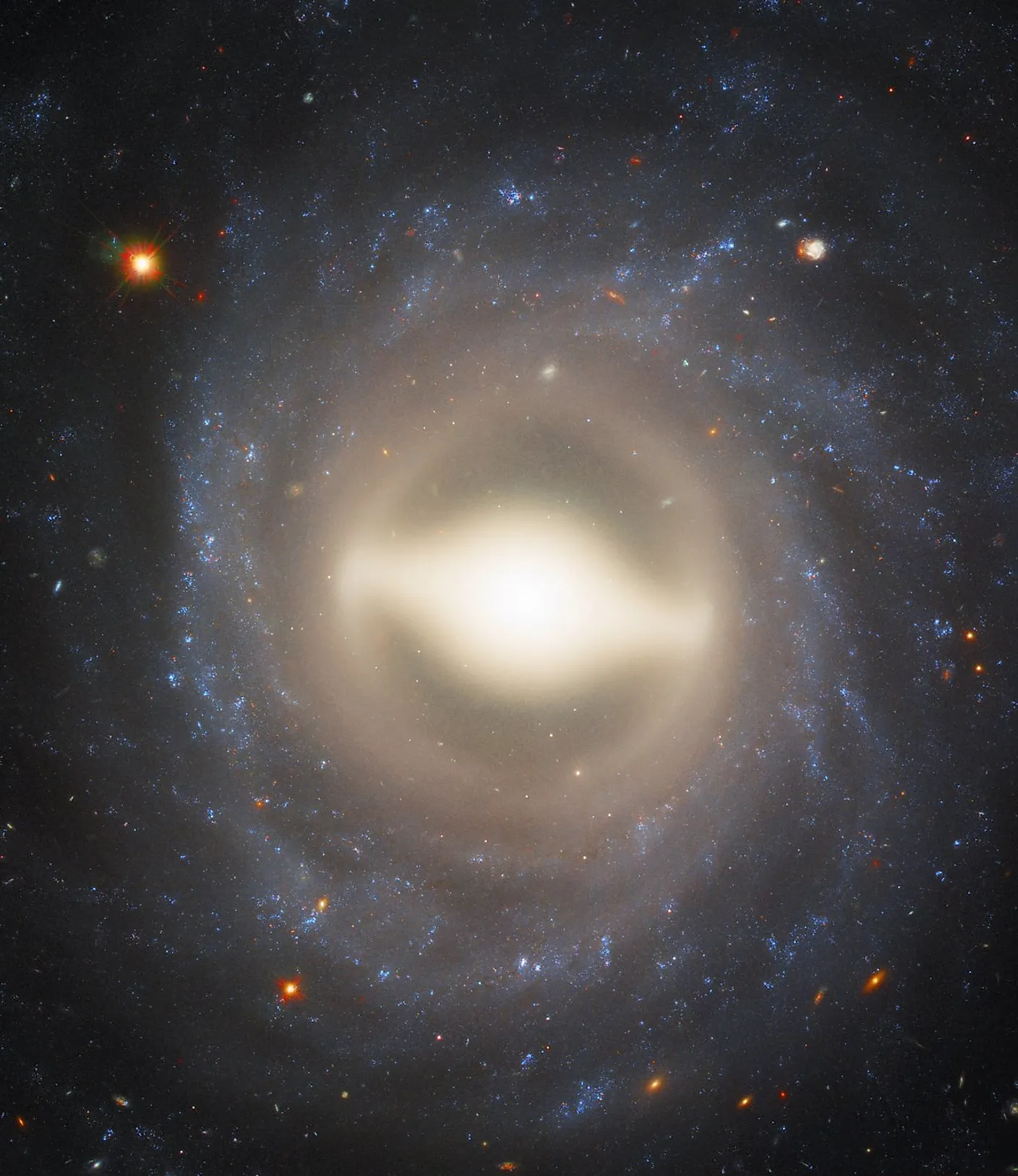
What Is A Light Year?
The distances between objects in space are so vast that everyday measurements such as kilometres or miles become too small to be reasonably used. Astronomers use light years as a measurement of distance in space. A light year is a simple form of measurement, being the distance light travels in one year of time. Although it is called a light year, it’s important to note that it is a measurement of distance and not time. Light is the fastest known thing in the universe, having a speed of 186,000 miles per second (300,000 kilometres per second). One light year is equivalent to 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometres).
Distance And Time
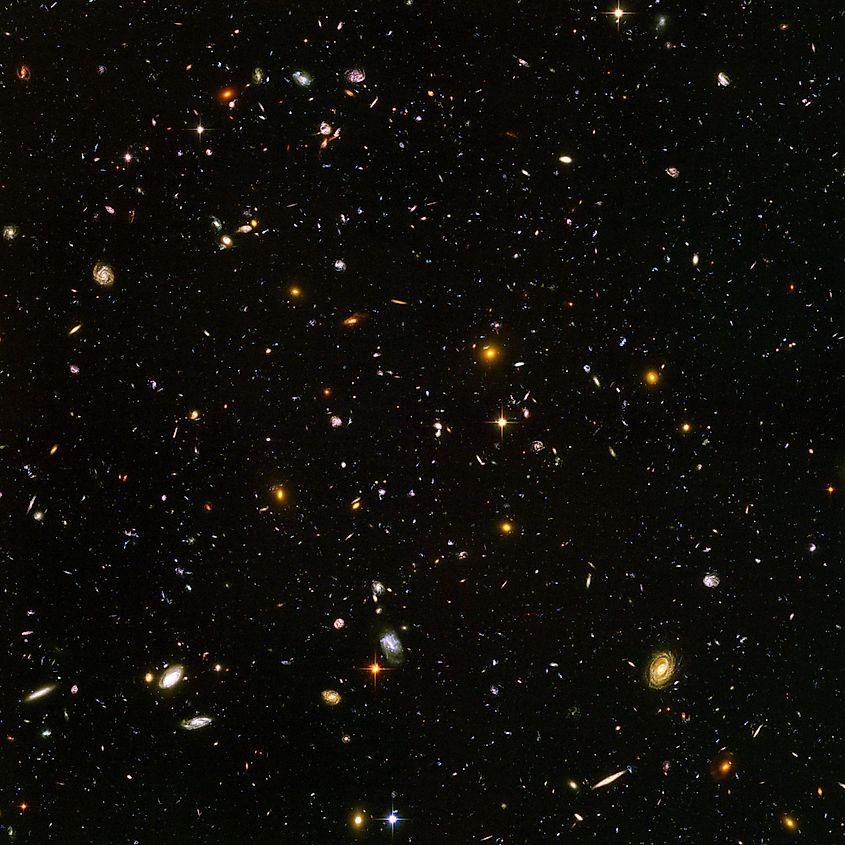

Although light is the fastest thing in the universe, its speed is still finite. It takes time for light emitted by one object to reach another. Whenever we look out into space, we are actually seeing through time itself. For example, light from the sun takes about eight minutes to reach the Earth. Thus, when we look at the sun, we are seeing it as it was eight minutes ago. If you were on Neptune, you would see the sun as it was four hours ago. For objects that are even farther away from us, we can see even further back in time. The nearest star to our sun is Proxima Centauri at 4.2 light years away, and so when we look at it through a telescope, we see it as it was 4.2 years ago. This simple yet profound fact about our universe means we can see the evolution of space through time. The farthest known galaxies are over 12 billion light years away, and so we can see the universe as it was 12 billion years ago. We can see objects that emitted their light many billions of years before our solar system even formed. The farthest we can physically see is the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR). The CMBR is the oldest form of light in the universe, having formed a mere 380,000 years after the Big Bang. That means that we can see nearly 13.8 billion years into the past, seeing the universe before the first stars and galaxies even formed.
If you were to travel away from the solar system, you could look back and see our solar system as it appeared in the past. For example, if you were to travel to a planet 6,000 light years away, you could look back and see the Earth as it was 6,000 years ago. If you had a powerful enough telescope that could resolve the Earth’s surface, you could witness the birth of civilization. Or if you travelled to a galaxy 4.5 billion light years away, you could look back and see our solar system forming.