What Are The Major Natural Resources Of The Democratic Republic Of The Congo?

The Democratic Republic of the Congo is an African nation that is considered to be one of the wealthiest countries regarding natural resources. Despite the presence of vast quantities of natural resources, Congo remains one of the poorest nations on earth. In 2017, the Congolese gross domestic product was roughly $37.24 billion, which was the 93rd highest globally. Even though the Congolese gross domestic product was among the top 100 in 2017, its per capita gross domestic product was ranked as the 179th globally. The most vital natural resources in the Democratic Republic of the Congo include the country's arable land, minerals, wildlife, and forests.
Natural Resources
Arable Land
In 2014, the World Bank estimated that roughly 11.56% of the Congo's territory was considered arable. The data indicated that since 2006, the amount of arable land in the Congo has been increasing steadily which can be partially attributed to the importance of agriculture to the country's economy. The Congolese government estimated that in 2012, agriculture accounted for 44.2% of the country's gross domestic product. The Congolese labor department estimated that more than 60% of the active Congolese labor force was employed in the agricultural sector. The Congolese climate can support a wide variety of crops such as cassava, corn, and coffee. The major challenge facing the Congolese agriculture industry is the poor development of the country's transport sector. Overreliance on traditional agricultural practices has also hampered the development of the country's agricultural sector.
Coffee
Coffee is one of Congo's most important crops since it is the country's top agricultural export item. In 2004, the Congolese government estimated that the roughly 33,000 tons of coffee were produced in the country. During the 1990s, Congolese coffee farmers produced roughly 97,000 tons of coffee each year. Most of the coffee in Congo, close to 80% according to several estimates, is grown in three provinces Haut Zaire, Kivu, and Equateur. Most of the Congolese coffee farmers grow Arabica coffee with only 15% of the country's coffee being Robusta. Congolese coffee is mainly grown for the export market with nations such as Switzerland, France, and Italy importing most of Congo's coffee.
Cassava
Although cassava is not one of the Congo's native crops, the Congolese people eat vast quantities of cassava each year. Historical evidence indicates that the Portuguese introduced cassava to the Congolese people during the 16th century. At the time, the Portuguese thought that the crop would feed the people during famines.
Forests
The Congolese government estimated that roughly 60% of the country's entire area is covered with forests. The Congolese forests are some of its most important natural resources since they are exploited to provide timber to the country. Botanical experts estimated that the Congo has roughly 600 unique species of trees used for timber production. Due to the excessive exploitation of forests in the Congo, the size of forest cover has decreased drastically. The Congo's forest cover also decreases because trees are destroyed to provide space for agriculture. The Congolese government estimated that since the 1990s, the country lost roughly 1,200 square miles of forest each year.
Wildlife
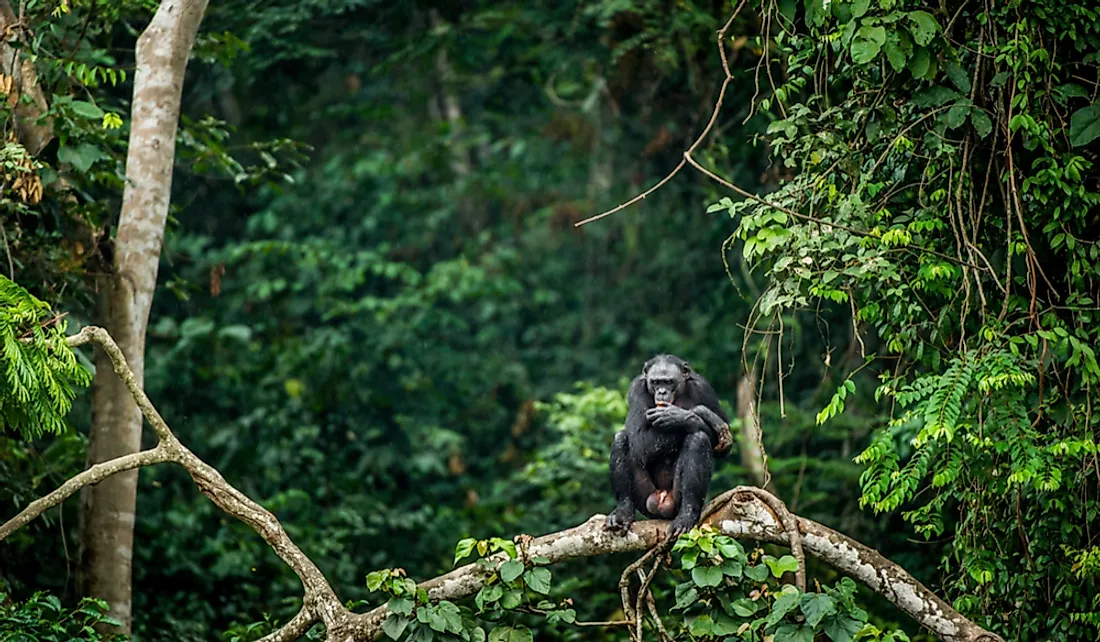
The Congo has been blessed with large numbers of unique wildlife that are some of its most important natural resources. Experts believe that the Congo is home to more than 1,000 species of birds as well as 400 species of mammals. The Congo is also home to over 250 species of reptiles. The Congo is also home to over 2,000 species of butterflies with close to 200 being endemic to the country. To conserve the country's unique wildlife, the Congolese government established five national parks. One of the unique wildlife species found in the Congo is the Bonobo, a species of chimpanzee, and the country is the only place where Bonobos freely roam in the wild. Apart from the bonobo, the Congo is home to several other primate species such as gorillas and the common chimpanzees. The major challenge facing Congolese wildlife is hunting and the destruction of habitats. Some of the wildlife species in the Congo have been classified as endangered due to the excessive hunting of wildlife. The Congolese government has attempted to conserve the country's wildlife by putting in place several policies.
Minerals
The Congo has vast deposits of minerals which are arguably its most important natural resource. A wide variety of minerals are located in the Congo ranging from cobalt to gold and tin. The mineral sector has faced several significant challenges that have hampered it from contributing significantly to the Congolese economy. One of the challenges that face the Congolese mining sector is the country's political instability. During the wars that ravaged the country, the minerals were illegally exploited by the various rebel groups fighting in the Congo. Due to the illegal operations of the rebel groups, several mining companies in the country were forced to shut down their operations. Another challenge facing the Congolese mining sector is the rampant corruption among the country's public officials. The Congolese government implemented some reforms in an attempt to make the country's mining sector more economically viable. One of the reforms that the Congolese government put in place was partnering with the International Monetary Fund and other nations such as Canada and Ireland to modernize the country's mining sector.
Copper
One of the Congo's most essential minerals is copper which is mainly extracted in the copper belt region. The Congolese government estimates that the country's copper belt has more than 70 economically viable deposits of copper. The copper deposits found in the Congo are some of the top high-quality copper reserves in the world. Experts believe that the copper deposits in some of the Congo's reserves could be more extensive than previously estimated. Most of the copper produced in the Congo is sold to other nations with the significant market for the nation's copper being China. Some of the companies that mine copper in the Congo are from other nations such as Metorex from South Africa and Anvil Mining from Canada.
Oil
Congo has some of the largest deposits of oil on the African continent and in 2008 the country was believed to have 180 million barrels of oil. The Congolese government estimated that in 2008, the nation produced roughly 19,960 barrels of oil each day.
Economic Challenges Facing the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Congolese economy faces a significant number of challenges with the major one being the country's political instability. The wars that have affected the Congo have hampered its economic development.