How Many Earth-Like Planets Are There In The Milky Way?

- Astronomers have identified over 4,000 planets around other stars
- The most common types of planets in our galaxy are super-Earths and mini-Neptunes
- Astronomers estimate there is anywhere from 300-million to 40-billion Earth-like planets in the Milky Way
The Earth is generally viewed as a unique planet, and in terms of all the planets in our solar system, it most definitely is. However, it may not be as unique as we perceive it when considering the sheer number of planets in the Milky Way galaxy. In 1997, astronomers confirmed the existence of the first planet to be discovered around another star, called an exoplanet. Since that time, astronomers have confirmed the existence of thousands of other exoplanets. It is now believed that planets are a natural part of star formation, and every star is likely accompanied by one or more planets. Most of these planets are probably far different from the Earth, yet astronomers estimate that there are likely billions of Earth-like worlds that could potentially support life. How many Earth-like planets are there in our galaxy?
Finding Earth-Like Planets

There are currently two methods used for finding planets around other stars: the radial velocity method and the transit method. The first method relies on observing the gravitational influence between a star and a planet. By measuring a star’s movement, astronomers can determine whether or not a planet is pulling on the star. The second method requires astronomers to observe the amount of a star a light emits, and see whether or not any of that light is blocked by a planet passing in front of the star. These methods have proven very reliable in finding planets, yet they do have some bias. Larger, more massive planets are easier to detect, and so they inevitably make up the majority of known planets.
Most planets found around other stars have been detected with NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope. Kepler uses the transit method for detecting planets, and over its lifetime, it confirmed the existence of over 4,000 planets. Data from Kepler suggests that the most common type of planet in the Milky Way are either super-Earths or mini-Neptunes. This is fairly promising as it is possible for super-Earths to become habitable.
How Many Earth-Like Worlds Have Been Found?
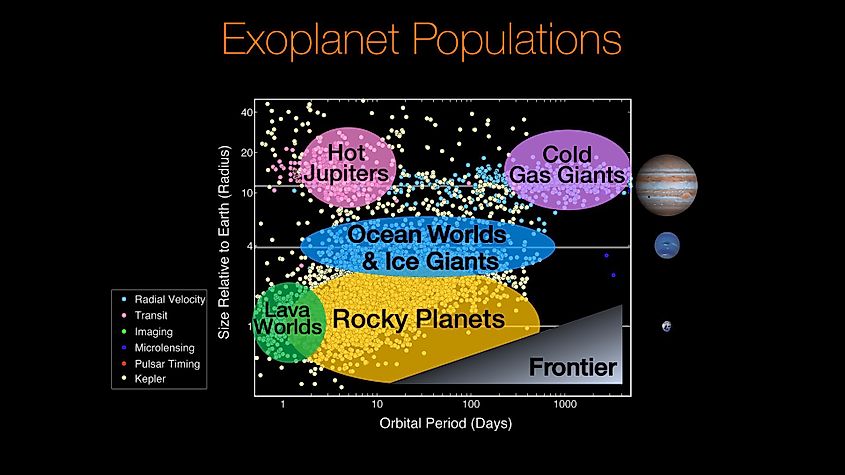
It is important to define what is meant by Earth-like. An Earth-like planet is not necessarily known to be habitable. Rather, it is simply a planet that has a size, mass, and composition similar to our home planet. Furthermore, it must also orbit within its star’s habitable zone, as the Earth finds itself near the middle of the sun's habitable zone. Since Earth is the only world we know of to have life, it makes sense to search for similar planets around other stars. To date, scientists have discovered 55 planets that could be Earth-like. In comparison to the over 4,000 known planets, 55 seems small. Earth-like planets are not going to be as common as other types of planets as too many conditions need to be met for them to exist. However, it is important to note that scientists have only observed a fraction of the number of stars in the Milky Way. Earth-like worlds may not be as common as other planets, but the sheer number of stars in the Milky Way suggests there could still be a vast number of potentially habitable worlds. Based on data from Kepler and other planet-hunting telescopes, astronomers estimate there could be anywhere from 300-million to upwards of 40-billion Earth-like worlds in the Milky Way. Even if just a fraction of those planets developed the conditions necessary for the existence of life, there would still be millions of planets in our galaxy alone that are home to living things.
Another interesting fact to note is that this data only represents what we know about the Milky Way Galaxy. The universe is home to an estimated 200-billion galaxies, most of which contain a hundred billion stars or more. If the number of potentially Earth-like worlds in our galaxy is true for other galaxies, it means that the universe could be home to hundreds of billions to even trillions of potentially habitable worlds.