Shasta Lake
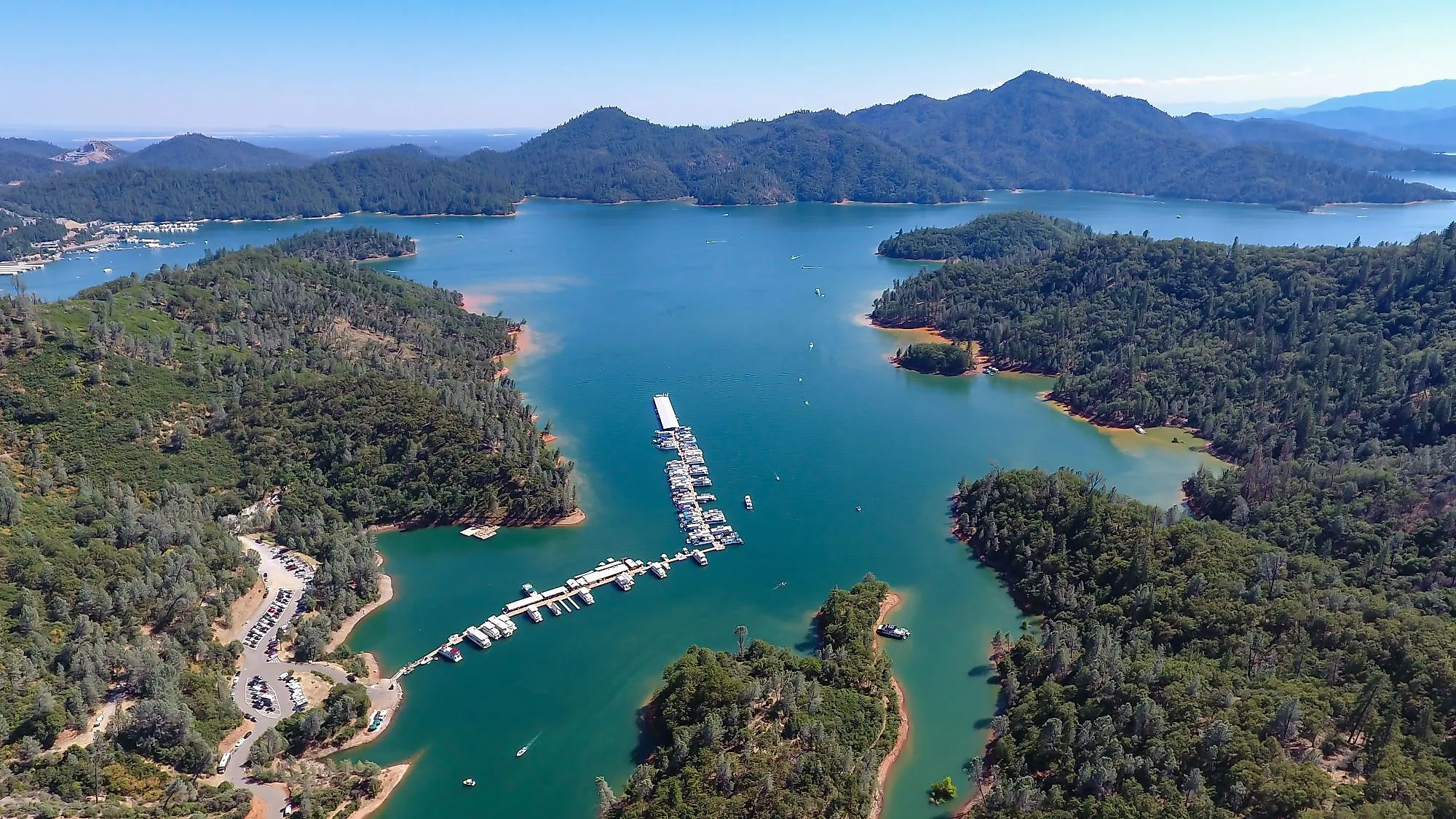
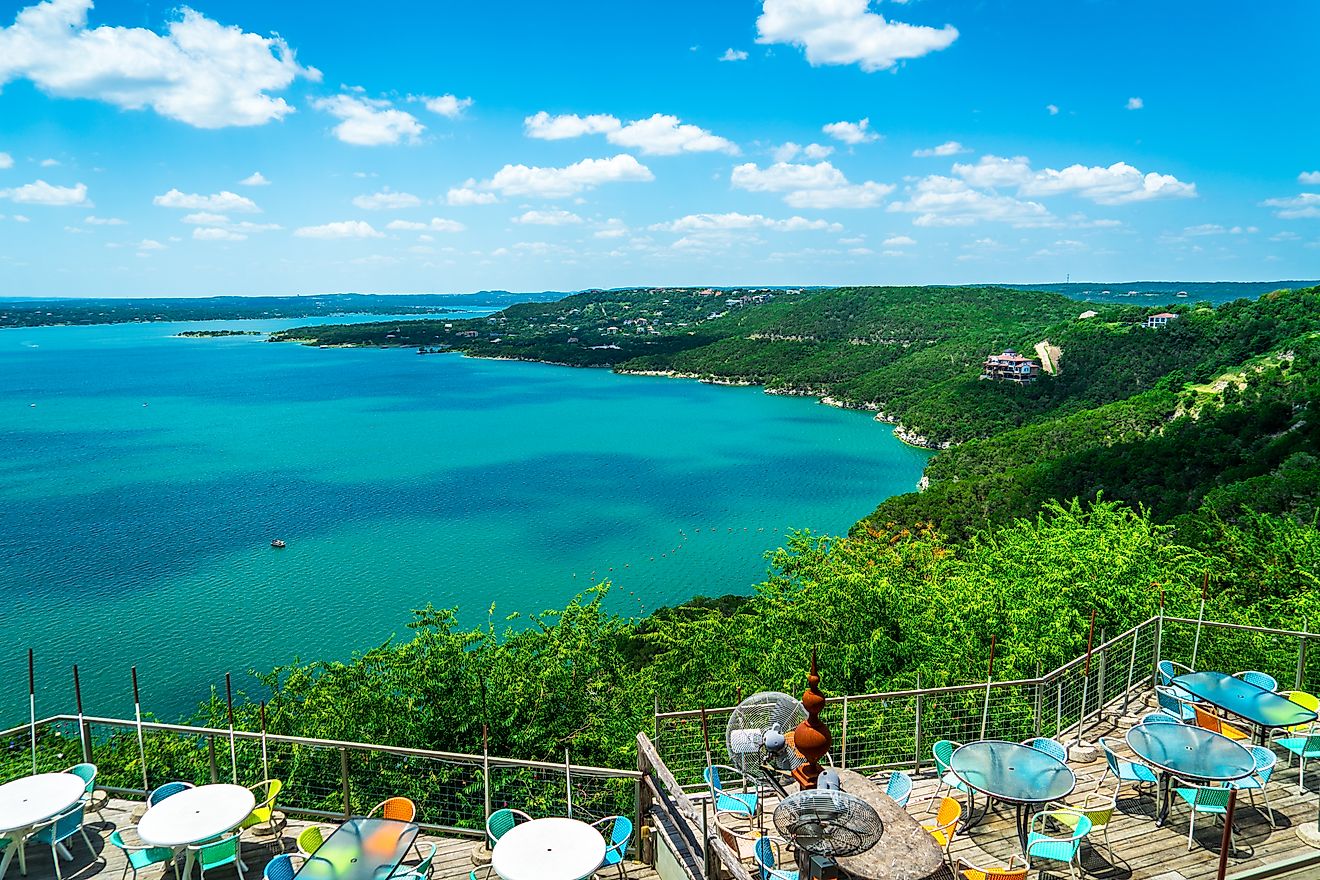
Shasta Lake is a large reservoir situated in the US state of California. This artificial lake has an area of 30,000 acres and a volume of 5.615 cubic kilometers, making it the state's largest reservoir. The lake is situated in Northern California, approximately two miles north of the city of Shasta Lake, ten miles north of the city of Redding, and 35 miles south of Mount Shasta. The Oregon border is approximately 95 miles north of the lake's northernmost arms. The city of Shasta Lake sits adjacent to Shasta Dam at Shasta Lake's southwestern point. The dam, at 602 feet tall, is the ninth- tallest concrete dam in the United States. Shasta Dam (originally Kennett Dam) was constructed between 1938 and 1945 and filled in 1948. Its construction and the subsequent creation of Shasta Lake flooded the gold rush-era town of Kennett and approximately 90% of the lands of the Winnemem Mintu indigenous people. Plans to raise the dam height further would flood dozens of sacred sites and destroy more salmon breeding grounds.
Geography Of Shasta Lake

When full, Shasta Lake has around 587km of shoreline with hundreds of bays and coves. It reaches a maximum depth of 158m. It sits at an altitude of 325m in a location where multiple rivers converge. The lake’s drainage basin covers an area of 26,300 square miles. The Sacramento, Pit, McCloud rivers and Squaw Creek provide the reservoir’s inflow sources. The reservoir comprises several inlets or arms, including the Sacramento River Arm, Pit River Arm, McCloud River Arm, Squaw Creek Arm, and Big Backbone Creek Inlet. Sacramento River Arm is the most historically significant and busiest of the waterways; the Oregon Trail lies underneath its waters. Impressive basalt rock formations can be seen near Gooseneck Cove. Grey limestone studded with fossils of prehistoric sea creatures can be seen above the McCloud Arm. Caverns created by water running through cracks for millennia lie within.
Ecology Of Shasta Lake

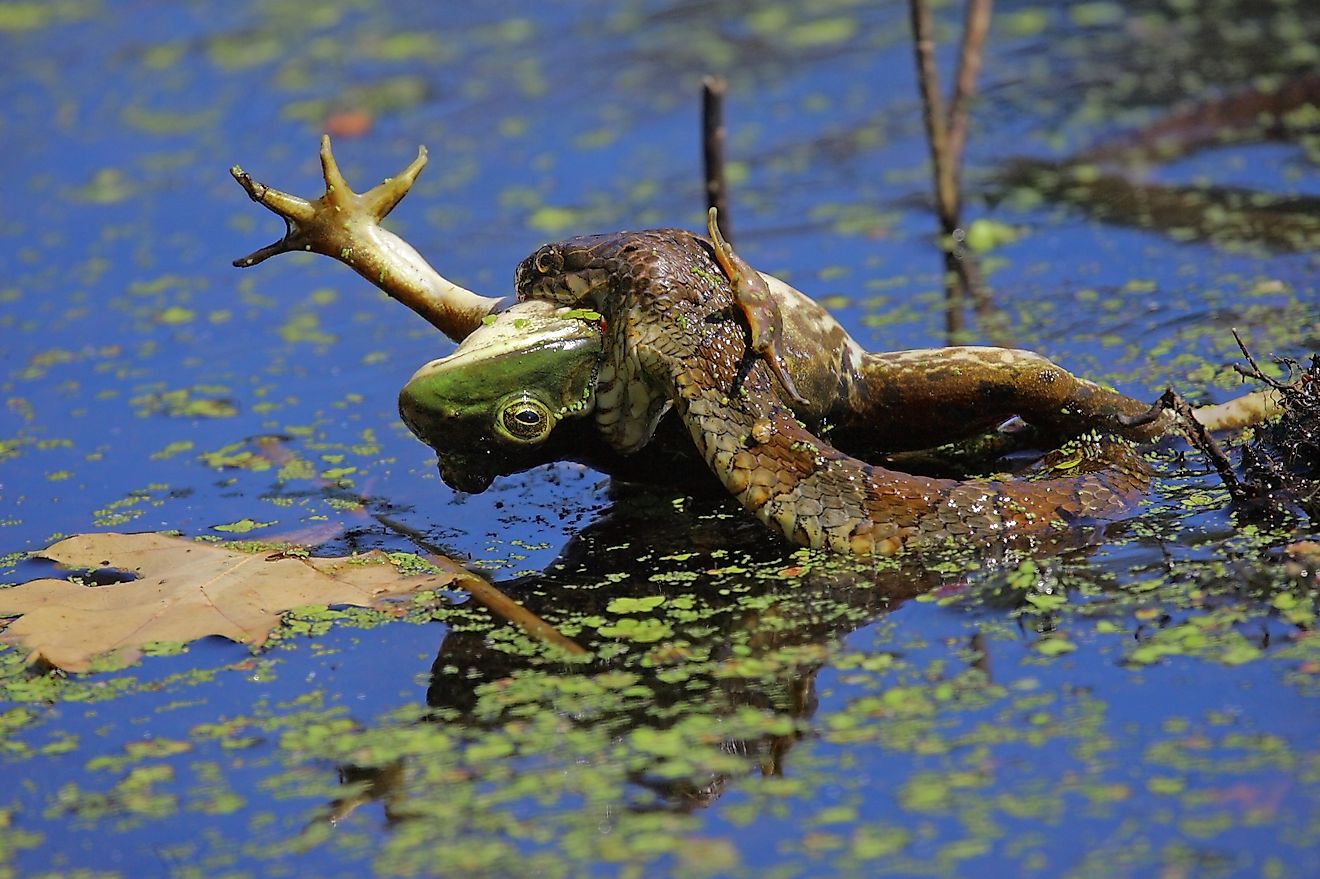
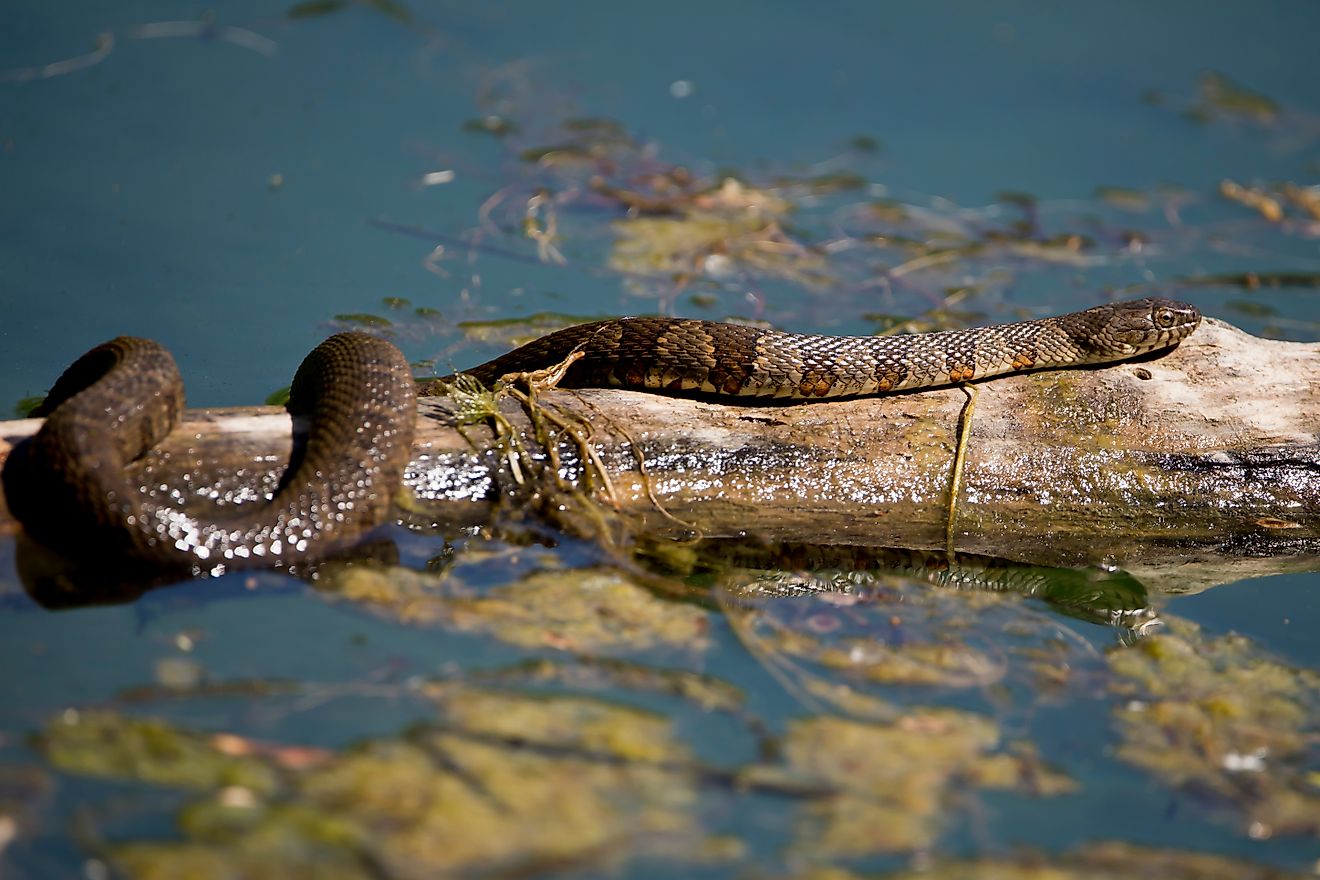
The shores of Shasta Lake are largely rugged and mountainous. They provide critical habitats for black bears, deer, elk, antelope, mountain lions, and bobcats. Otters can also be seen in lake waters. Some of the fish that are found in Shasta Lake include trout (eagle lake, brown, brook, and rainbow), salmon, smallmouth bass, crappie, sturgeon, and catfish. Hundreds of bird species also live or visit the area, including northern flicker, tundra swans, Virginia rails, and seven varieties of hummingbirds. Invasive New Zealand mud snails have also been found in Shasta Lake.
Economy Of Shasta Lake
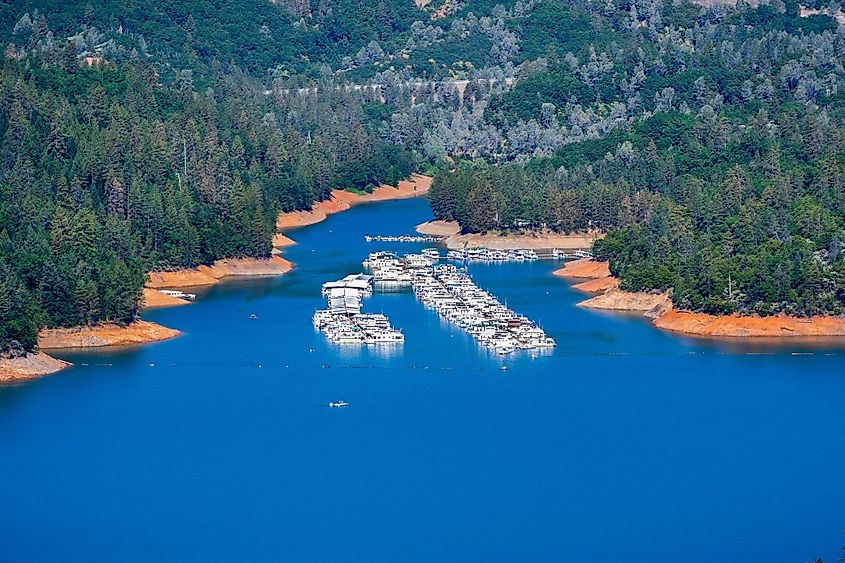

Shasta Lake is a popular recreation area with various water-based activities, including sailing, boating, and fishing. Snow sports can be carried out in the mountains and on trails surrounding the lake. Campgrounds, picnic sites, RV parks, marinas, and resort cabins are found along the lake’s shores. It can be divided into six distinct recreation areas; Lakehead, Salt Creek, Gilman Road, O’Brien, Jones Valley, and Shasta Dam, with Gilman Road and O’Brien being among the more rugged and remote. Multiple popular shoreline trails offer opportunities to explore the area, including Bailey Cove, Waters Gulch, and Clikapudi. The lake also functions as a water source for drought-susceptible Central Valley farms and cities. At its fullest—or full pool—Shasta Lake holds enough water for 23 million people for an entire year.