Aleutian Islands
Formerly referred to as the Catherine Archipelago, the Aleutian Islands are a chain of volcanic islands, a major portion of which belongs to the US State of Alaska while few islands belong to the Russian territory of Kamchatka Krai. The Aleutian Islands form a part of the Aleutian Arc and extend for more than 1,900km. The islands cover a large area of 17,666 sq. km in the North Pacific Ocean, extending from the edge of the Alaska Peninsula to Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula. The Aleutian Islands separate the Bering Sea in the north from the Pacific Ocean in the south.
Geography
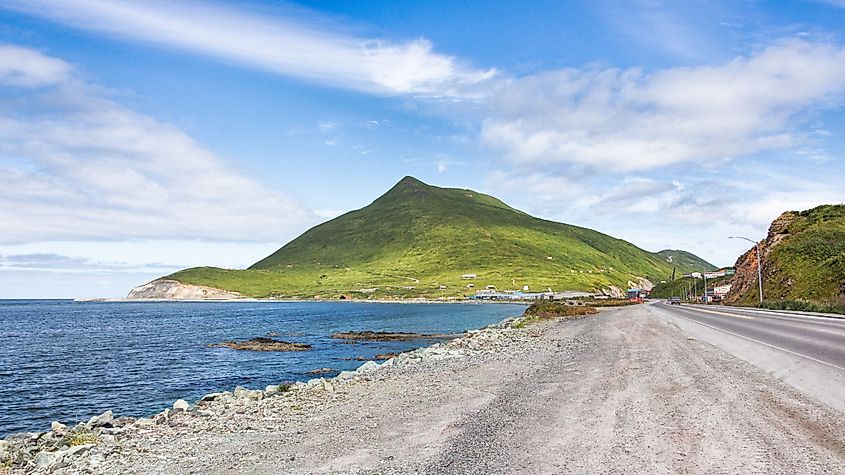

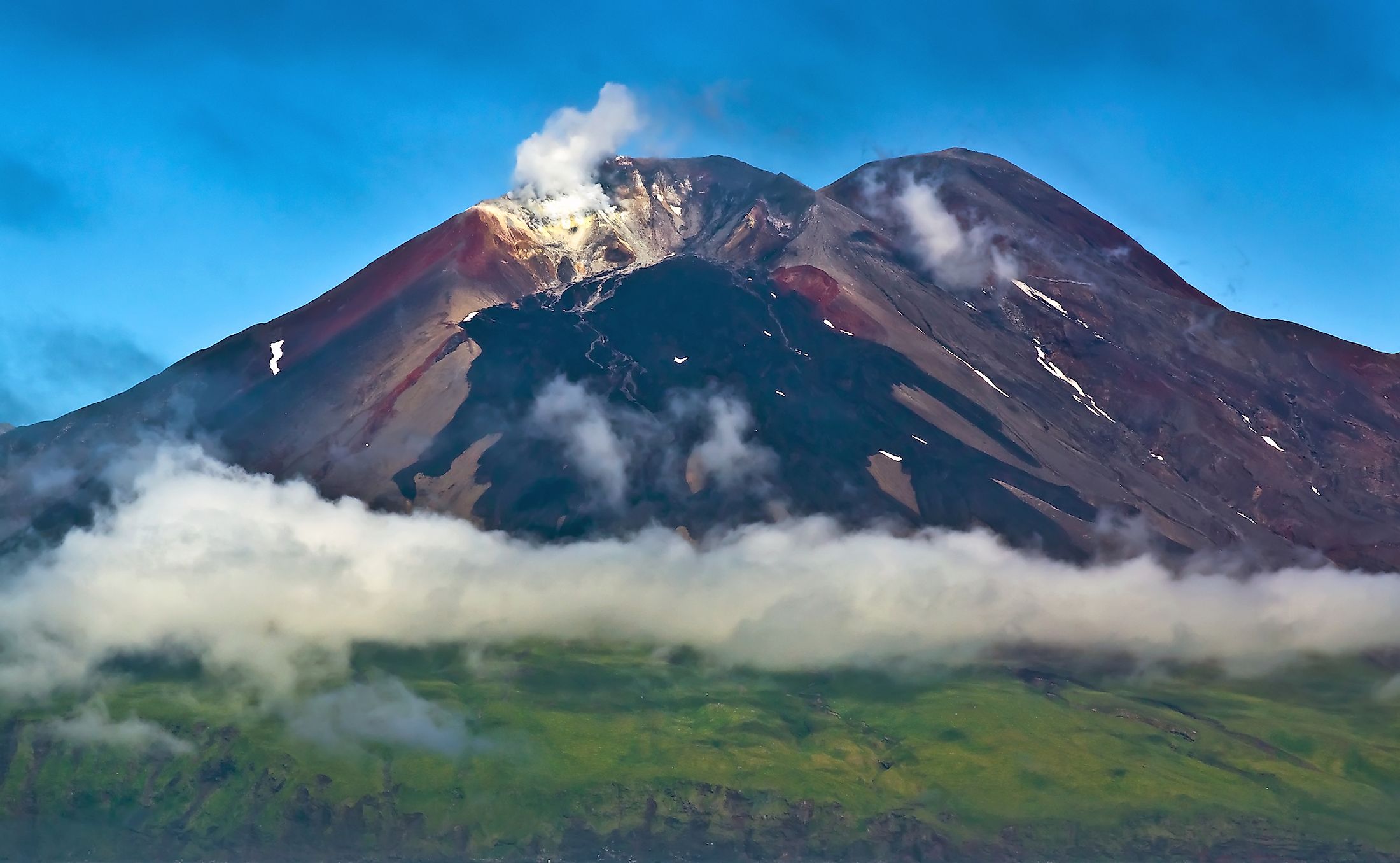
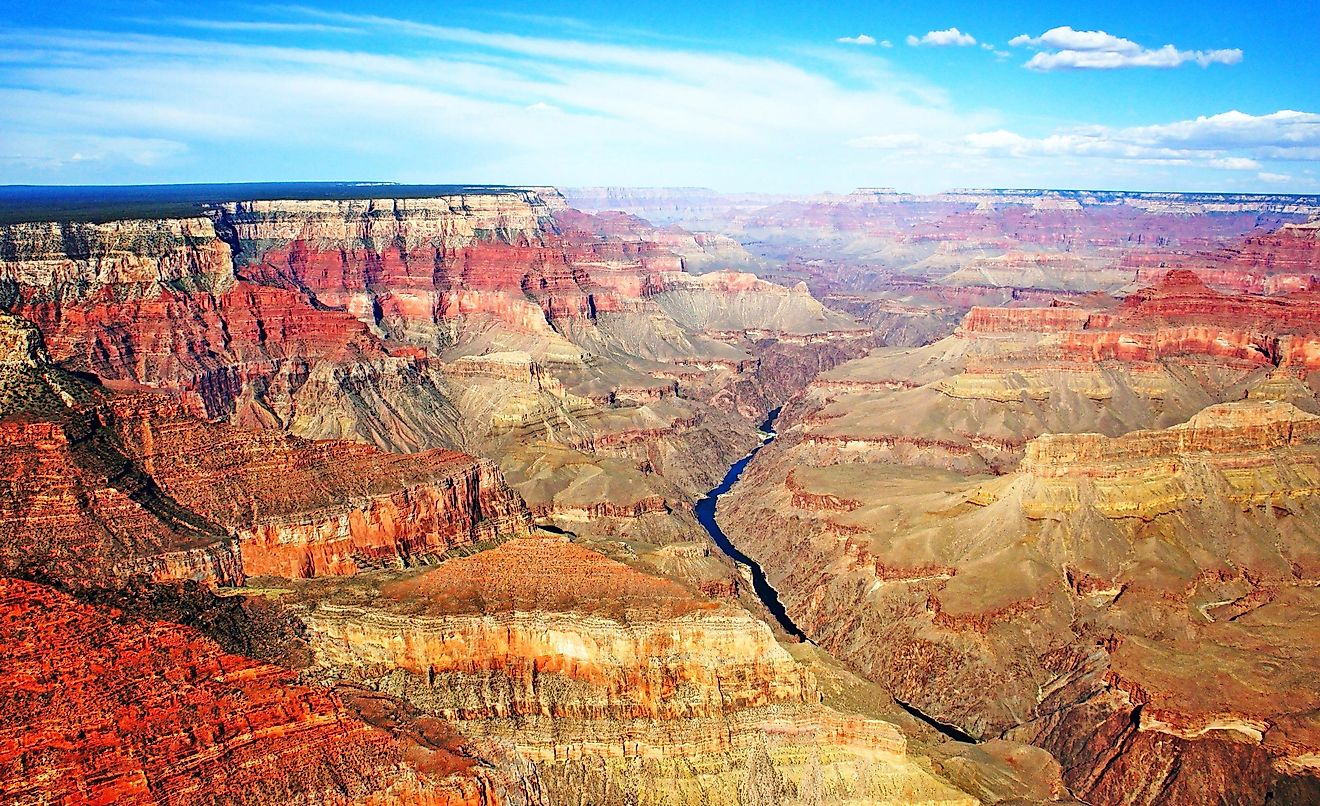
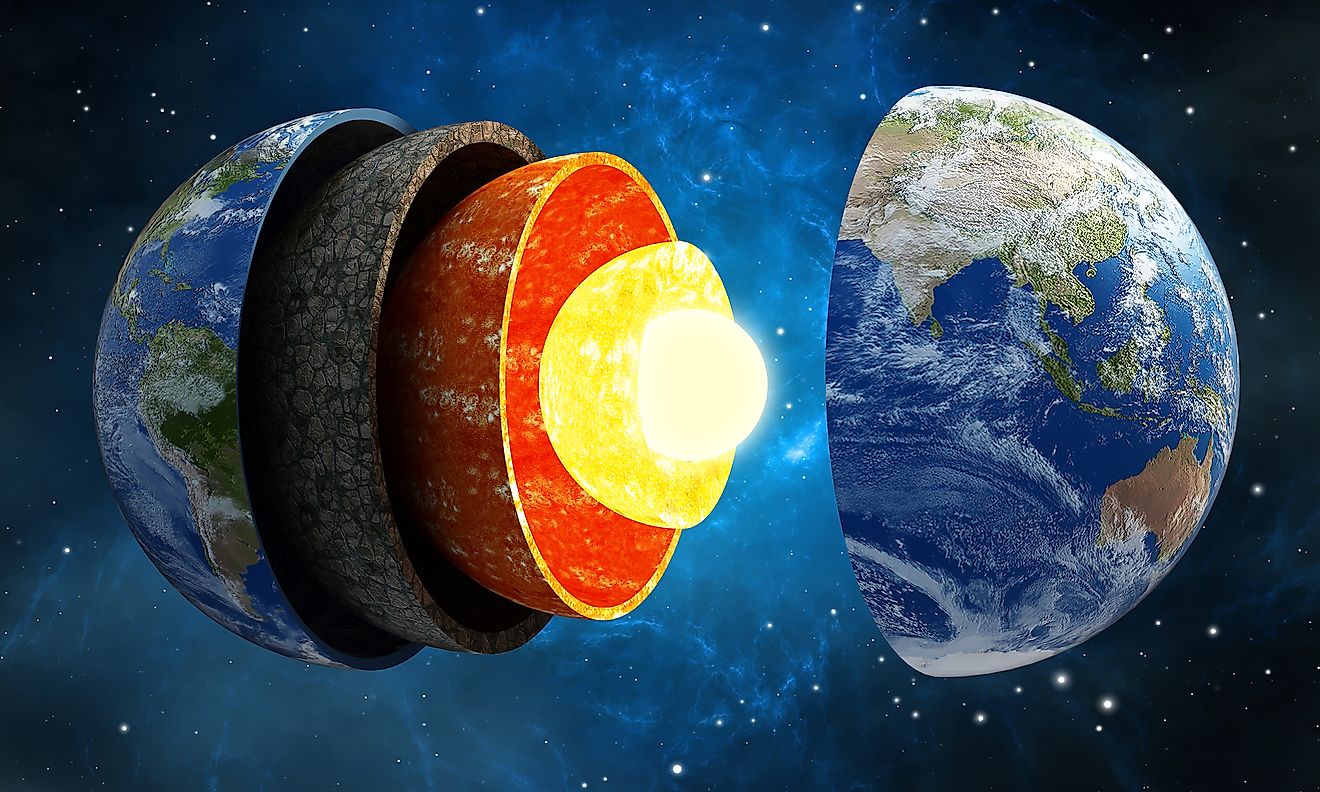
Situated on the northernmost section of the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Aleutian Islands are made up of 14 large and 55 smaller volcanic islands and numerous islets. It is believed that during the Early Eocene, the Aleutian Island arc was formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the North American Plate. The Aleutian Islands stretch across the 180° longitude and therefore the Aleutian archipelago includes both the Amatignak Island, which forms the westernmost region of the United States by longitude, and the Semisopochnoi Island, which forms the easternmost region of the United States by longitude.
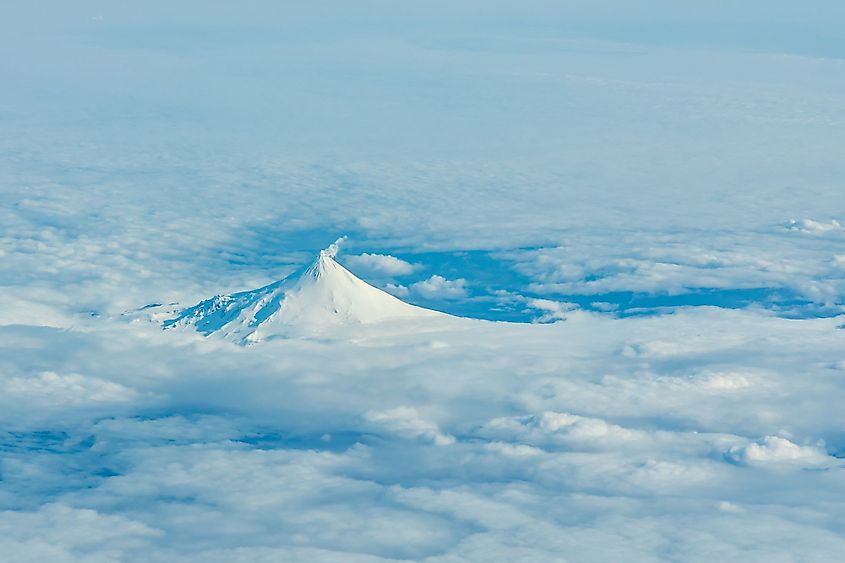

The six principal groups of islands are Andreanof Islands, Commander Islands, Fox Islands, Islands of Four Mountains, Near Islands, and the Rat Islands. A major part of the Aleutian Islands is located within Alaska, while few such as the Commander Islands are administered as Russian territory. The largest islands in the Aleutians include the Attu Island, Unalaska, Unimak, and Umnak Islands. Except for the Attu Island, the remaining three large islands forms a part of the Fox Islands group. Of these islands, the Unimak Island which covers an area of 4,069.9 sq. km is the largest, followed by the Unalaska Island which covers an area of over 2,600 sq. km. Most of the islands display marks of their volcanic origin and it is estimated that there are a total of 57 volcanoes in the Aleutian Islands. Mount Shishaldin, located close to the heart of the large on the Unimak Island is considered to be a moderately active volcano, which rises to an elevation of 2,857m and is the highest point in the Aleutian Islands.
Climate
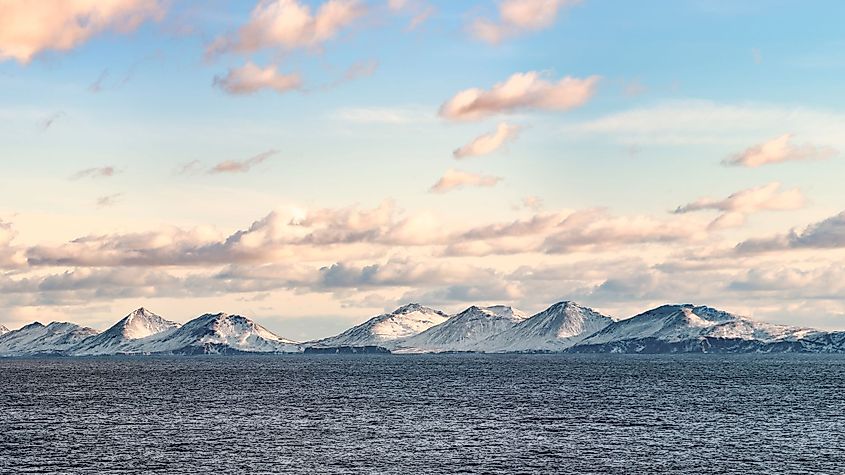

The Aleutian Islands experience an oceanic climate that is characterized by relatively uniform temperatures throughout the year. The islands receive heavy rainfall with strong winds and continuous fog. The Unalaska Island has an average annual temperature of 3°C, with -1°C in January and 11°C in August. The Aleutian Islands receive an average annual rainfall of about 2,000m and the Unalaska Island that has over250 rainy days per year is considered to be one of the rainiest places that is located within the United States.
Flora and Fauna
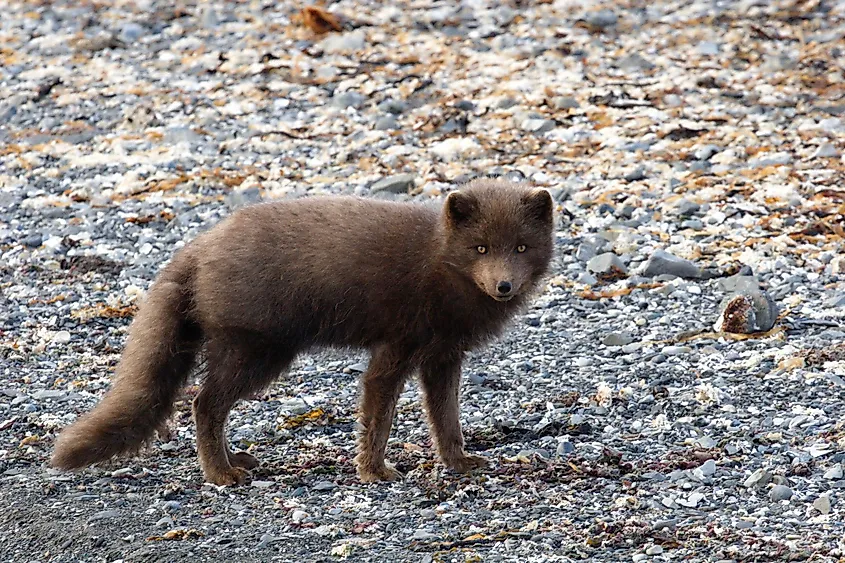

The Aleutian Islands are devoid of native trees and are covered with a luxuriant growth of grasses, shrubs, sedges, stunted willows, and several flowering plants. The growing season lasts from the beginning of May to late September, but agriculture is mainly limited to the growing of few vegetables only. A few conifers introduced by the Russians grow on the islands of Umaknak and Adak. The Aleutian Islands provide critical nesting habitat for numerous seabirds including auklets, fulmars, murres, and puffins. Many Asiatic migrant birds including bluethroat, common rosefinch, lanceolated warbler, Siberian rubythroat, etc. In addition to this more than 450 species of fish, 26 species of marine mammals, and sea corals are also found in the Aleutian Islands. However, the wildlife of the Aleutian Islands is facing serious competition from several introduced species such as cattle, reindeer, foxes, etc. The Aleutian Islands are protected as a part of the Aleutian Islands Unit of the large Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge.
Demography and Economy
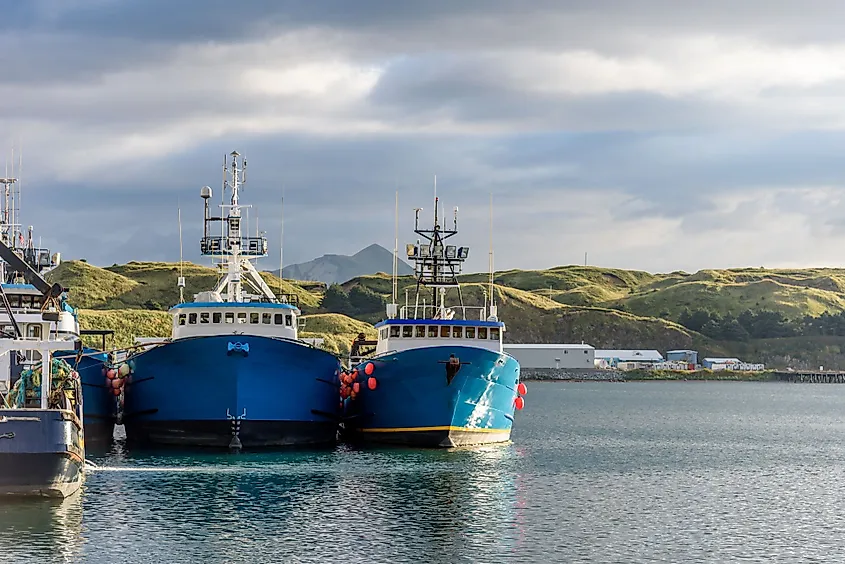

The indigenous people residing in the Aleutian Islands are known as Unangan but are usually referred to as Aleut by the non-natives. The people living in the Aleutian Islands speak in the Aleut language. As per the 2000 US Census, the Aleutian Islands support a total population of 8,162 people of which 4,283 people live on the main island of Unalaska. Dutch Harbor – the largest fishing port in the United States is located in the Aleutian Islands. Currently, the economy of the Aleutian Islands is mainly dependent on fishing and the presence of the United States military.
Brief History

For more than 10,000 years, the indigenous Aleut people were the only inhabitants of the Aleutian Islands. In 1741, the Danish cartographer and explorer Vitus Bering and the Russian navigator Aleksei Chirikov were sent by the Government of Russia on a voyage of discovery in the North Pacific region. However, after a powerful storm had separated their ships, several eastern Aleutian Islands were discovered by Chirikov, while many western Aleutian Islands were discovered by Bering. After Bering’s death during the voyage, many of his crew members returned to Russia and informed about the abundance of fur-bearing animals on the discovered islands. The fur hunters from Siberia reached the Commander Islands and slowly moved in the eastern direction crossing the Aleutian Islands into the Alaskan mainland. The Russians mercilessly slaughtered the indigenous Aleut people thereby gaining a strong foothold in the North American continent. In the 1867 Alaska Purchase, the Aleutian Islands along with the rest of Alaska were sold to the United States by Russia. During the Second World War, the Attu and Kiska Islands were occupied by the Japanese troops. In May 1943, the Attu Island was reoccupied by the US forces after a fierce battle and the Kiska Island was evacuated by the Japanese forces before the arrival of the US troops. From 1965 to 1971, the United States conducted underground testing of nuclear weapons in the Amchitka Islands which belong to the Rat Islands group of the Aleutian Islands.