The Culture Of Palau
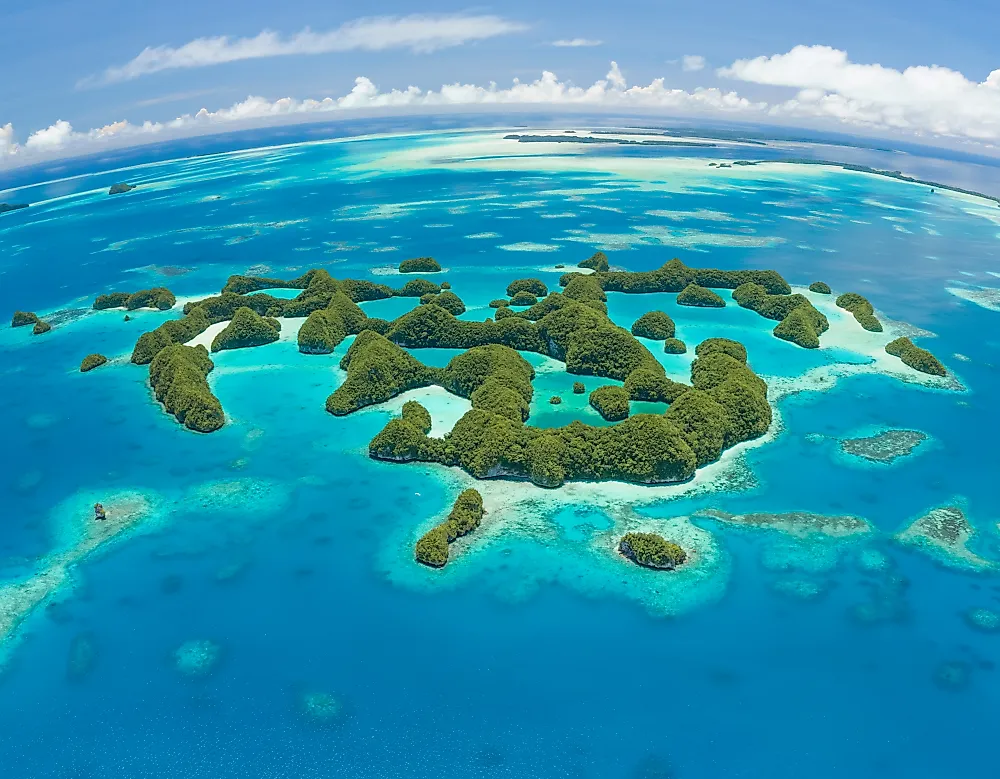

The island country of Palau in the western Pacific Ocean is home to a small population of around 21,516 individuals. Ethnic Palauans (Micronesians with Melanesian and Malayan admixtures) comprise 73% of the country’s population. Ethnic minorities residing in the country include Carolinians, many Asian ethnic groups, Caucasians, and others.
The Palauan language is the most popular language spoken in the country. English is also an official language and is spoken widely. Filipino, Chinese, and other Micronesian languages are spoken by the ethnic minority communities residing in Palau.
Most Palauans are Christians with Roman Catholics and Protestants representing 45.3% and 34.9% of the country’s population.
Cuisine In Palau
The cuisine of Palau features both internal produce like cassava, taro, potato, fish, pork, yam, and important grains, fruits, and vegetables. Western cuisine is growing in popularity, especially in urban areas. Alcoholic drinks made from coconuts and an intoxicating drink produced from the roots of the kava plant are consumed by the locals. Chewing of betel nuts is also a common practice. The dietary preferences of the Palauans often vary between different clans. Each clan has its own food taboos and dietary rules.
Today, rice is a staple of the Palauan diet along with taro and tapioca. Fish in the primary protein source in the diet.
Literature And The Arts
Written literature in Palau is not very well-established. Poetry is the most developed form of literary works of Palau. The country has produced poets of great repute. Oral literature in the form of folk tales and legends, historical accounts, etc., are, however, an important part of the country’s culture.
Palau has a rich tradition of graphic arts. The village meetinghouses are often decorated with low-relief painted carvings. They depict the region’s history and the traditional way of life of the people. Palauan craftsmen engage in shell jewelry making, wood carving, and waving. Paintings of traditional village scenes and natural landscapes are popular themes used in Palauan art.
Performance Arts In Palau
Dancing and singing is an integral part of Palauan culture. It is often the major form of entertainment in Palauan villages. Female dances are elegant and often involve two lines of women dancing to rhythmical tunes. Men’s dances include stick dances and war stances. Village elders recite historical chants. The scene is very different in Palauan cities where contemporary music and dance influenced by Western styles are popular among urban youth.
Sports In Palau
Baseball and football are the two most popular sports played in Palau. The former game was introduced to the country by the Japanese in the 1920s. The national baseball team of Palau is quite successful and won gold medals at several international competitions including the 2007 Pacific Games and the Micronesian Games. The country also has a national football team that is managed by the Palau Soccer Association. The Palau Soccer League is organized by the association. Other popular sports include swimming, fishing, canoeing, etc
Life In Palauan Society
In the traditional Palauan society, gender roles were well defined. Men were expected to execute the labor-intensive tasks like the construction of homes and other buildings, farming, and fishing. Women were engaged in household chores, childcare, shellfish collection, and some farming activities. Both senior males and females played an integral part in the leadership domain. Inheritance was largely matrilineal in nature. Today, however, men and women are both active in wage labor of all sorts, especially in the urban areas. Women in the country now serve as doctors, business managers, lawyers, etc. However, there are still very few women in the country’s government and politics.
Arranged marriages were the norm in Palau in the past. Today, however, individuals usually select their own partners. Marriages between members of the same clan are, however, a strict taboo even today. Divorces and re-marriages are now on the rise in the Palauan society.
Matrilineal practices are strictly followed in a Palauan society, especially in rural areas. Such practices are visible in nearly every aspect of the country’s social life like marriage, funeral, inheritance, and the passage of traditional titles.
The traditional Palauan residence is matrilocal in nature where people descended from one woman and their families reside together as an extended family. However, most families of the present-day are nuclear in nature.
Respect towards the elders is highly valued in the Palauan society. The head of the family is usually the eldest male or female of the household. Their advice is regarded as useful and wise.