What Are The Major Natural Resources Of Armenia?

Armenia is a landlocked country located in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia. Armenia is bordered by Georgia in the north, the Republics of Azerbaijan and Artsakh in the east, Nakhchiva (Azerbaijan's exclave) Iran in the south, and Turkey in the west. Armenia occupies a land area of 11,484 square miles. The population of the country is estimated at 2.9 million. Until independence, the economy of Armenia heavily depended on industry. The industry relied on outside sources. The main domestic energy source is hydroelectric. The country’s vast majority of energy is produced with imported fuel from countries such as Russia.
Natural resources play an important role in boosting the economy of Armenia. The natural resources are used domestically and are also exported. Geographically, Armenia is mountainous. This geographical peculiarity renders the country rich in mineral resources. The mineral resources of Armenia include iron, zinc, aluminum, copper, molybdenum, gold, lead, silver and antimony. The country is also rich in other rare and hard to find metals. Armenia possesses some of the world’s most diverse nonmetallic minerals including tuff, zeolites, nephelite syenites, perlite, scoria, marble, pumice stone, and basalts. The industrial minerals found in the country are cement, diatomite, limestone, and gypsum.
The mining industry is, therefore, one of the principal areas of Armenia’s economy. In 2017, the output of the mining industry grew by 14.2% while the mineral product exports, excluding precious metals and stones, grew by 46.9% accounting, for 30.1% of all exports.
Mines
More than 670 solid mineral mines are registered in the state inventory of mineral resources. This fact is according to the Armenian Development Agency. The registered solid mineral mines include 30 base metals and precious metal mines. 400 of the registered mineral mines are under exploitation among them 22 base metals, precious metals, and non-ferrous metal mines.
Some of the precious metal and base metal deposits include 13 gold and gold-poly-metallic mines, 3 copper mines, 7 copper-molybdenum mines, 2 iron ore mines, and 2 poly-metallic mines.
An additional 115 deposits of various minerals have been discovered, aside from the mineral deposits registered in Armenia’s state inventory of mineral resources.
Molybdenum and Copper
These two minerals are the most important natural resources of Armenia. In fact, Armenia is a major producer of molybdenum, ranking seventh in the world in molybdenum production in 2010.
The two top producers of copper and molybdenum concentrates in Armenia are the Zangezur Copper-Molybdenum Combine and the Agarak Copper-Molybdenum Combine.
Large molybdenum deposits are concentrated in the Karajan deposit in Syunik Province. The deposits in this region are owned by the Zangezur Copper-Molybdenum Combine. Initially, the plant used the sub-surface mining before shifting to the open-pit mining method in 1959. Today, the plant produces 10 million tons of copper and molybdenum concentrates per annum. The copper concentrate is transported to Armenian Molybdenum Production Company and Alaverdi metallurgical plant in Yerevan where it is processed further.
The molybdenum concentrate is transported to the Yerevan Clear Iron Plant where its final treatment takes place. The derivatives of molybdenum are ferromolybdenum and molybdenum oxide. These derivatives are used primarily in the steel industry for heat resistance, strengthening, and corrosion resistance.
Copper is primarily used in industrial production. In 2015, copper ore exports of Armenia sharply increased to 67%. The copper ore was exported to countries such as Bulgaria, Romania, Georgia, Switzerland, and China. The same year, exports of molybdenum ore increased by 6.6%. Molybdenum was mainly exported to the Netherlands.
Apart from the Karajan deposits, other deposits of copper are found in the Shamlugh, Akhtala, Alaverdi, Lichq and Kashen mines. Other copper-molybdenum deposits are found in the Teghut, Hankavan, Agarak, Kapan, Dastakert, and Hankasar mines.
Gold
Significant gold deposits are located throughout Armenia in mines such as the Mghart Mine, Meghradzor, Sotk Mine, Sofi Bina, Amulsar Mine, Terterasar, and Bardzradir mines. In other regions, gold is mined as gold oxide or in combination with other minerals such as copper, silver, zinc, lead, uranium, and molybdenum. Gold forms an important sector of Armenia’s economy. It contributes to about half of the country’s total exports. About 13 gold and gold poly-metallic mines are under exploitation in Armenia. The gold-bearing poly-metallic deposits in Armenia occur mainly in the south of the country while the quartz traces containing silver and gold, are located in the northern parts of the country. Various international companies such as the United States-based Global Gold Corp have shown interest in investing in developing gold deposits in Armenia.
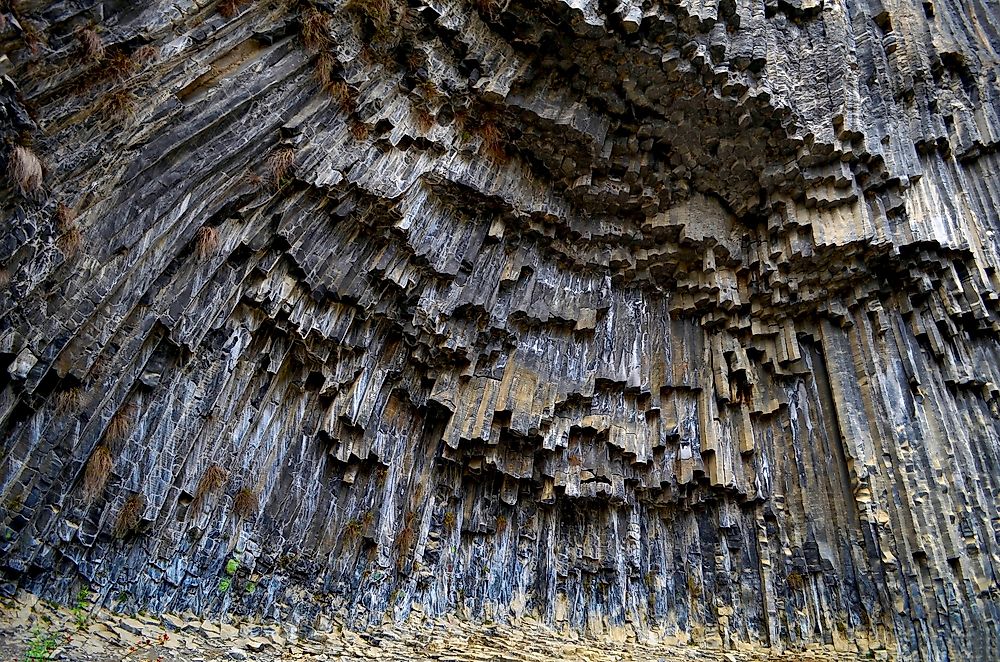
Rocks
Armenia is home to various unique and high-quality stones. Nearly all types of mineral rocks are found in this territory among them, tuff, scoria, nephelite syenite, perlite, basalts, marble, pumice stone, granites, and zeolite. Yerevan, the capital city and largest city of Armenia, is unique because of the color of the stone widely used in architecture in Armenia. This stone is the Armenian Tuff. The Armenian tuff has been used in construction in Armenia since ancient times.
The tuff is a beautiful, high-quality volcanic rock. It comes in different colors fluctuating from pink to red. Besides, the tuff can be black or brown. The Armenian tuff is a requisite rock in the territory. It is used for indoor and outdoor decoration and building pavements, facades, barbeques, and fireplace applications.
Salt
Salt is also one of the natural resources of Armenia. Large deposits of salt have been discovered Armenia’s territory of Avan. The only salt-producing company in the region is the Avan Salt Plant. Armenia is rich in mineral water as well. Several cities in the territory such as the cities of Sevan, Hankavan, Arzni, Bjni, Dilijan, and Jermuk, are well known the medicinal and organoleptic qualities of their waters. Small amounts of coal, gas, and petroleum in the territory have not yet been developed, thanks to the complex geography of Armenia.