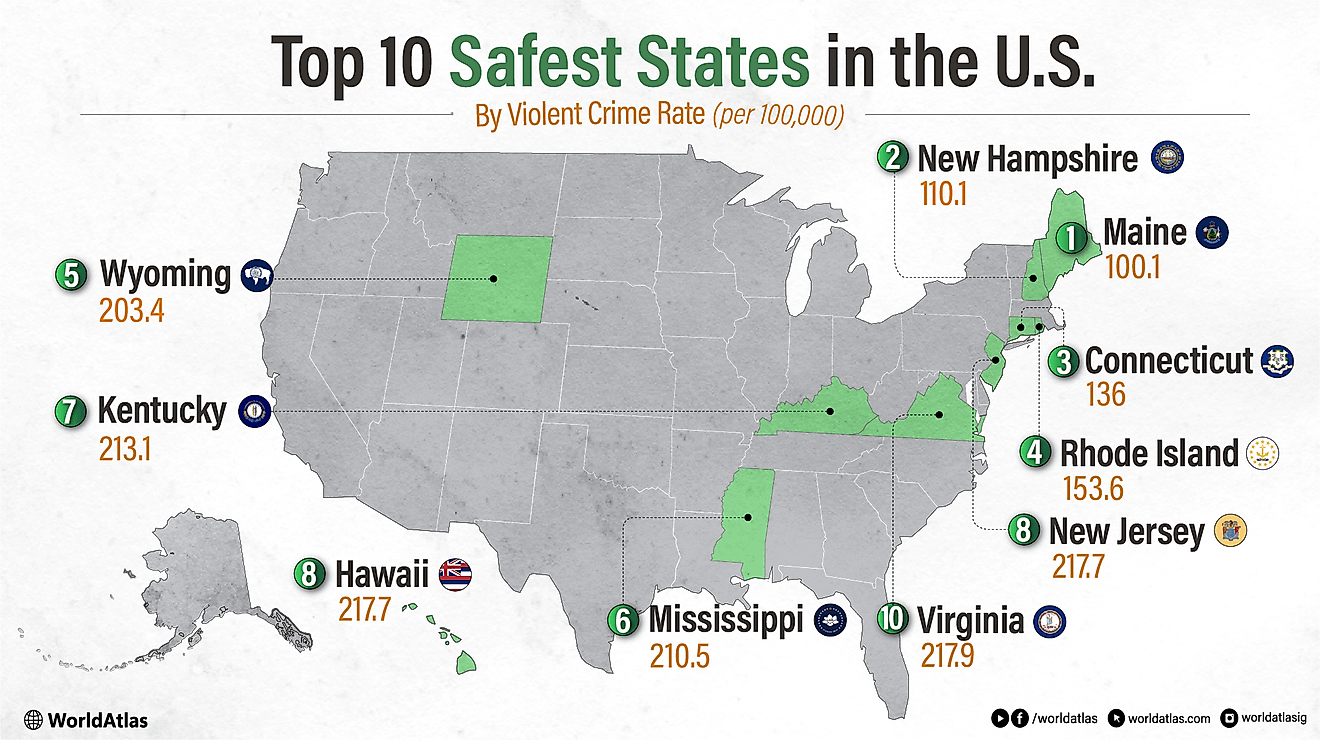
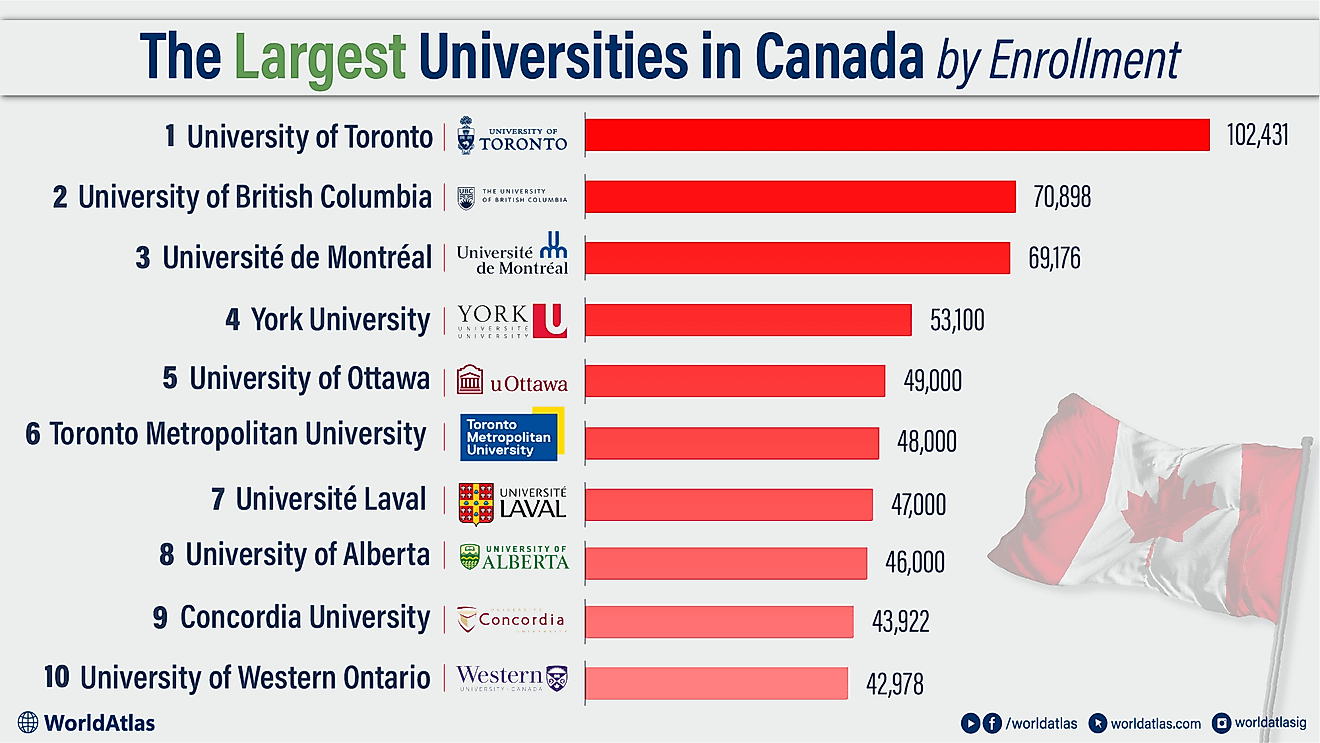
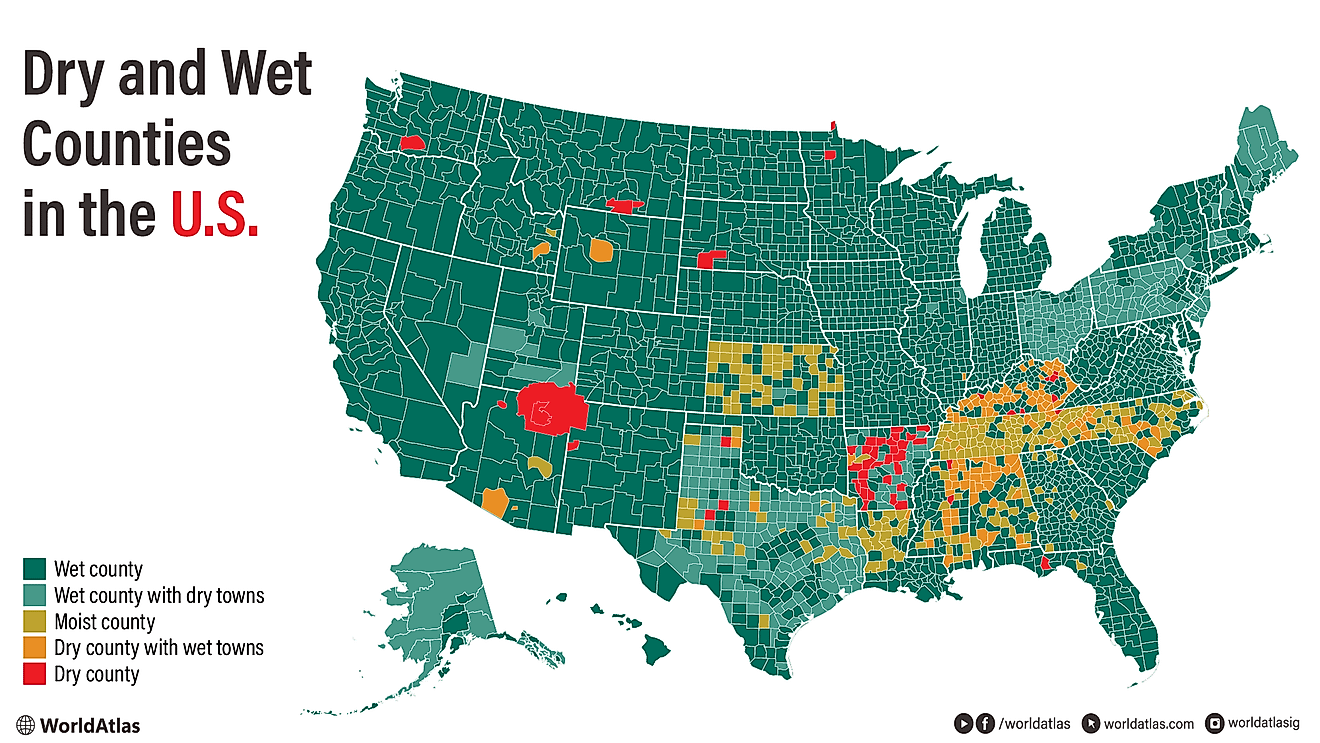
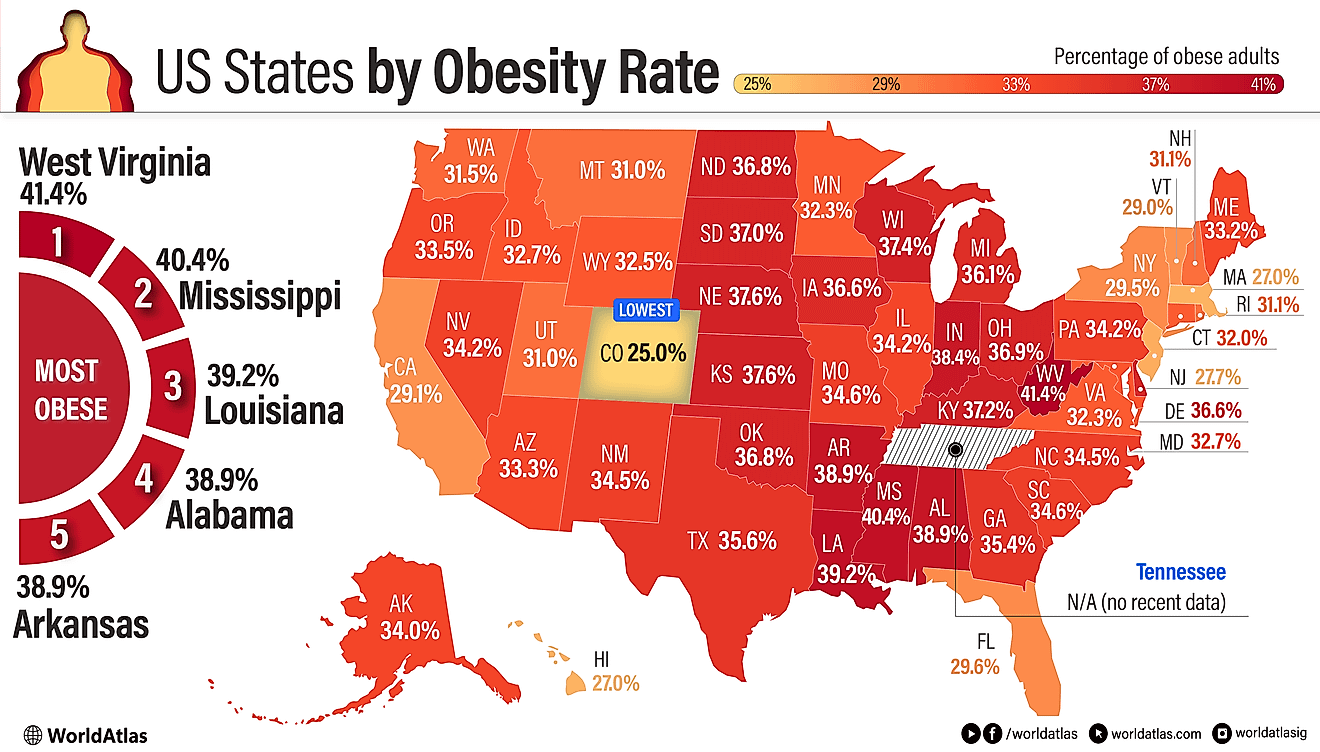
The Culture Of Georgia
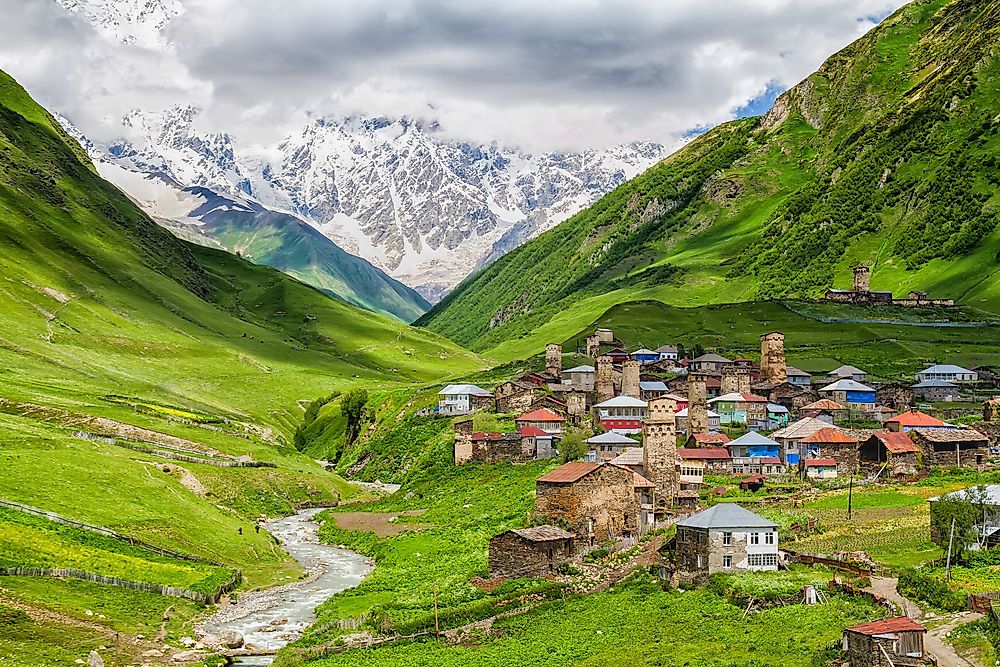

Georgia is a European country with a culture that has evolved over a period of centuries. The country has a strong literary tradition that has helped develop a strong sense of national identity.
Ethnicity, Language, And Religion
Georgia is home to 4,926,087 individuals. 86.8% of the country’s population comprises of ethnic Georgians. Azeri, Armenian, Russian, Ossetian, Yazidi, and Ukrainian are some of the minority ethnic groups residing in Georgia. Georgian is the official language and is spoken by 87.6% of the population. The various minority communities speak their own languages. Orthodox Christianity is the state religion of Georgia and is practiced by 83.4% of the population. 10.7% of the population adheres to Islam.
Cuisine
Georgian cuisine reflects certain influences of Caucasian, Middle Eastern, and Eastern European cuisines. The various historical provinces of the country have their distinct culinary traditions. The Georgian diet is rich in meat dishes but a number of vegetarian dishes from the country are also quite popular. Various spices and herbs are added to the dishes to enhance the taste. A supra is a traditional Georgian feast involving a wide array of dishes accompanied by local wine. Abkhazian, Megrelian, Gurian, Rachian, Adjarian, and Kartlian are some of the regional cuisines of Georgia.
Literature And The Arts
Georgia has a vast body of literature in the Georgian language. The origin of this literature date to the 4th century when Christianity first arrived in the region and the Georgian alphabet was developed. Initial literary works were of religious nature and included translations of works produced in other languages. Over the centuries, Georgian literature flourished and became internationally renowned. The country’s writers and poets explored newer genres of their field and were influenced by the different European literary movements. In the 20th century, however, Georgian literature suffered a setback during the Soviet regime and after the economic downfall following independence. Today, the country’s writers and poets have once more started producing literary works of high quality that are adding to the vast wealth of Georgian literature.
Like literature, Georgia also has a rich tradition of art and craft. The art of the country has evolved for millennia but is still rooted in the archaic and ethnic traditions of the nation. The movement of merchants, travelers, conquerors, and missionaries in and out of Georgia has deeply influenced the Georgian art scene. Roman, Byzantine, Persian, Greek, Anatolian, and Mesopotamian art have all influenced the works of Georgian artists.
Performance Arts
Georgia is known for its rich and vibrant music scene. The country has one of the Christian world’s earliest polyphonic traditions. Georgia also has a thriving folk music tradition that includes at least 15 regional styles. Georgian panpipe, flute, bagpipe, harp, panduri, and chonguri are some of the traditional instruments used by the country’s musicians.
Sport
Historically, Georgia has been known for its physical education. Even the ancient Romans appreciated the training techniques and physical qualities of ancient Georgians. Today, these people continue to excel in sports. The most popular sports in the country are football, basketball, wrestling, weightlifting, judo, and rugby union. Wrestling is a traditional game and the Kakhetian style is adopted by most Georgian wrestlers. Georgia has also produced many elite basketball players who have made a mark internationally.
Society
Women constitute a large part of the country’s workforce. Most women in urban areas are employed. However, top-level government, political, and business jobs have fewer women than men. Women are hardly found in leading positions as religious leaders. However, the government provides Georgian women with several facilities like paid pregnancy leaves and earlier retirements to encourage them to work and earn a living for themselves.
Marriages are generally not arranged by the family but are based on the free will of the couple. Monogamous relationships are the norm and late marriages are more common. Most urban households are nuclear in nature but the grandparents of children might occasionally stay with the family. Extended families are rare but exist in some rural and mountainous areas.
Kinship is considered important and relatives are expected to share the joys and sorrows of life. Attending weddings and funerals and performing other social duties is considered important in Georgian society. Education is highly valued and the country has high literacy levels. The Georgians love to socialize, they interact closely if they share a good bond. It is common to greet strangers in the countryside. Shaking hands is a common form of greeting. Kissing on the cheeks is also common.