What Is The Rare Earth Hypothesis?
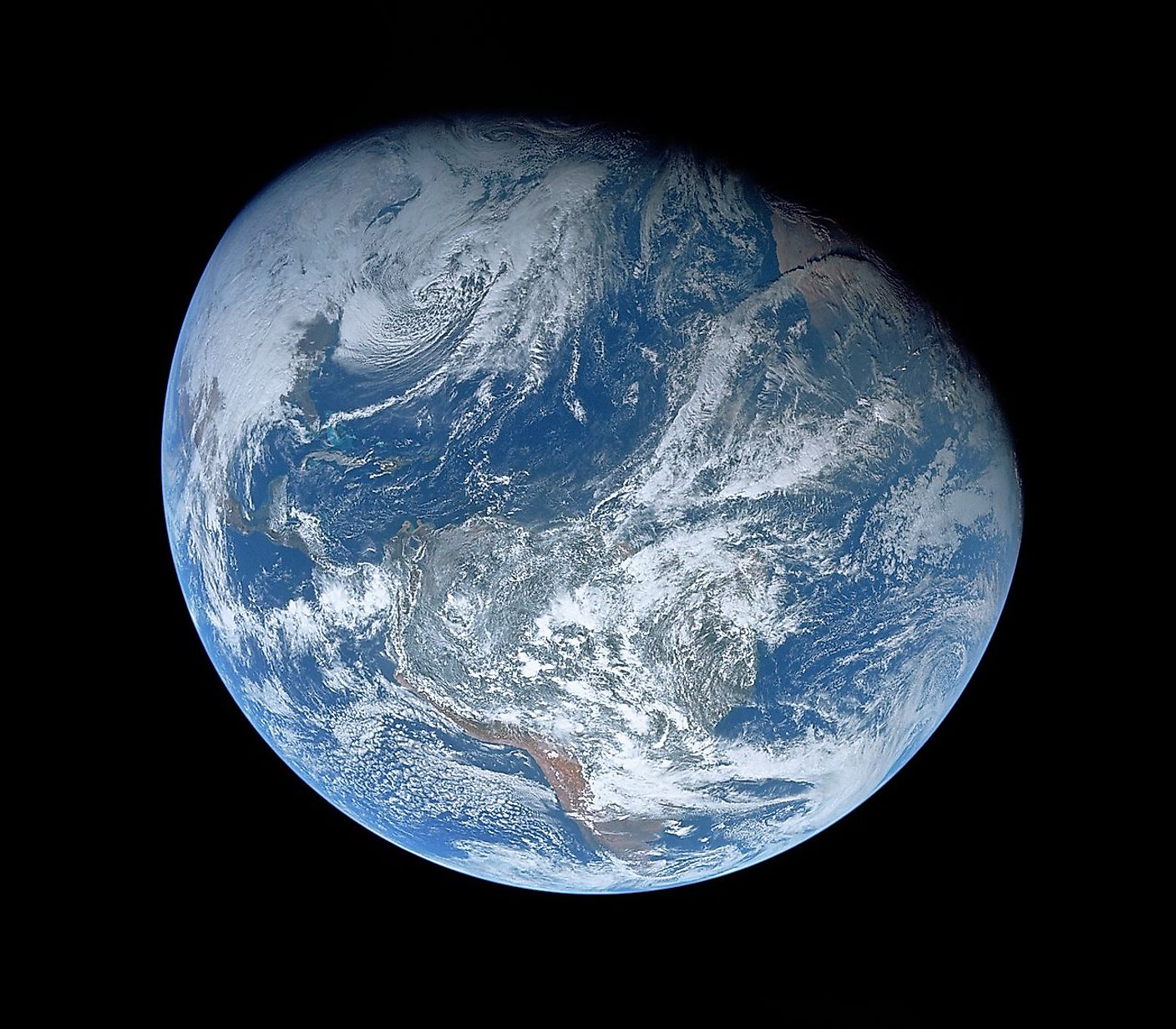
Earth is the only world we know of where life has not only arisen, but also evolved into millions of complex forms. Biological organisms are the most complex known systems in the universe. Even bacteria are vastly more complex than the largest galaxies. In the last 30 years, astronomers have uncovered thousands of planets around other stars, a couple dozen of which are Earth-sized worlds that orbit in the habitable zone of their stars. Based on the number of known Earth-like planets, astronomers estimate that our galaxy alone is home to tens of billions of rocky planets that orbit in the habitable zone. Life may be complex, yet with so many potential places it can exist, it seems very unlikely that Earth is the only planet inhabited by life. However, although it is statistically unlikely that we are alone in the cosmos, there is one hypothesis that claims that the existence of life is exceedingly rare. This hypothesis is known as the Rare Earth Hypothesis.
Is The Earth Rare?
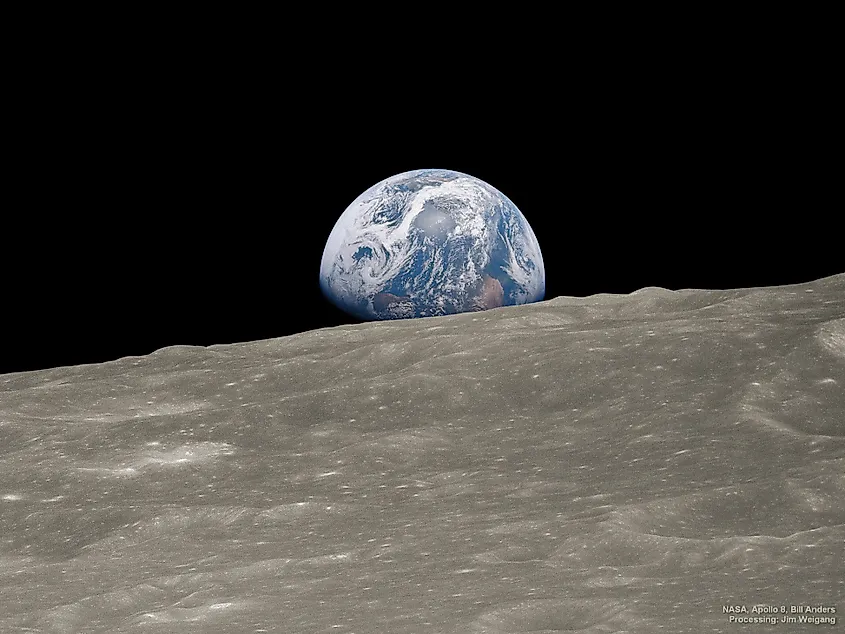

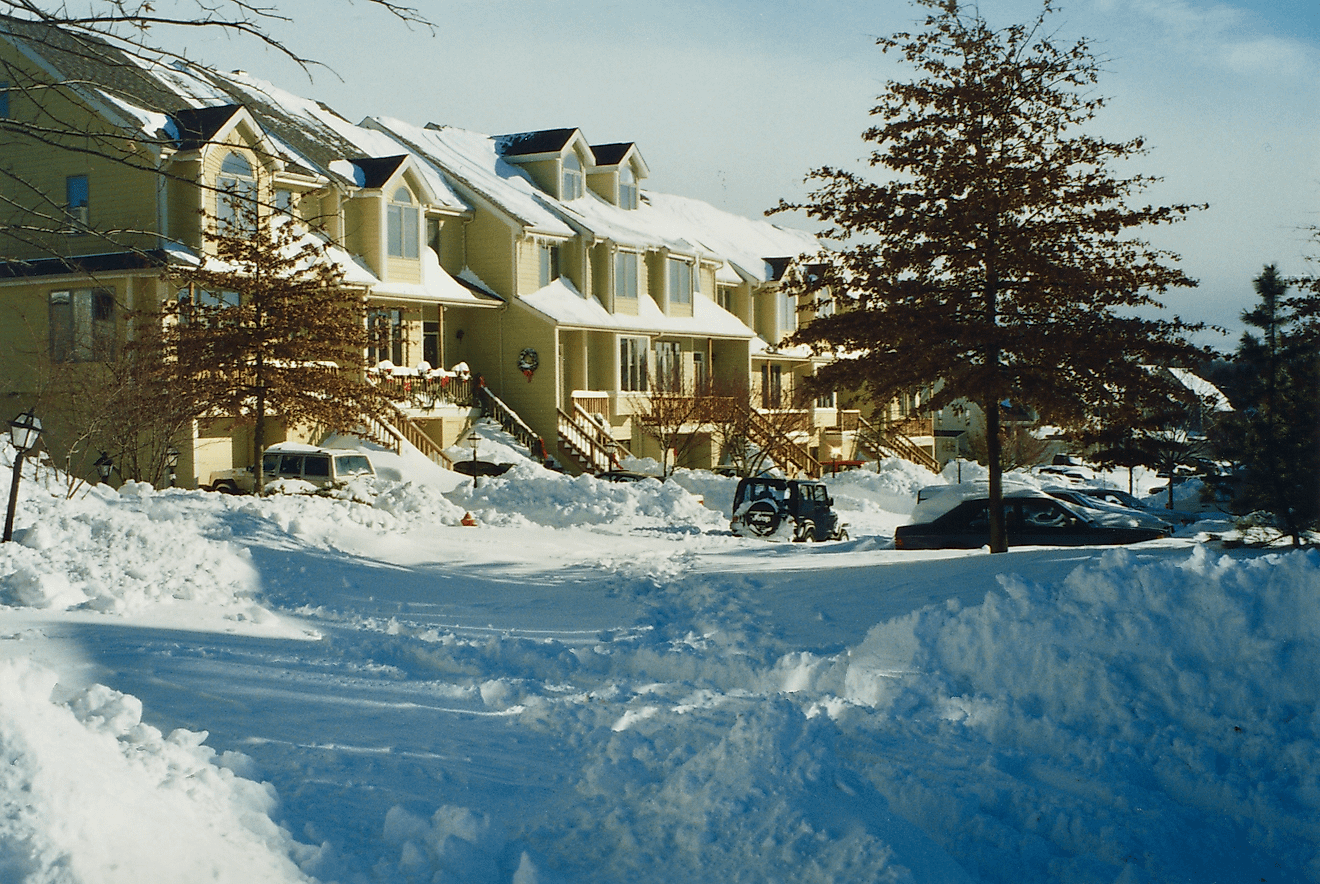
The main argument of the Rare Earth Hypothesis is that the conditions on Earth that allow for the existence and flourishment of life are extremely rare in the cosmos. A large number of factors needed to be met in order for life to not only arise, but also evolve into complex organisms. The Earth needed to orbit the sun at just the right distance so that liquid water could form on the surface, a stable atmosphere with just the right chemicals was needed, and surface temperatures must remain stable for extended periods of time. Furthermore, the hypothesis lists other factors that possibly helped with the evolution of life, including the solar system’s distance from the Milky Way’s core, the size of our moon, the interaction between all the planets in our solar system, and geologic forces on Earth. Without any of these factors, it is entirely possible that life on Earth would have never evolved beyond single celled organisms.
The main argument of the Rare Earth Hypothesis is that all of the listed factors will be exceedingly rare in the cosmos. It argues that the probability that all these factors will be met is so rare that complex life may never evolve on the majority of habitable worlds. It is important to note that simple forms of life, such as bacteria, may still be very common, yet conditions may never allow them to evolve into more complex forms.
Counterpoints
The Rare Earth Hypothesis is a fairly contentious hypothesis in astronomy. Although it makes several good arguments, many argue that they are too biased towards Earth life. Since Earth life is the only form of life we know of, any assumptions we have about alien life are going to be biased based on what we know. Life on Earth may have required many of the factors listed by the Rare Earth Hypothesis, yet they may not be a requirement for life in general. Furthermore, many of the factors in the Rare Earth Hypothesis may not be true at all. For example, astronomers are finding that rocky planets orbiting in habitable zones are quite common in our galaxy. Other factors, such as the size of our moon and the interaction between the planets, may also not be necessary for the evolution of complex life. Life on Earth has adapted to the conditions our world experiences over the course of many billions of years. On another planet that has different conditions, life may do the same.