What Color Is The Sky On Each Planet?
Here on Earth, we are accustomed to the bright blue sky of our world. Every planet in our solar system has its own unique color of sky, yet some are similar to each other. What determines the color of a planet’s sky is both its chemical composition and the angle at which sunlight hits the atmosphere. What color is the sky on each planet?
Mercury - Black
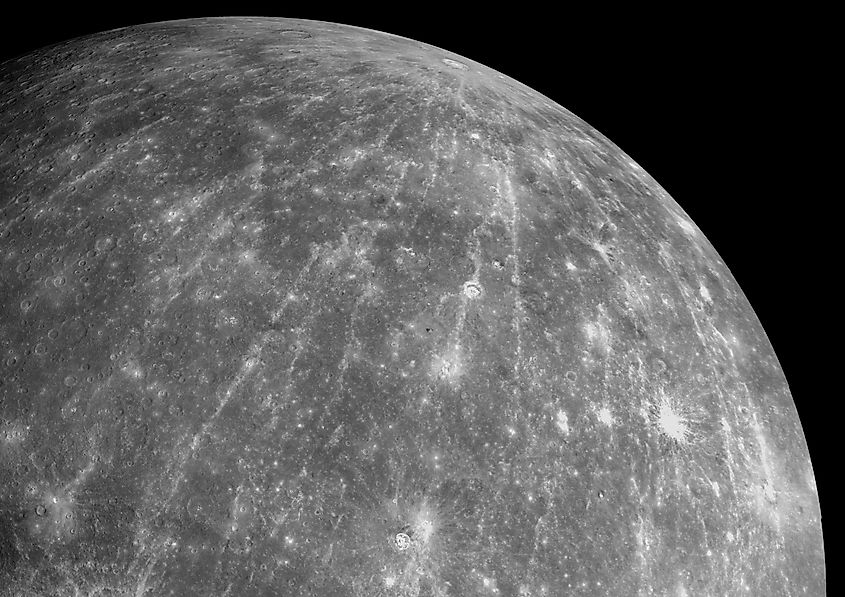

Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system and the closest planet to the sun. Its low surface gravity and proximity to the sun makes it nearly impossible for Mercury to hold onto a significant atmosphere. Like the moon, the atmosphere of Mercury is negligible, and so there are no chemicals that can capture and spread light from the sun. Thus, the sky on Mercury would not have a distinct color, and the sky would simply appear black.
Venus - Orange
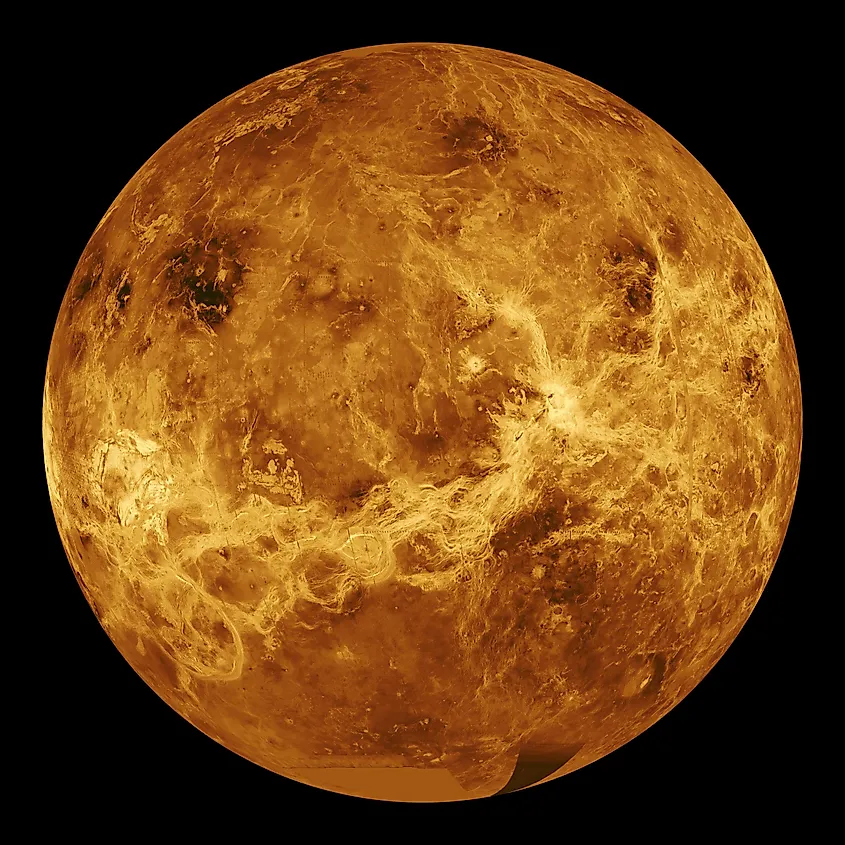

Venus is the closest planet to the Earth and the second closest planet to the sun. Although Venus is closer to the sun than the Earth, its surface actually receives far less sunlight than Earth’s does. This is due to the thickness of the Venusian atmosphere, which is around 90 times denser than Earth’s. Sunlight cannot penetrate the atmosphere on Venus as easily as it does on Earth’s, and so the lack of sunlight makes the sky on Venus look like an eternal sunset or sunrise.
Earth - Blue
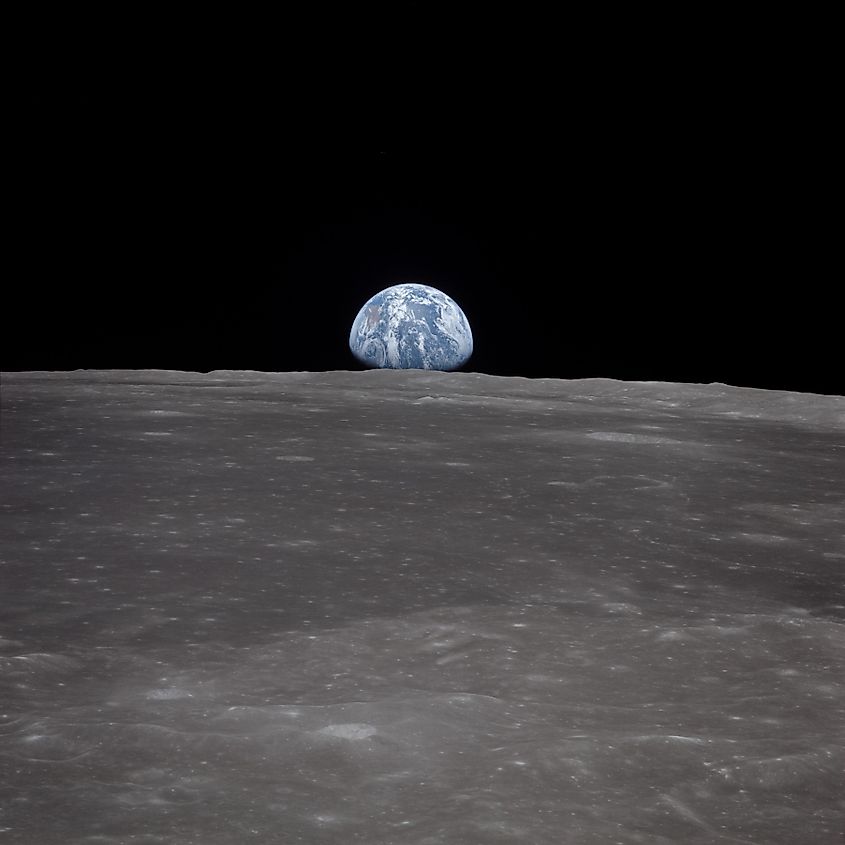

Our home world, Earth, is widely called the “Blue Planet”. This is because the skies above are a brilliant, bright blue. Bodies of water, such as the oceans, reflect this blue color and make our entire world look blue from space. The reason why the sky is blue is due to the scattering of blue light in our atmosphere, caused by a combination of chemicals and the angle at which sunlight hits our atmosphere.
Mars - Red
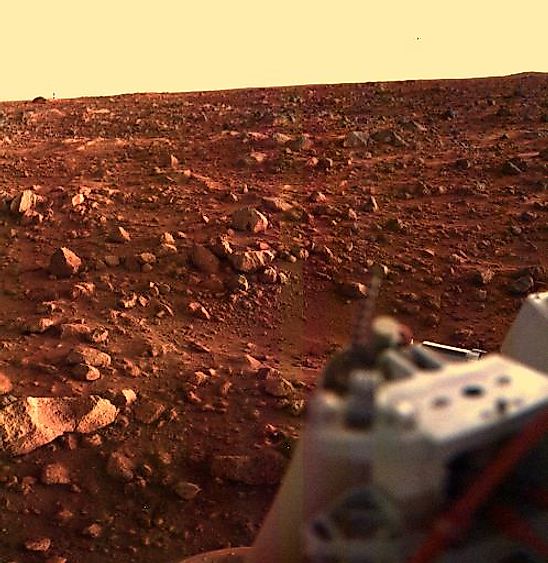

Earth is the Blue Planet, and Mars is the Red Planet. Both the surface and sky of Mars are red, and there is no coincidence why they are the same color. The surface itself is red due to the oxidation of Martian rocks. In other words, Mars is a rusty world. Furthermore, Mars experiences frequent dust storms, some of which can grow to cover the entire planet. These dust storms whip up dust particles and spread them throughout the atmosphere. Combine this with a low surface gravity, and red dust particles can remain in the atmosphere for extended periods of time. It’s these red dust particles that cause Mars to have a red sky.
Jupiter - Dim Blue
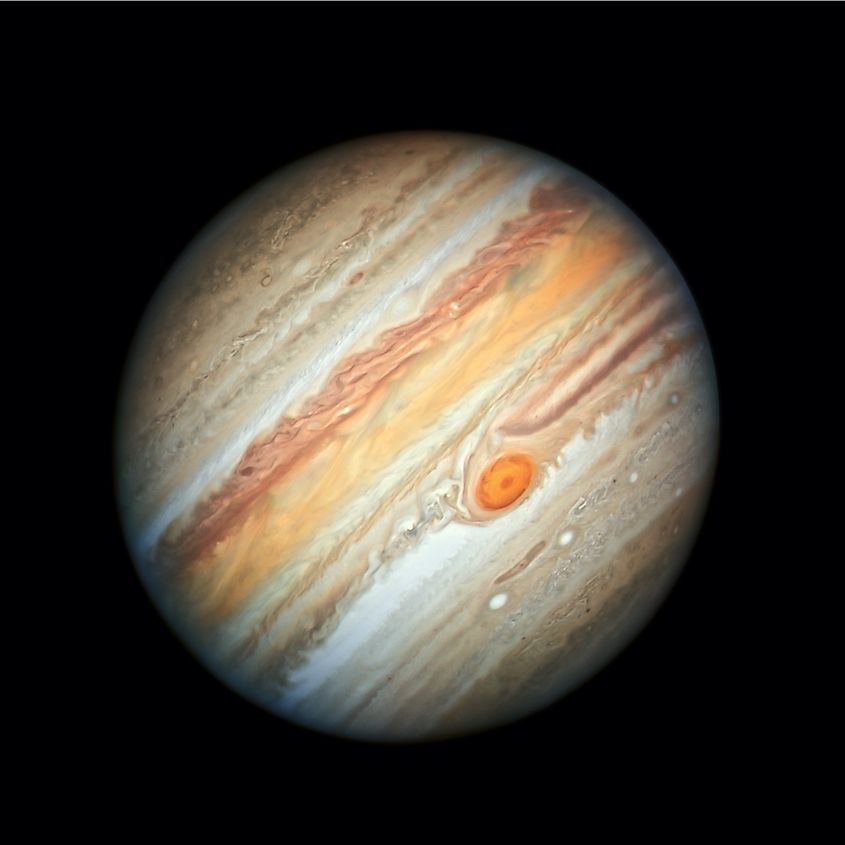

Like Earth, Jupiter is also believed to have a blue sky, although it is much dimmer than on Earth. This is because Jupiter receives far less sunlight than Earth does, and so the sky would appear much dimmer. Although the exact cause of Jupiter’s blue skies remains unknown, one of the factors is likely similar to what happens on Earth, wherein blue light from the sun is scattered in the atmosphere.
Saturn - Yellow
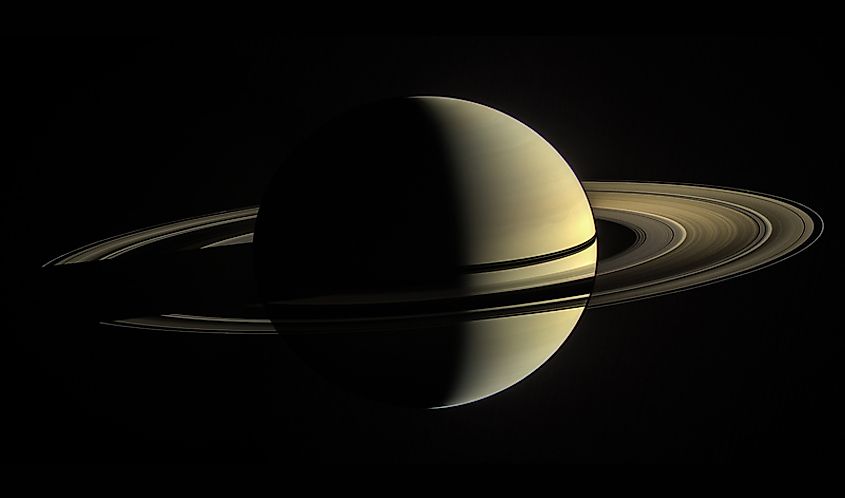

Jupiter and Saturn have a lot in common, and no two planets in our solar system are probably as similar to each other as Jupiter and Saturn. The color of their sky, however, is something that is different between them. While Jupiter is believed to have blue skies, Saturn’s are a yellowish color. The yellow color is likely due to the presence of ammonia crystals in the upper atmosphere, which scatter incoming yellow light across the sky.
Uranus - Cyan
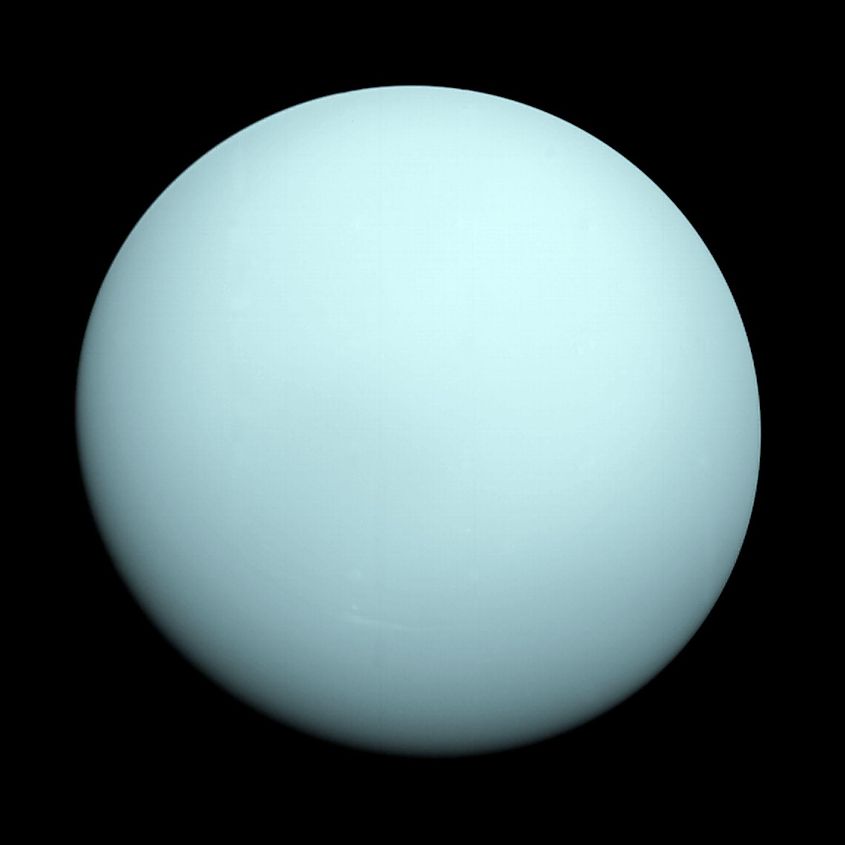

At first glance, Uranus is a rather dull world. Compared to the rings of Saturn or the vast storms of Jupiter, Uranus appears rather featureless. This likely has to do with a kind of haze in the upper atmosphere of Uranus that obscures any detail. Interestingly, the sky of Uranus is believed to be cyan in color, a result of methane in the atmosphere scattering both blue and green light.
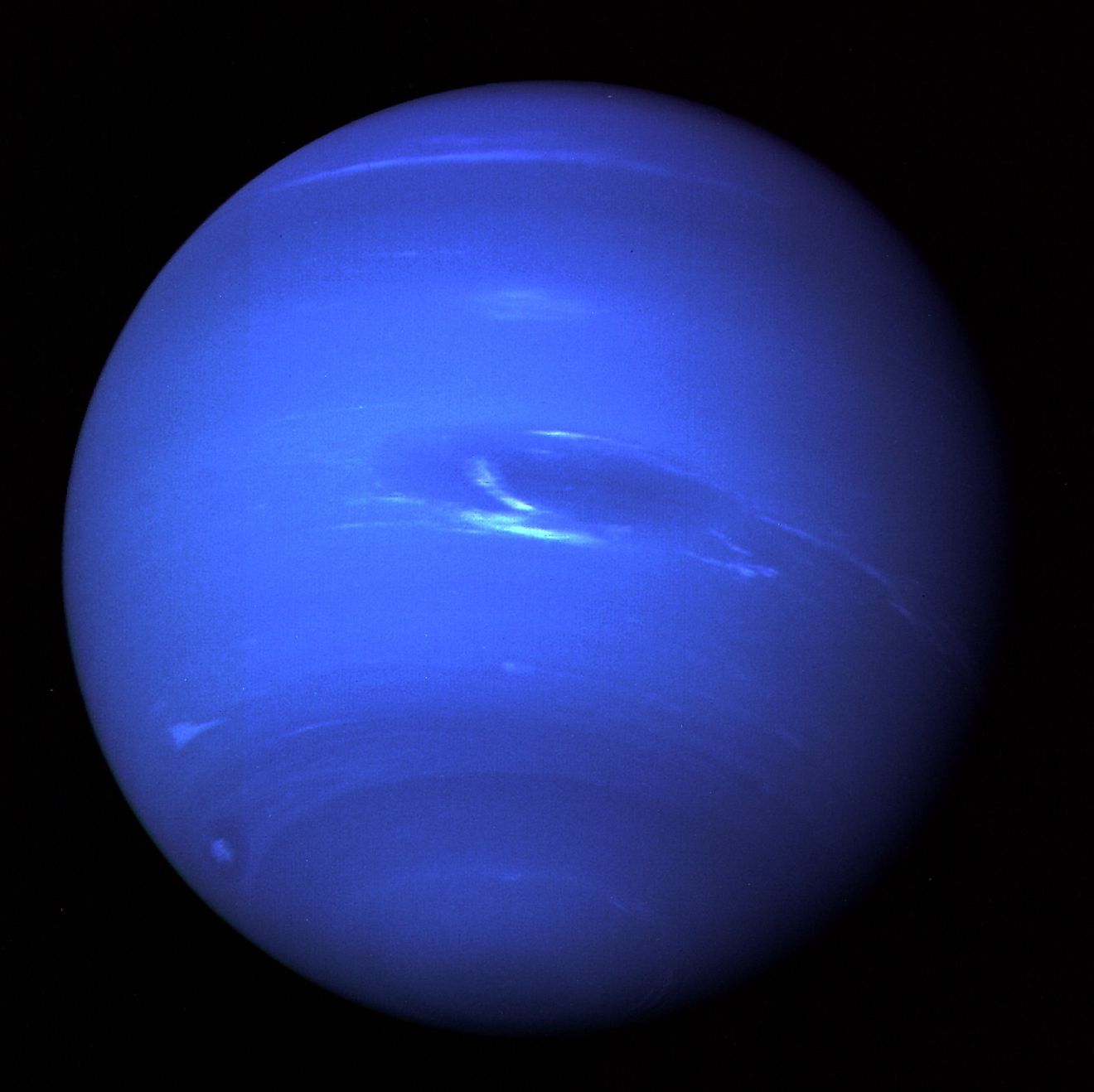
Neptune - Blue
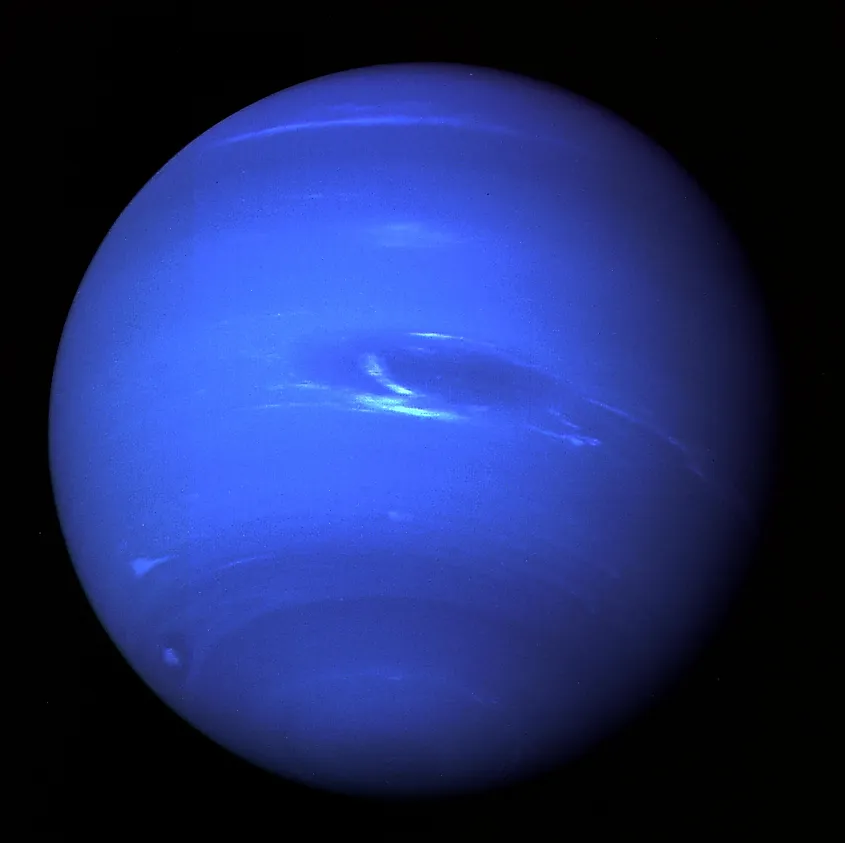

The sky on Neptune is probably the most similar in appearance to Earth’s sky. However, this is actually rather strange given that the sky on Uranus is more green. This is because both planets are very similar in composition, and methane is believed to be the culprit behind the color of both planets. How can methane be the reason for the color of both planets when both have a different color of sky? The exact reason remains unknown, yet it could be due to the higher density of Uranus’ upper atmosphere and the extreme storms on Neptune.
Color of the Sky on Each Planet
| Planet | Sky Color |
|---|---|
|
Mercury |
Black |
|
Venus |
Orange |
|
Earth |
Blue |
|
Mars |
Red |
|
Jupiter |
Blue |
|
Saturn |
Yellow |
|
Uranus |
Cyan |
|
Neptune |
Blue |