Kattegat Bay
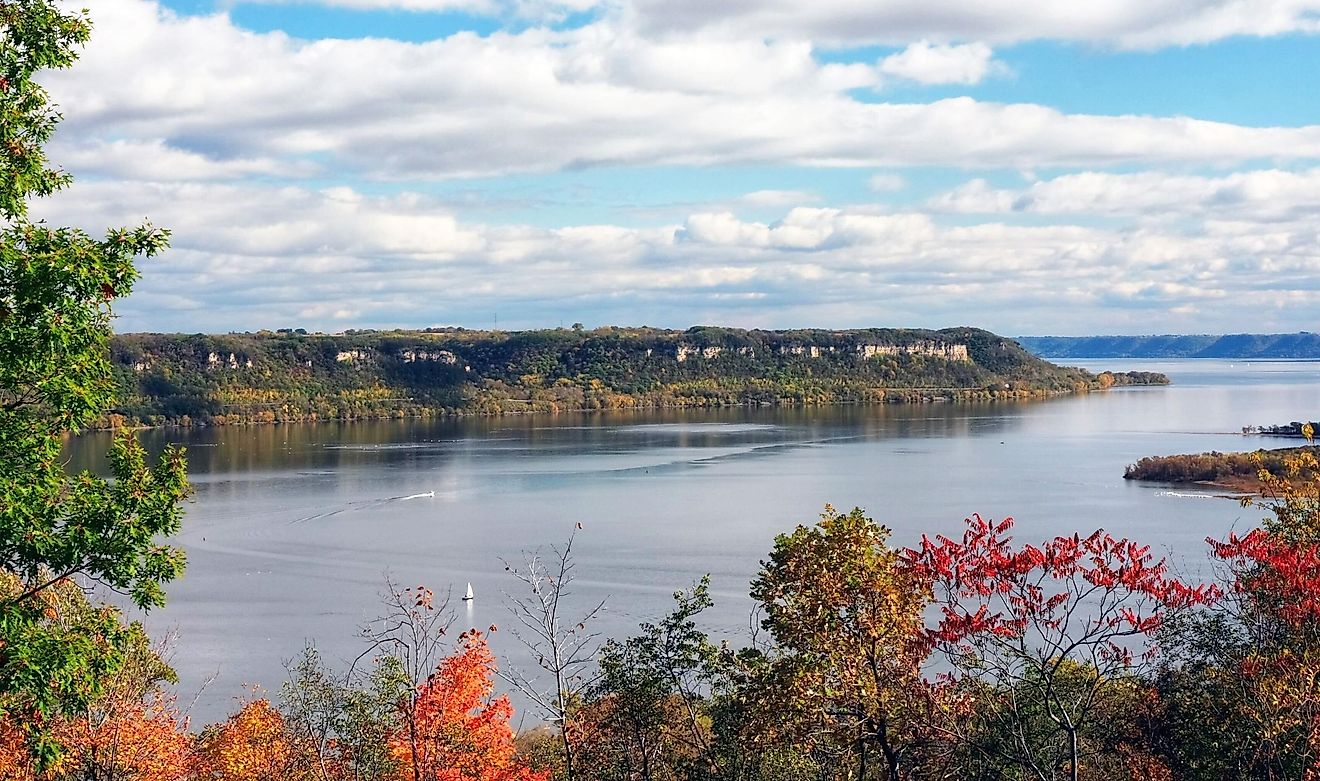
The Kattegat, or Kattegat Bay, is an intriguing body of water mirroring the sky between Denmark’s Jutlandic Peninsula and Sweden’s eastern coastline. The name “Kattegat” comes from the Dutch words “kat,” meaning cat, and “gat,” meaning hole or throat. The description of a “cat throat” or “cat hole” is incredibly apt, considering the narrow, bottleneck shape of the bay. The bay forms a bridge between the Baltic and North Seas and is not just a geographical beauty but an area known for its historical and cultural significance.
Location and Geographical Region
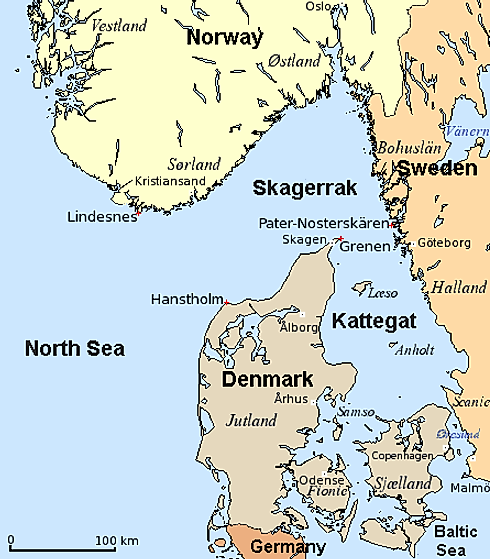
Kattegat is part of Northern Europe and covers an area of approximately 12,000 square miles. It plays a big role in the strait system, known as the Skagerrak-Kattegat area, connecting the Baltic Sea with the North Sea. The strait flows north-south and is immensely important for international shipping and trade. In prehistoric times, the Kattegat region experienced significant geological shifts, as evidenced by its Quaternary sedimentary history. The bay is still filled with sandbanks and reefs today, which once made it very challenging to navigate.
Climate Of Kattegat Bay
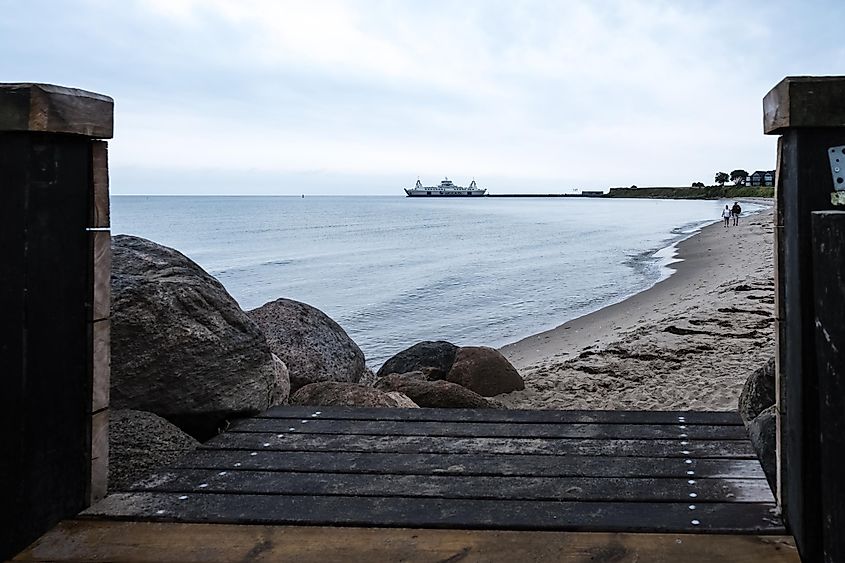

When looking at Kattegat on a map, you can see the bay sandwiched between the Baltic and North Seas. This unique position directly influences the climate in the bay. The local climate is also closely tied to the climatic conditions of the greater Baltic Sea region. Here, long, cold winters reign, while the summers are short and relatively warm.
Impact Of Climate Change
Recent scientific studies confirmed climate change affects both Kattegat and the broader Baltic region. One study in particular highlighted changes in the species composition of benthic fauna in the bay, which points to alterations in the local ecosystem. Moreover, the warming trend for the entire Baltic Sea basin is around 0.08°C. Along with rising water temperatures, ice coverage is decreasing while mean precipitation continues to increase over the northern regions.
Scientists, however, reiterated that climate change is not the only environmental stressor in Kattegat Bay. Ocean acidification and eutrophication also pose significant threats. Collectively, these factors put severe pressure on the marine ecosystem. Lastly, studies have also determined that extreme weather events may become the norm in Kattegat Bay, echoing similar trends observed worldwide. Storm surges in the bay come with the potential to devastate the natural ecosystem and human settlements in the area.
Marine Life In Kattegat Bay
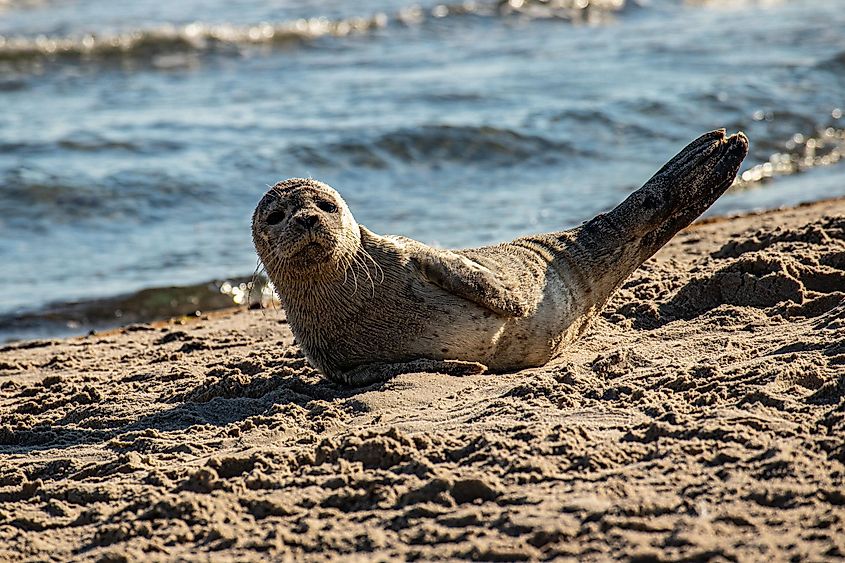

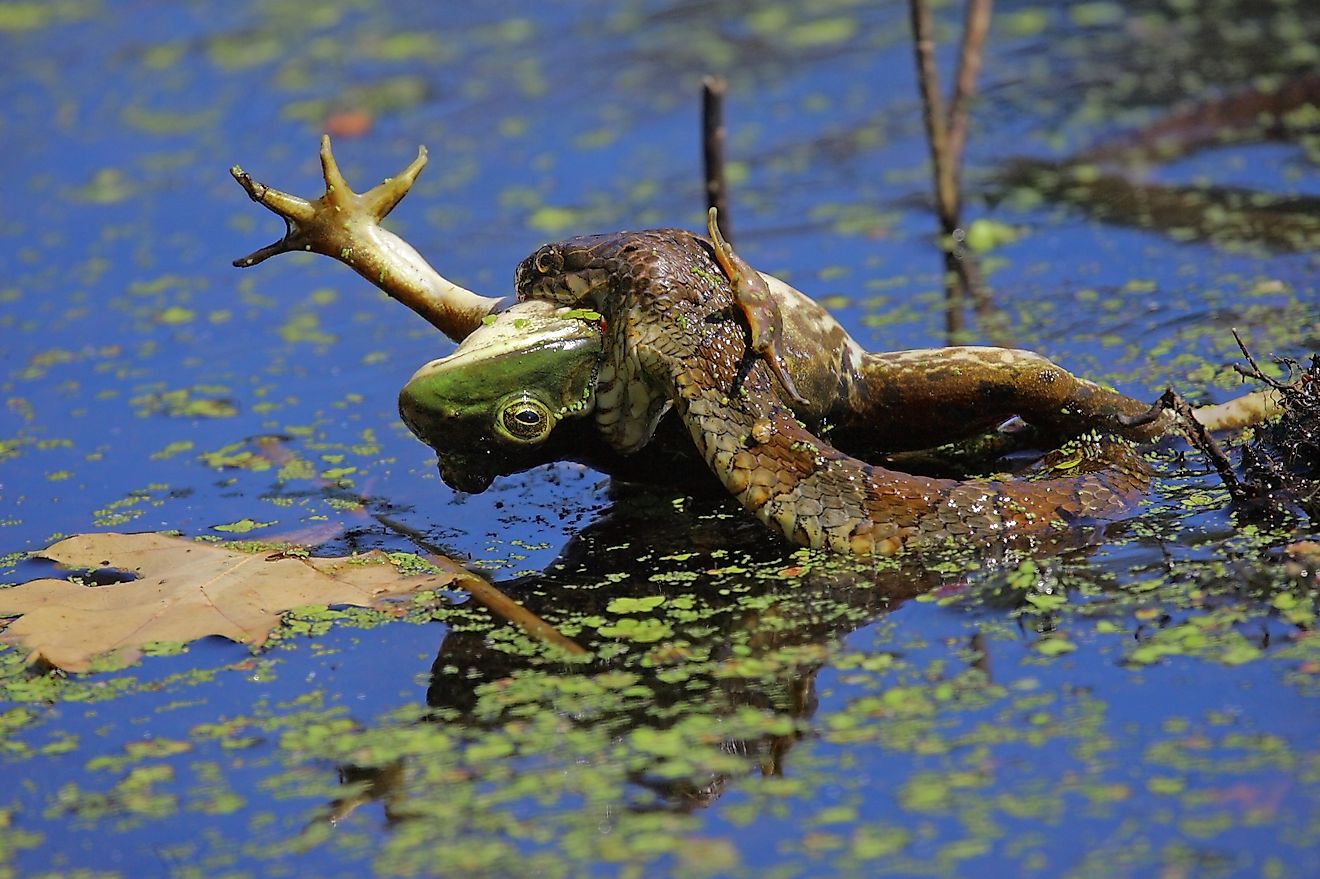
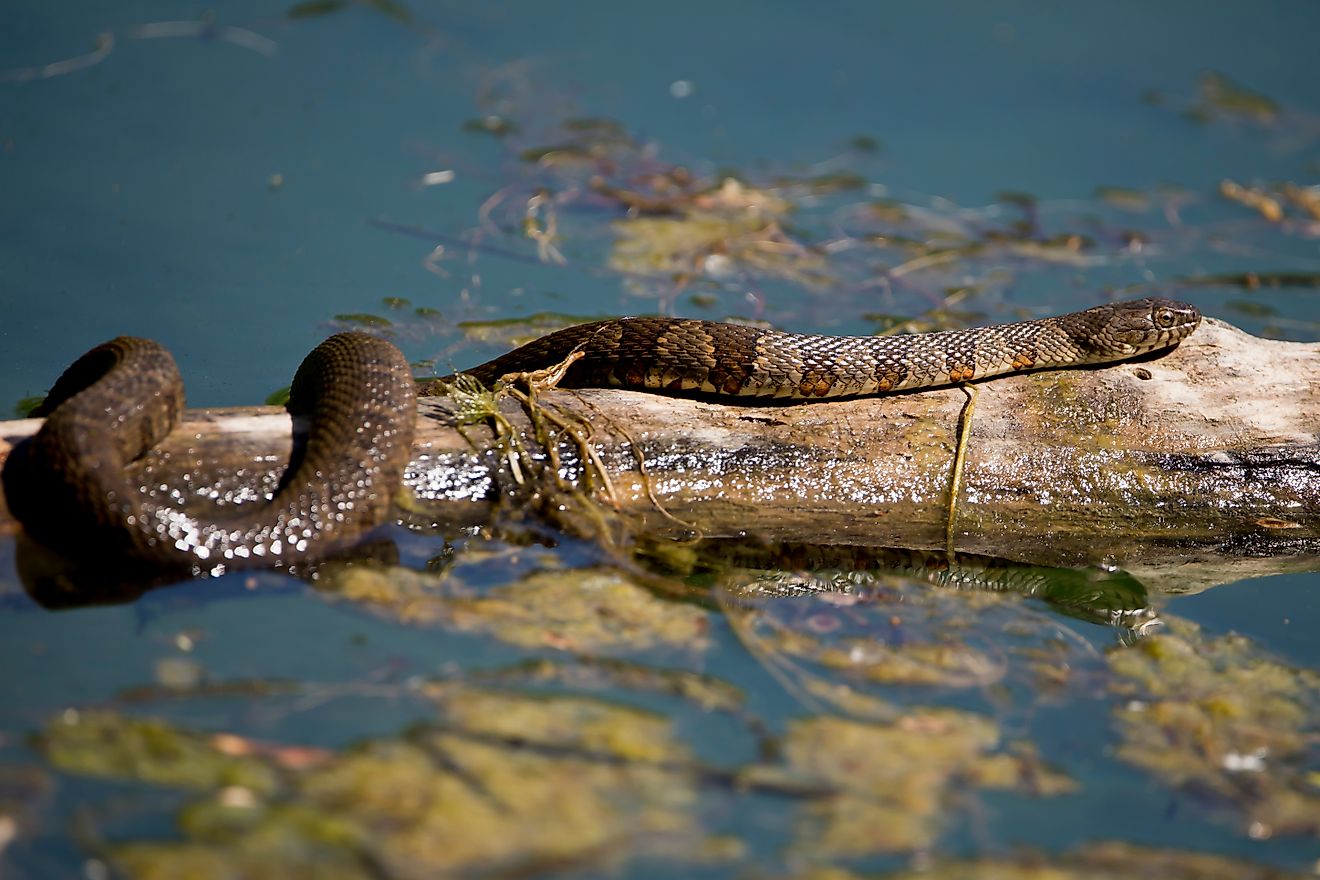
Kattegat is a habitat for herring, cod, and flatfish, amongst many other fish species. The strait is home to playful seals and lazy porpoises. Due to this wonderful biodiversity, Kattegat is the subject of ongoing studies aimed at understanding the impact of fishing on the environment. Marine biologists are also fascinated with the variety of sea currents in the bay and have started studying them periodically.
Kattegat Bay Islands
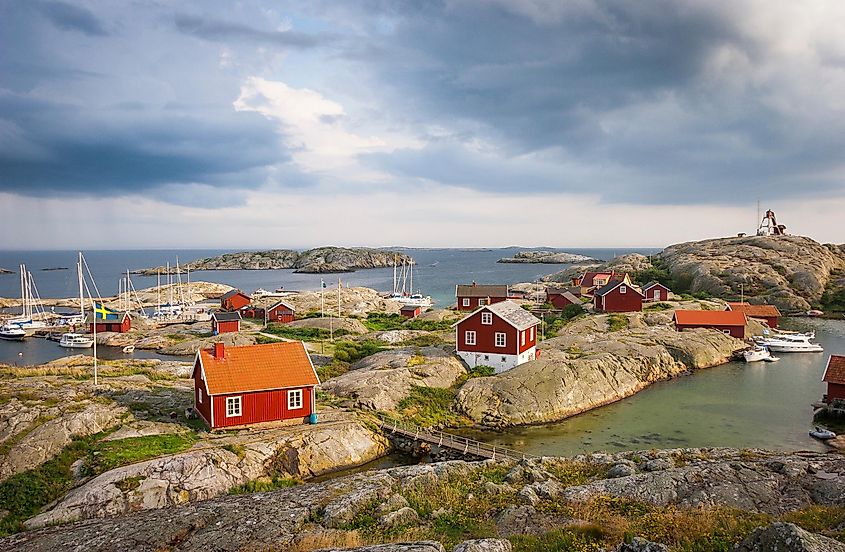

Several islands surround Kattegat Bay and have become a haven for marine life. These islands, which form part of the Danish Straits, are popular with tourists because of their scenic beauty and multiple outdoor activities. The islands include Samsø, Anholt, and Læsø, and they all offer a blend of fine sand beaches, emerald forests, and quaint villages.
Human Settlements In Kattegat Bay
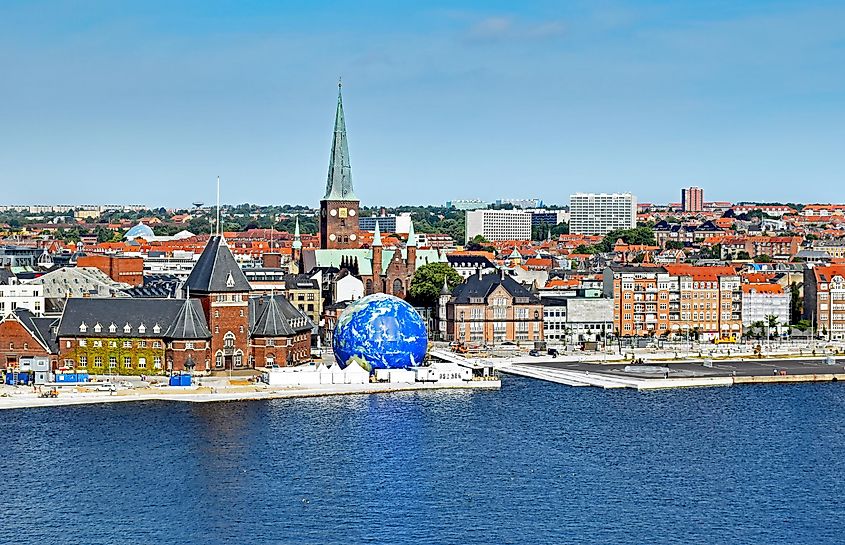

Speaking of villages, the coastal region surrounding the Kattegat has been inhabited for centuries. Major cities, including Gothenburg and Aarhus, hold tight to their ancient sea traditions while offering modern urban living. Smaller fishing villages dot the entire coastline, and their inhabitants continue to look to the Kattegat to sustain their livelihood. As a side note, Kattegat Bay is commonly associated with the fictional Kattegat city of the TV series Vikings. While this city is not a real location, the actual Kattegat does have a connection to Viking history.
History Of Kattegat Bay
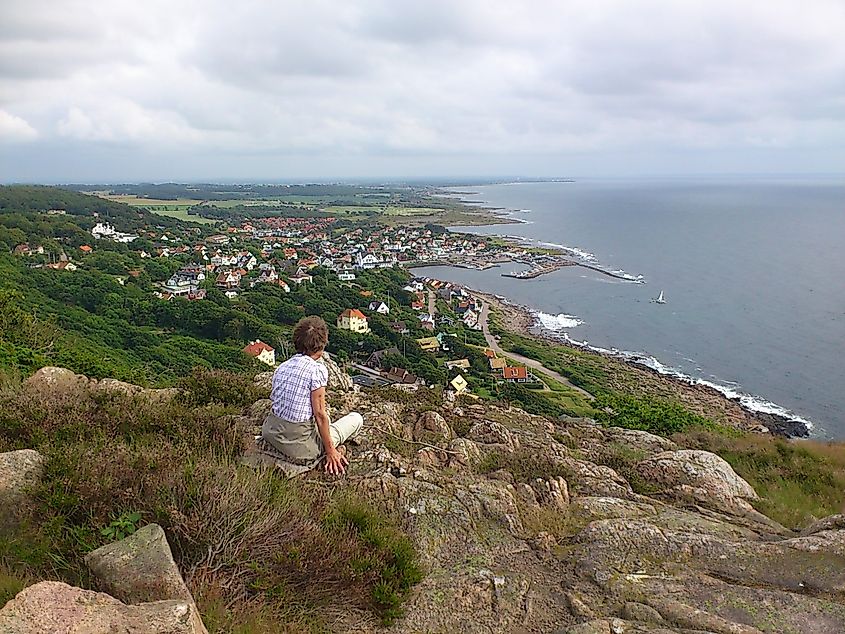

Kattegat Bay has long been a strategic area for Nordic countries, mainly Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It has seen the passage of numerous historic ships, including those of the Dutch, who were among the first to navigate its treacherous waters. The area was also a vital route for Vikings who traveled from their homelands to different parts of Europe.
Over the years, Kattegat has experienced the fallout of several conflicts and naval battles, but fortunately, it has remained a peaceful trade route. In modern times, Kattegat remains an integral marine area for fishing and shipping. Cooperation between the Nordic countries aims to manage the natural resources in the region. That said, strict regulations are in place to minimize the impact of overfishing on marine life.
Kattegat Bay is more than just part of a fictional tale or another body of water. It is a unique area in a beautiful part of the world that continues to fascinate and urge everyone to explore its depths and understand its global significance.