How Far Is The Moon From Earth?
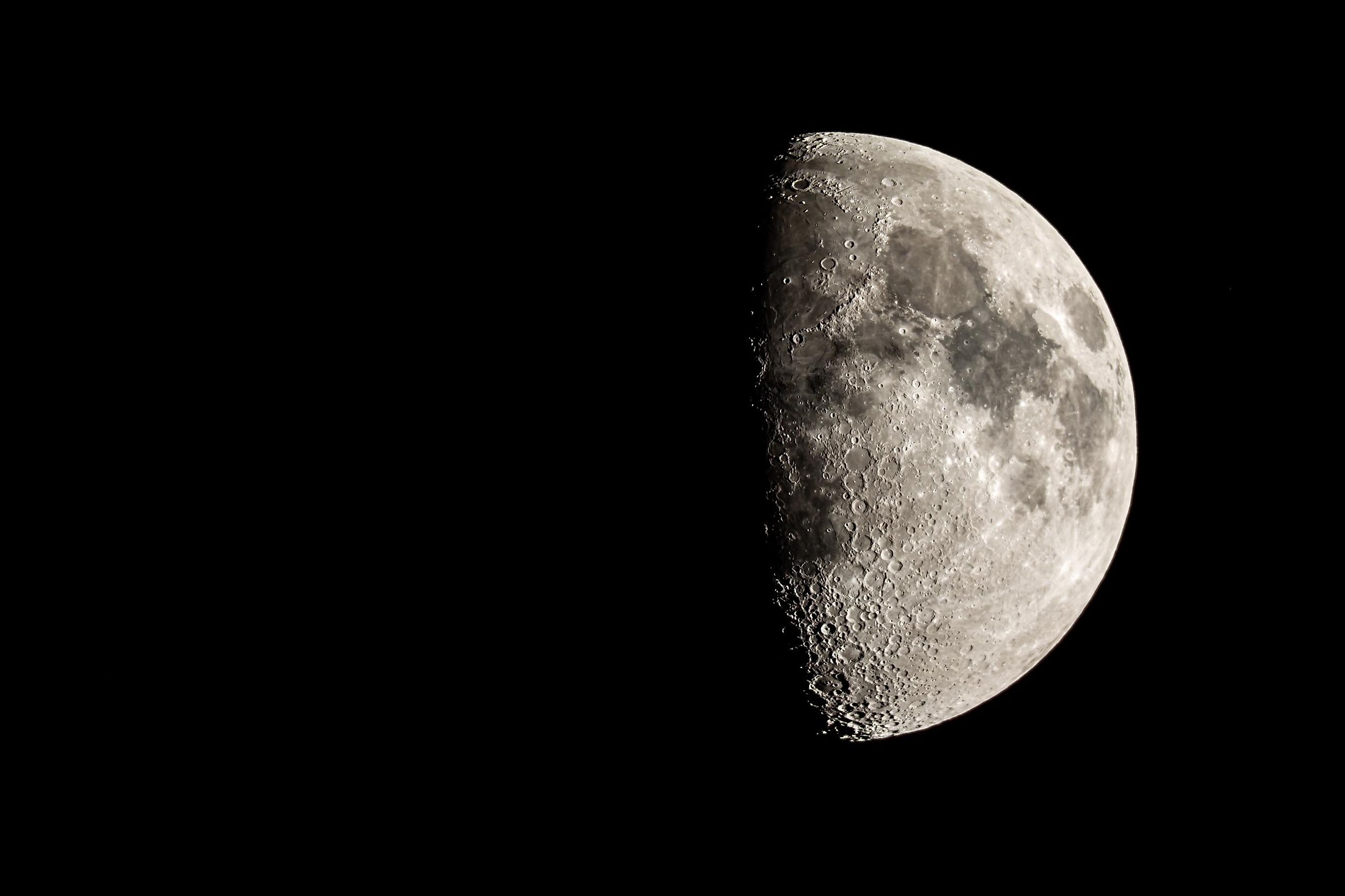
How far is the Moon from Earth? The canonical answer, used in celestial mechanics and lunar navigation, is a mean center-to-center distance of precisely 384,400 km (238,855 mi). Because the Moon follows an elliptical orbit, the Earth-Moon distance oscillates between perigee at roughly 363,300 km and apogee near 405,500 km every 27.3-day sidereal period.
Understanding this variable separation is essential for calculating spacecraft trajectories, predicting eclipses, modelling tides, and calibrating radar and laser-ranging experiments.
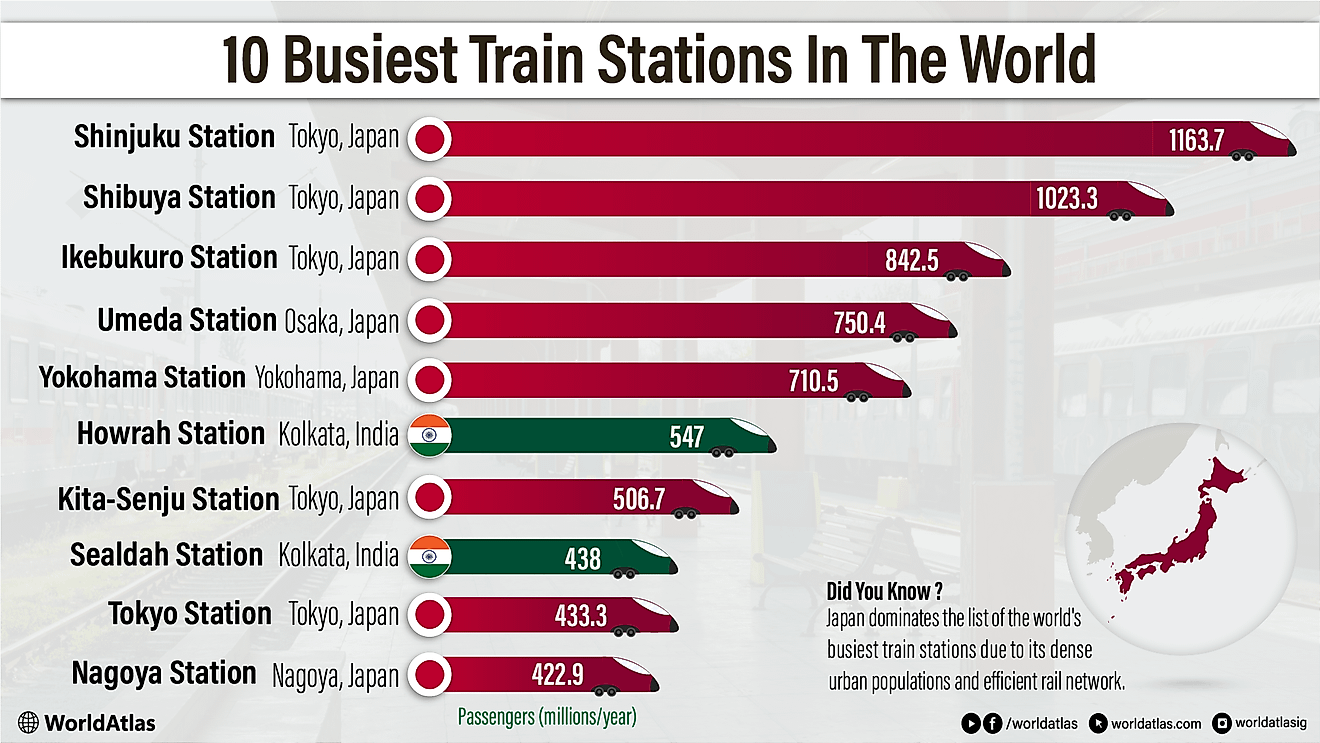
The Distance To The Moon
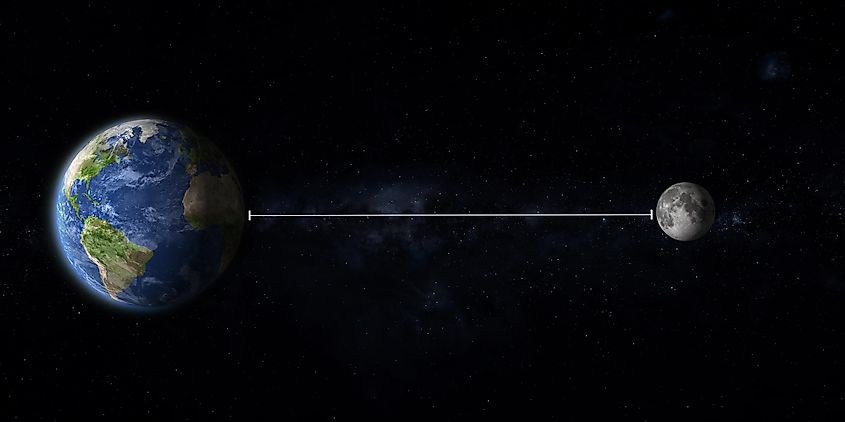

It may seem like a simple question with a single answer, yet the number varies depending on when you ask it. It may not look obvious, but the distance between the Earth and the moon changes over the course of the moon’s orbit. That’s because the moon doesn’t orbit the Earth in a perfect circle, but rather in an elliptical manner (think of it as slightly egg-shaped).
The moon has both a maximum and minimum distance from the Earth. During its furthest approach to the Earth, the moon is about 251,000 miles away. During its closest approach, the moon is around 226,000 miles away. Although the difference between these two numbers may not seem significant, it’s a difference of about four Earths. How the distance between the Earth and the moon changes may not appear too important, but it actually has a profound impact on our world and how we perceive our nearest celestial neighbor.
The Distance To The Moon And Its Impact On Earth
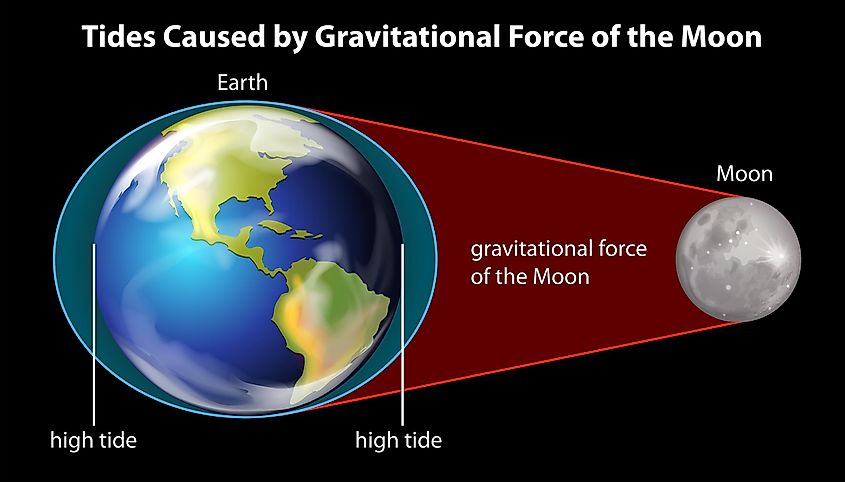
The primary way the moon’s distance affects our planet is through ocean tides. If you've ever been near a beach, you might have noticed how the shoreline's size varies with the water level. How does the ocean flow back and forth against the shore? As the Earth-moon distance fluctuates, the moon’s gravitational influence on Earth varies too. When the moon is farthest from Earth, its gravitational force is at its weakest, and at its closest, it exerts the strongest pull. Throughout its orbit, the moon gently tugs on the Earth, causing slight shifts. This gravitational effect is what drives the tides in and out along the shore.
Super Moons And Solar Eclipses

As expected, the moon’s size appears to change based on its distance from the Earth. Supermoons occur when a full moon is at its closest approach to our planet. Remarkably, during a supermoon, the moon looks 17% brighter and 30% larger compared to when it is at its farthest distance. Another notable phenomenon arises when a solar eclipse coincides with the moon’s farthest point. If the moon passes in front of the Sun while it is 251,000 miles away, it will not entirely cover the Sun; instead, a ring of light will be visible around the moon, resulting in what is known as a ring of fire solar eclipse. Although the question of how far the moon is from the Earth may seem straightforward, it is often the simplest inquiries that profoundly influence our understanding of the natural world.
Updated: 6/10/2025