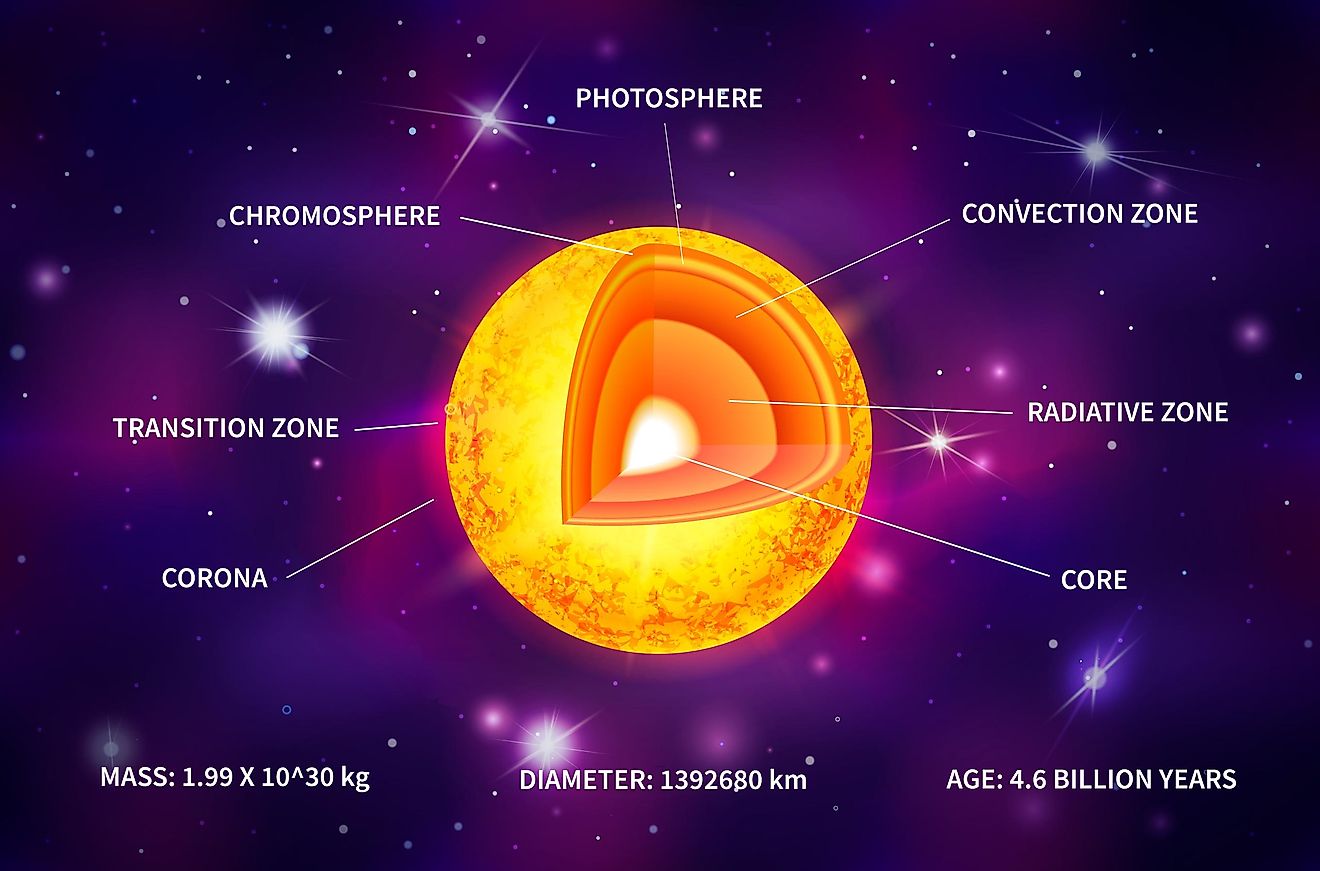
The Fastest Thing In The Universe

The universe has a cosmic speed limit. This means there is a maximum speed at which objects in space can travel. This speed limit is about 186,000 miles per second, and there is only one thing in the cosmos that travels at that speed: light. Light is the fastest known entity in the universe, which is why the cosmic speed limit is referred to as the speed of light. No matter how hard you try, you cannot exceed the speed of light. Similar to gravity, the cosmic speed limit is a fundamental law of nature that cannot be violated. Whether it originates from a star or your cellphone flashlight, every beam of light travels at 186,000 miles per second.
The Fastest Known Planet

Over the last 30 years, scientists have uncovered thousands of planets that orbit stars outside our solar system. Many of these worlds are vastly different from those orbiting our Sun. Regardless of the type of planets orbiting a star, one thing they all have in common is how their orbital velocity relates to the distance between them and their star. Planets that orbit close to their star complete an orbit faster than those farther away. Mercury is the fastest planet in our solar system, completing one rotation every 88 days. That may seem fast, yet it is nothing compared to some other planets in our galaxy. The fastest planet ever discovered was found in 2013 by NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope. Named Kepler-78b, it orbits its star at a distance of only 900,000 miles. For comparison, Mercury orbits the Sun at a distance of 36 million miles. With very little space between Kepler-78b and its parent star, the planet orbits its Sun at extreme speeds. It takes a mere 8.5 hours for Kepler-78b to complete one orbit around its star. Imagine living on a planet where a year lasts only 8.5 hours. As of now, no other planet has been found with a shorter orbital period, making Kepler-78b the fastest known planet in the universe.
The Fastest Known Star

It may not seem like it from our perspective here on Earth, but the Sun is actually racing through space. Like the planets that orbit the Sun, the Sun is also in orbit around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. At this moment, the entire solar system is moving through space at 448,000 miles per hour. That may sound fast, but it takes the Sun 230 million years to complete one orbit due to the immense size of the Milky Way Galaxy. Compared to some other stars, our Sun is relatively slow. The fastest known star in the universe exists near the very center of the Milky Way. Called US-708, it has been measured moving at a speed of 2.7 million miles per hour. When scientists first discovered US-708 and measured its velocity, they believed it was orbiting a black hole. The gravitational pull of the black hole would be so strong that it could have accelerated US-708 to tremendous speeds. However, subsequent observations revealed that US-708 may have actually been propelled to its current speed by an exploding star. US-708 was once part of a binary star system, where its companion star eventually exploded in a supernova. The resulting explosion was so energetic that it propelled US-708 to become the fastest known star in the universe.
The Fastest Human-Made Object
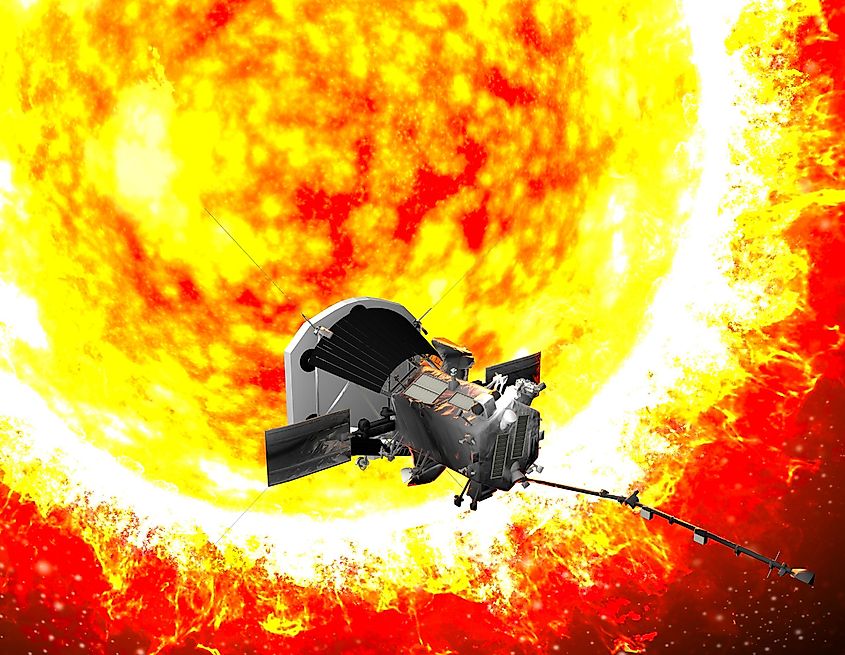

We have discussed what some of the fastest things in the universe are, but how does humanity measure up? What’s the fastest thing humans have ever created? As one might expect, the fastest human-made objects are generally spacecraft. Currently, the fastest human-made spacecraft is the Parker Solar Probe, launched by NASA in 2018 to approach the Sun closer than any spacecraft before. When NASA launched the Parker Solar Probe, it reached a speed of 39,500 miles per hour. On its journey to the Sun, the Parker Solar Probe made several flybys of Venus to increase its speed, utilizing a technique called gravity assist. As of February 2020, the Parker Solar Probe has become the fastest human-made object in history, achieving a speed of 330,000 miles per hour. That’s fast enough to circle the Earth 13 times in one hour! For humanity, this is truly a remarkable achievement. However, even at this speed, the Parker Solar Probe has only reached 0.05% of the speed of light.
Updated: 6/10/2025