The United States Navy (USN)

History of the US Navy
The United States Navy, a branch of US Armed Forces, is responsible for combat at sea, in the ocean, or other bodies of water which might act as an entry route for rival or enemy troupes. The idea behind a Naval force came from the long tradition of sea-based professions including sailors and shipbuilders that took hold during colonial times. Representatives from the original 13 colonies began debating the need for a permanent Navy at the Second Continental Congress in 1775. The two sides of the argument were that the Navy would protect the coasts and that challenging the British Navy (then the largest in the world) would be foolish. While still being debated, George Washington was already buying ships (some with his personal money!) and launched the first in September of 1775, one month before the official establishment of the US Continental Navy. The Continental Navy was dissolved after the Revolutionary War. It was not until the Naval Act, which established a permanent navy, was signed in 1794 that the US would have another Navy force. The first US Navy warships were launched in 1797 to protect merchant ships from the advances of Barbary pirates.
Notable Battles
The US Navy has been instrumental in winning several wars. During the War of 1812, Naval forces kept British ships off of Lake Champlain and Lake Erie thus keeping that territory ruled by the US. Again during the Mexican-American War naval forces played a critical role. They blocked all Mexican ports, captured and burned Mexican ships, and took control of major cities in Baja California peninsula.
The American Civil War saw two iron ships, the USS Monitor, and the CSS Virginia, fight each other for the first time. After the Civil War, the US Navy wouldn’t be of major significance until the reign of the steel industry 20 years later which quickly expanded and improved American fleets. These fleets were later used during World War I when they fought against submarines.
Later, during World War II, the Navy was quite powerful. Japanese forces tried to neutralize this power by attacking Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. But this didn’t stop the Navy, which went on to fight in 6 other battles. By the end of the war, the fleet had been expanded to hundreds of ships and 18 aircraft carriers, among other additions. These advances were continued throughout the Cold War with the Soviet Union.
The US Navy has participated in every major war, battle and operation since the Vietnam War and most recently Operation Iraqi Freedom as part of the US-led “War on Terror”. Today, it is largely involved in missions to support US interests.
Role in US National Defense
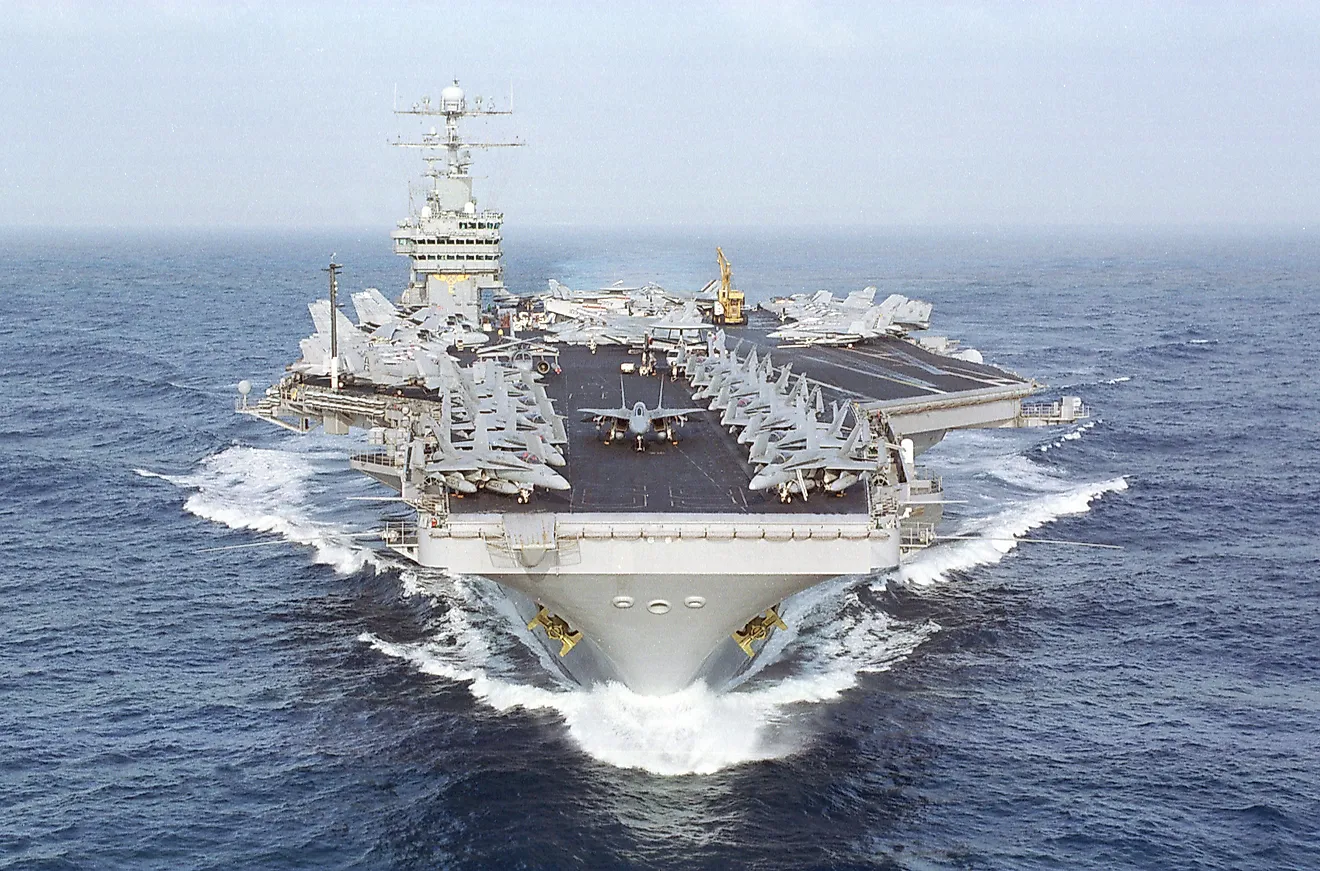
The US Navy is the largest, most advanced naval warfare branch in the world. There are currently 328,194 active duty members and 101,199 in the Navy Reserves. It is the owner of ten aircraft carriers, two others in the Reserves and three more under construction. In addition, the Navy has 272 deployable combat vessels and more than 3,500 aircrafts. This branch works most closely with the US Marine Corps and the US Coast Guard. Since they Navy and the Marines are both focused on sea-based operations, they both fall under the Department of the Navy. The officers and sailors of the US Navy provide medical and religious support to the Marine Corps. The US Coast Guard is a peacetime agency and works under the Department of Homeland Security. US Coast Guard members work aboard Navy vessels as Law Enforcement Detachments.
Major Naval Bases
Some of the major naval bases in the eastern US are located in: Norfolk, Virginia (the Atlantic Fleet); Annapolis, Maryland (US Naval Academy); and Groton, Connecticut (Naval Submarine Base New London). They are also located throughout the western US and Hawaii and include Puget Sound, Washington; Naval Base of San Diego, California; and Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. There are also bases overseas which include: US Fleet Activities Yokosuka in Japan, Guantanamo Bay in Cuba, and the Naval Support Activity in Bahrain.
Famous Personnel
Famous Navy Personnel includes Bob Feller, Cleveland Indians baseball pitcher; Bill Cosby, comedian, and actor; Sean Connery, actor; John Coltrane, jazz sax player; and John F. Kennedy, ex-President of the US.
The United States Navy (USN)
| U.S. Navy | Facts |
| Current Fleet Strength | 328,000 active duty; 102,000 reservists; 430 ships; 3,700 aircraft |
| Headquarters | Pentagon, Arlington, Virginia, U.S.A. |
| Role | Naval and Aerial Warfare |
| Founding | October 13th, 1775 |
| Governing Body | U.S. Department of Defense |