What Are The Different Types Of Maps?
- Road maps, politic maps, and cadaster maps are a few different types of maps.
- Shallow water is usually depicted as a deeper blue color whereas deeper water is depicted as a lighter blue on maps.
- Maps have been used for centuries.
A map is a symbolic representation of a real-world element or area on a flat surface. Maps are useful because they illustrate specific, detailed features of a given area, region, or object. They depict features such as boundaries, topography, physical features, climate, and even economic activities. There are different kinds of maps, including dimensional, static, dynamic, and interactive maps. Maps have been in use since ancient times, when they were produced and used as necessary tools for identification and navigation. Maps became increasingly accurate and factual in the 17th to 19th centuries, as various countries adopted national mapping programs. The widespread use of aerial photography during World War I contributed significantly to the map-making process. Discussed below are some of the different types of maps.
Topographic Map
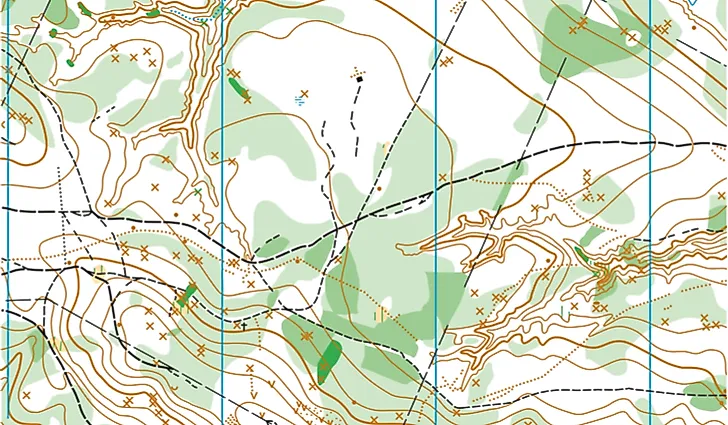
A topographic map is a detailed, large-scale map that depicts relief through contour lines and other methods. It displays both natural and human-made features, based on extensive surveys that reveal various landforms and elevations. These maps are useful for activities like geographical planning, civil engineering, large-scale architecture, and recreation such as hiking. Features are typically represented by standard signs and symbols, with colors often used to distinguish different types of roads. Explanations of these signs are usually provided below or along the edges of the map. In addition to contour lines, topographic maps show forests, water bodies, and buildings.
Geologic Map
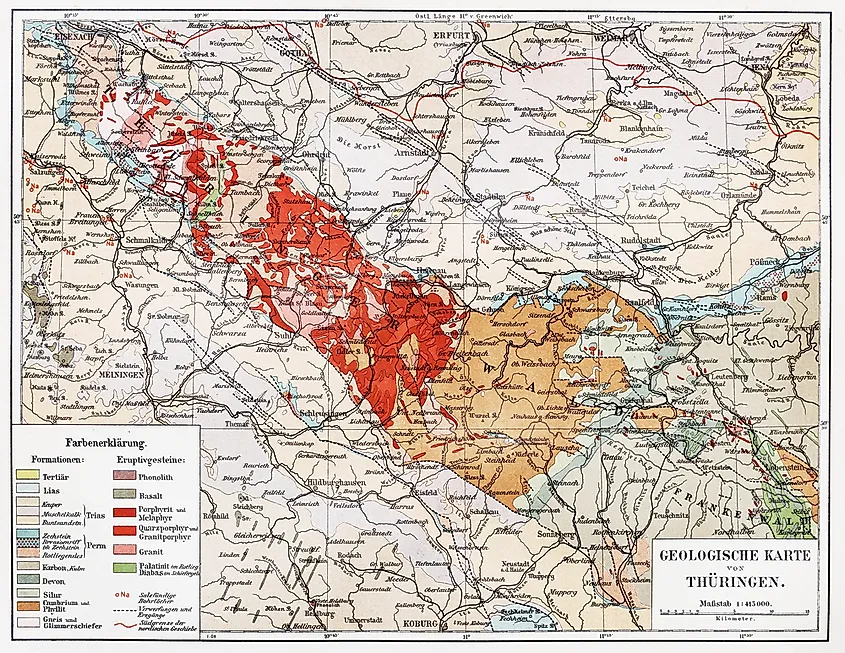
A geological map is a map that shows geological features such as geologic strata and rock units. The locations of these features beneath the Earth's surface are shown by symbols or colors. Other features, such as fault lines, foliations, and folds, are shown with strike and dip symbols, which give them a three-dimensional orientation. There are two main types of orientation measurements: orientation of planes, measured as “dip” and “strike,” and orientation of lines, measured as “trend” and “plunge.” Trend and plunge are symbolized by single arrows and are used for linear features, while strike and dip are symbolized by a long strike line perpendicular to the direction of the slope. In the US, geologic maps are superimposed over topographic maps, with additional color masks and letters to represent a geologic unit. In the UK, the term “geological map” is used instead of a “geologic map.”
Political Map
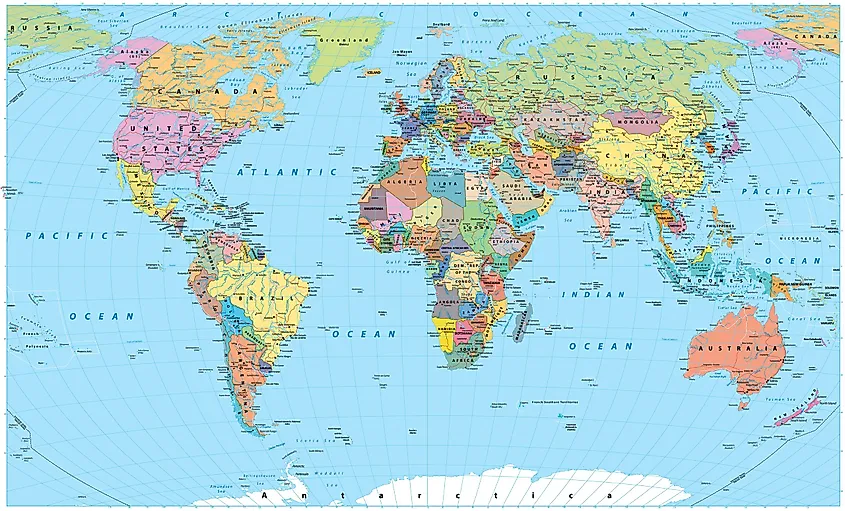
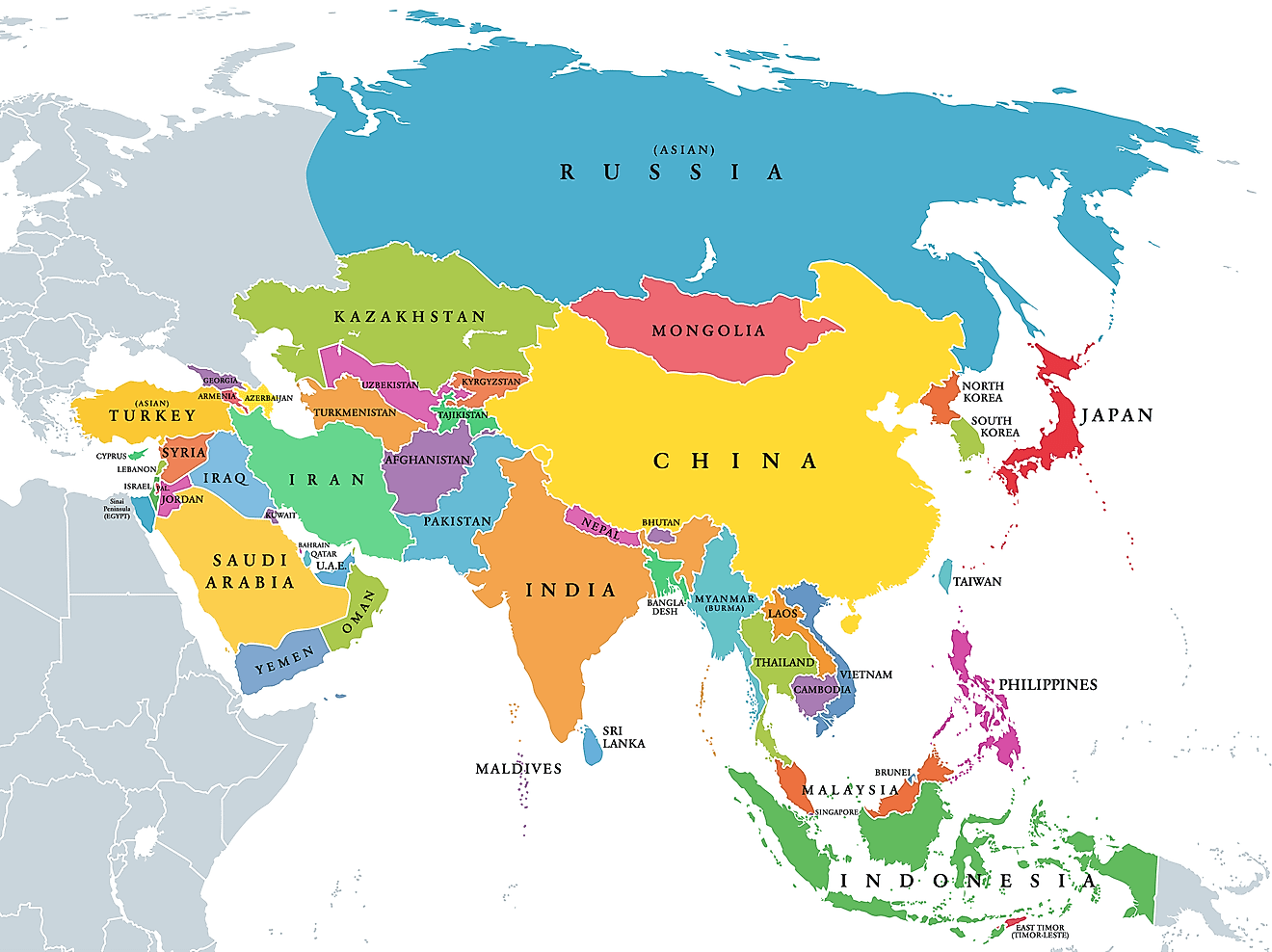
World maps are typically classified as either political or physical. A political map highlights the borders between countries, cities, and states, as well as major land features like water bodies. These maps come in various sizes, from those covering an entire continent to those focusing on a specific region, state, or country. The defining characteristic of a political map is its depiction of boundaries, which are marked by lines separating different regions. They are essential for understanding world geography and are often the first maps students learn about in school. Also called "reference maps," they can be printed on physical media or paper, or created digitally for online viewing.
Physical Map
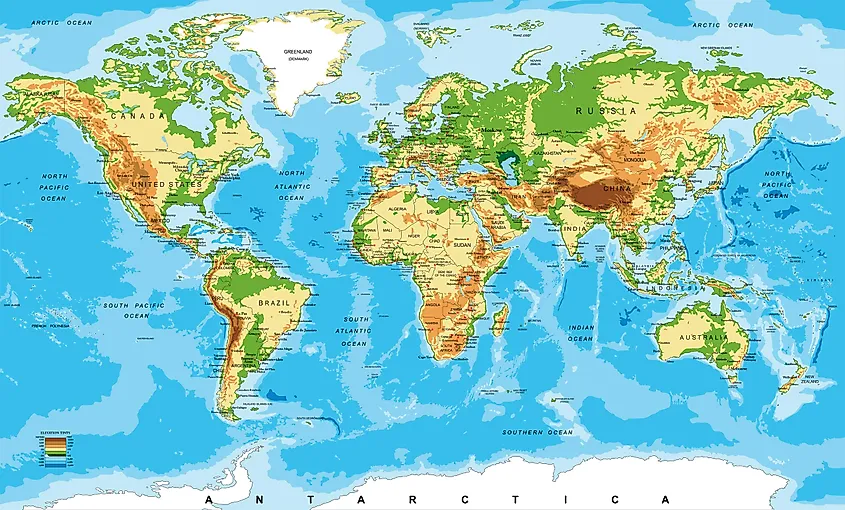
As the name suggests, physical maps are designed to show the Earth's physical or natural landscape features. They typically depict geographical features such as soil type, mountains, and land use, including infrastructure like roads and buildings. Physical maps are among the most colorful, with different colors used to indicate different physical features. Most maps use a green-to-brown-to-gray color scheme to show elevation. Dark green indicates near-sea-level elevations, and brown indicates higher elevations. Water bodies such as lakes, rivers, and oceans are often shown in blue (light blue for shallow areas and dark blue for deeper waters). Ice and glaciers are shown in white. Cultural information is not a focus of physical maps but may be included on the map for geographic reference.
Road Map
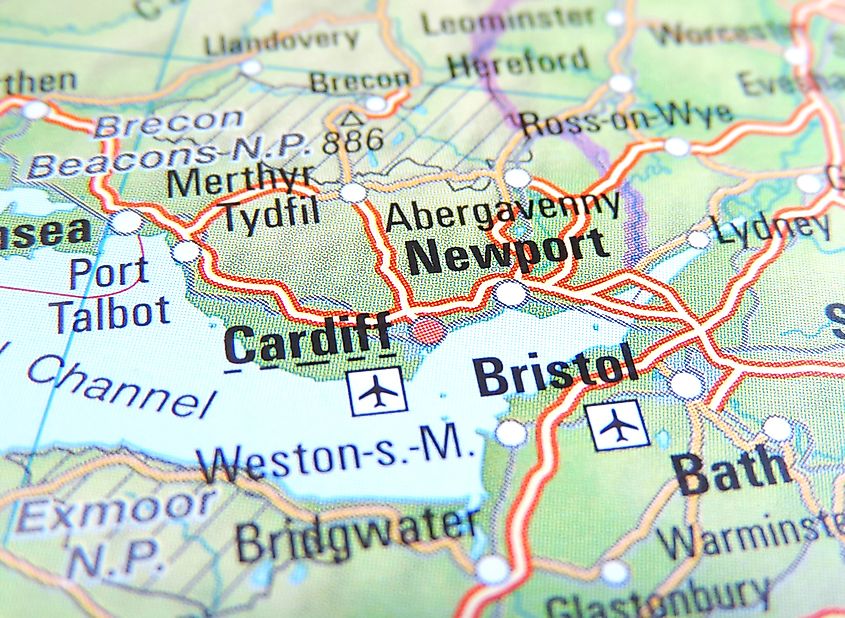
Road maps, also known as route maps, show roads and other transportation links. They are navigational maps that also include political boundaries, making them part of political maps. In addition to roads and boundaries, road maps show points of interest such as tourist sites, prominent buildings, recreational facilities like parks and restaurants, train stations, and airports. The maps come in different sizes, shapes, and scales. Small maps provide an overview of a region’s major roads or routes, while large maps offer greater detail and cover a larger area. Highway maps give an overview of major routes within a region. Street maps mainly cover areas within a city or metropolitan area. A collection of road maps bound together in a book is called a road atlas. Road maps often use thin lines to indicate minor roads and thicker or bolder colors to indicate major roads.
Cadaster Map
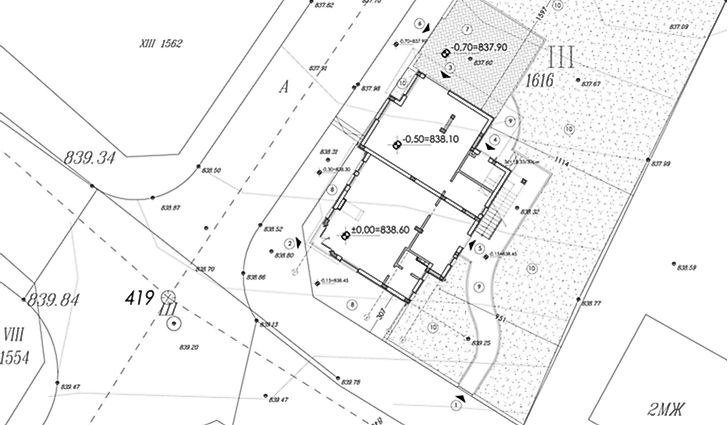
A cadaster map is a map showing the real estate of a country. It includes the location, area, ownership, value, and tenure of an individual parcel of land. According to the International Federation of Surveyors, a cadaster is an up-to-date land information system that contains records of interests in land, such as restrictions, rights, and responsibilities. It includes the geometric description of the land and is used alongside other records that describe the nature of the interest, controls of such interest, and the value of the parcel of land. Some maps also show additional information such as the parcel’s identification number, survey district name, certificate of title number, adjacent street names, and the position of existing structures.
Dot Distribution Map
A dot distribution map, as the name indicates, uses dot symbols to represent the presence of features and relies on visual scattering to display spatial patterns. There are two main types: one-to-one and one-to-many. In a one-to-one map, each dot corresponds to a single feature. In a one-to-many map, a dot represents multiple features, but their actual locations are not shown, as dots are placed arbitrarily. These maps are useful for illustrating features that vary smoothly across space. However, the random placement of dots can sometimes hinder the map's ability to effectively communicate its message.
Thematic Map
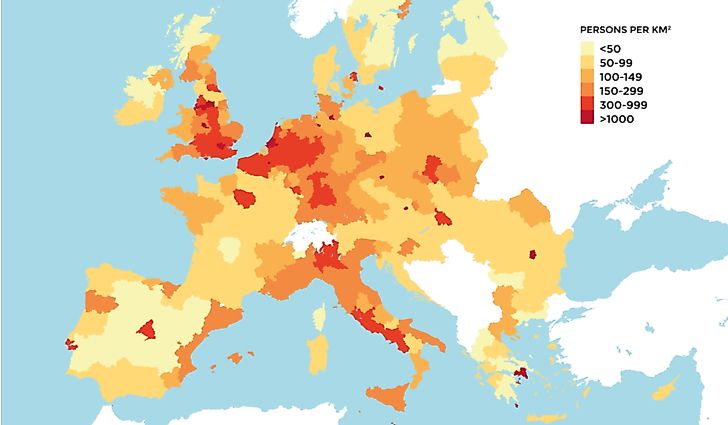
A thematic map is designed to highlight a theme related to a specific geographic area. Unlike a general reference map that shows several phenomena (geographic, political, and geological), a thematic map focuses on a specific subject area and uses base data only as a point of reference for the feature being mapped. Thematic maps also emphasize spatial variation across a number of geographic distributions, such as climate, population density, and health. The map serves three main purposes: to provide specific information, to provide general information about the spatial pattern, and to compare patterns across different maps.