Fun Facts About The Ancient Egyptians

- Ancient Egypt was one of the first civilizations with a written language.
- Egyptian women were considered equal to men in every aspect except occupation.
- The Ancient Egyptians invented the first breath mints.
- Many of their inventions are still in use today.
Egypt was one of the greatest civilizations in Ancient history. It had a sophisticated society long before many other parts of the world. Some of their earlier inventions are things that we still use today, such as high-heels, surgical instruments, toothpaste, and the 365-day calendar to name a few. Here are some fun facts about Ancient Egypt.
1. They Were One Of The First Civilizations To Read And Write
Credit: Shutterstock image by matrioshka
Along with the Mesopotamians, the Egyptians were one of the first civilizations to invent reading and writing. They began using pictograms as early as 6000 BCE, and eventually added other elements, such as alphabet-like characters to denote certain sounds. Egyptian hieroglyphs can be found in many of the country’s Ancient structures.
2. Signed The Earliest Treaty In History
The treaty of Kadesh, between Hittite King Hattusilis III and pharaoh Ramses II, is the earliest known peace agreement in history. Made in 1269 B.C between Ancient Egyptians and Ancient Hittites, with whom they were at war for many years. It not only brought peace between the two civilizations, but it also forged an alliance between the two, with both parties promising to help each other in the event of an attack. Some call it an Ancient form of collective security.
3. They Loved Board Games
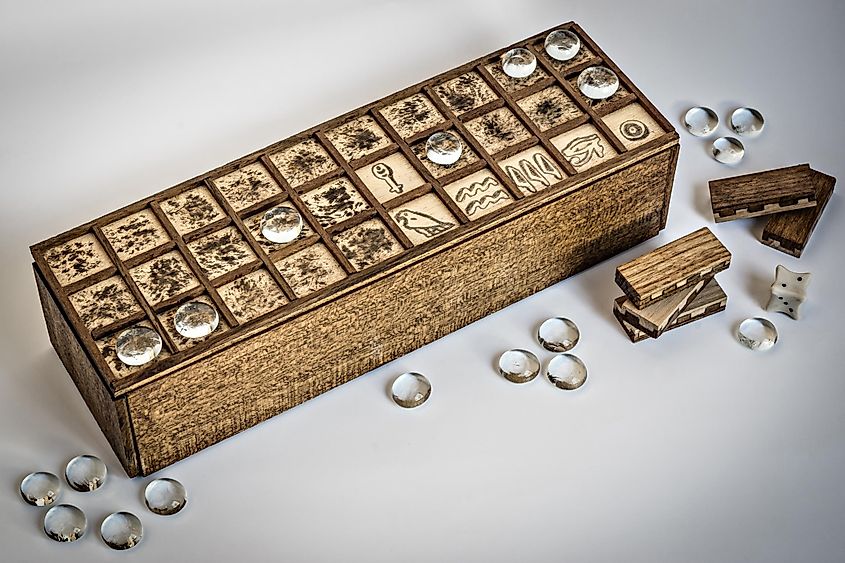

Credit: Image by Metropolitan Museum of Art
Long before Monopoly ever saw the light of day, Ancient Egyptians enjoyed their own leisure games. Archeologists believe Senet, a forerunner to Backgammon, to be one of the earliest know board games beloved by Queen Nefertiti and boy-king Tutankhamun. Experts postulate the Ancient Egyptians believed ceremonial games offered them a glimpse into the afterlife. Senet was thought to reveal future obstacles.
4. The Held The Very First Labor Strike
The first recorded labor strike in history happened in 1159 BC at the site of the royal necropolis of King Ramses III. Like other civilizations of the time, Ancient Egypt employed slave labor, however, some workers were compensated. When they were not paid their grains as promised, the tomb-builders set down their tools and refused to continue the work. They marched down toward the city shouting “We are hungry” and later staged the very first sit-in.
4. Slaves Did Not Build The Pyramids
Anyone familiar with the Biblical story of Exodus - which recounts the Israelites deliverance from slavery- may think that slaves built the pyramids, however, recent discoveries suggest that notion was false. Egyptologists believe that paid laborers, issued from poor families, were the ones responsible for such treasures as the Sphinx and the Great Pyramid of Giza. The builders were greatly respected and upon their deaths, many were accorded the privilege of being buried in the tombs near the sacred pyramids of their pharaohs.
6. Women Had Unprecedented Rights And Freedoms

Credit: Shutterstock image by leoks
While in most of the Ancient world women were often treated as little more than property, Egyptian women were considered equal to men in every area except occupation. While still a patriarchal civilization, women had the right to buy and sell property, make wills, enter into legal contracts, and serve on juries. They could also divorce and remarry, and in the event of a divorce, were entitled to compensation. Women were held in great esteem in Ancient Egypt, something that is apparent in everything from their religious beliefs to social customs.
7. They Had Household Pets
Egyptians saw animals as incarnations of gods and were the first civilization to have pets. While dogs were revered for their ability to hunt and protect, cats were believed to be magical, capable of bringing good fortune to their household. Wealthy families would often dress them up in jewels and feed them delicious treats. Once they died, many pets, especially cats, were often mummified and buried with their owners who would shave their eyebrows as a sign of bereavement.
8. They Hated Being Hairy
In Ancient Egyptian culture, being hairy was considered a mark of inferior social status, while a shaved head was a sign of nobility. Egyptian priests would even shave their entire bodies every three days. The civilization is credited with many cosmetic experiments, such as wigs and makeup, as well as a primitive tool used for shaving and the very first waxing paste: a mixture of sugar and beeswax that is still used to this day.
9. They Invented Breath Mints
While specialized medicine existed in Ancient Egypt, and historical accounts mention doctors trained in many medical fields, there were no dentists. Their oral hygiene was so poor, in the young as in the old, that they often suffered from tooth decay which resulted in foul breath. To mask this, Ancient Egyptians invented the first mints: a combination of frankincense, myrrh, and cinnamon boiled with honey and shaped into pills.
10. They Revered Over 2 000 Deities

Credit: Shutterstock image by tan_tan
For all Ancient people, the world was a mystery. Because much of what they experienced was unclear, they worshiped thousands of different gods and goddesses, to gain an understanding of their everyday life and death. Some deities were considered more important than others, often representing a specific region, role, or ritual and remain well-known even to this day. The goddess Isis, for example, the mother of all pharaohs, became one of the most important divinities of the Ancient times, transcending civilizations. Her worship was widespread; from the Roman Empire all the way to England and Afghanistan, she is still revered in pagan religious rituals across the world.