Yale University - Educational Institutions Around the World
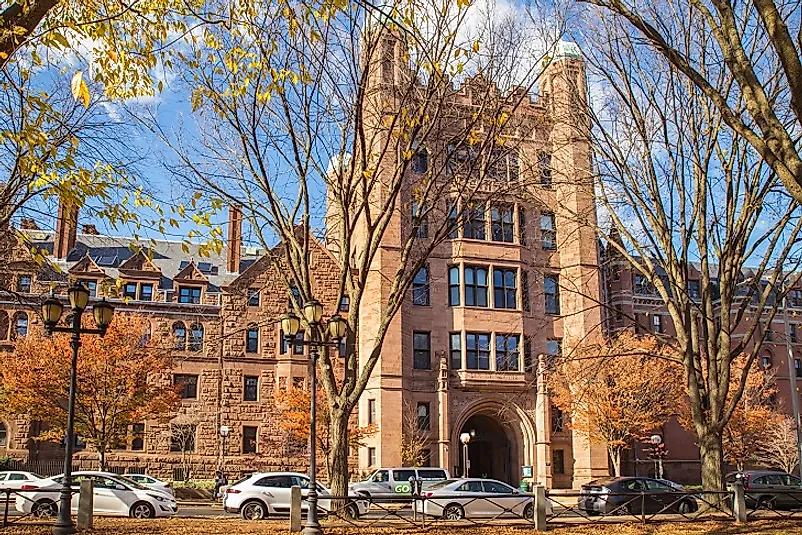

5. Founding
Founded in 1701 in Saybrook Colony as the Collegiate School, Yale University is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States. Later on, in 1716, the school was moved to New Haven, Connecticut. In 1718, it was renamed Yale College after Elihu Yale, who was an important patron for the school. Originally the university was founded to train up and coming clergymen in the New World, especially in the liberal arts, theology, and the sacred languages. As time moved on, Yale included an ever more expansive range of diverse disciplines and subjects.
4. History
As one of the pioneering universities in the Americas, the development of Yale University has been closely tied to social changes in the United States. In its earliest years, Yale University was deeply influenced by European thinking. Responding to the awakening of religious ideals and those from the Age of Enlightenment, early Presidents of Yale, namely Thomas Clap and Ezra Stiles, built Yale's curriculum around religious and scientific studies. The Classics and language arts were the most important components of Yale's curriculum. With the rise of Victorian culture in the 1800s, course offerings in the social sciences were greatly expanded throughout the 19th Century. Then, in the 20th Century, natural sciences, applied sciences, medicine, and American historical studies became integral parts of the university curriculum, which continues to evolve into the present day.
3. Structure
Yale University has six faculties. Namely, these are the faculties of Biological Sciences, Engineering, Health and Medicine, Humanities, Physical Sciences, and Social Sciences. The university also serves as a home to 13 schools. These are Yale College, the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, the School of Architecture, the School of Art, Yale Divinity School, the School of Drama, the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, the School of Forestry and Environmental Studies, Yale Law School, the School of Management, Yale College of Medicine, the School of Music, and the School of Nursing, as well as the School of Public Health. It also has more than 30 research institutes and more than 20 libraries, with many of their collections being open to the general public.
2. Rankings
Yale is considered to be one of the best universities both within the United States and around the world. It has consistently been ranked by Times Higher Education, QS, and Academic Ranking of World Universities as in their top 20. It is ranked by the US News and World Report as the third best university in the country. Yale Law School, Yale Medical School, Yale Department of English and Comparative Literature, as well as the Yale Philosophy Department are each among the top across the globe of their respective types. In the 1990s, Yale was the hotbed of the New Criticism Movement and many world renowned philosophers. These included Paul de Man, and Jacques Derrida taught at Yale as well. Yale is highly selective, with an acceptance rate of only 6.4%.
1. Alumni
As one of the best universities across the world, over the years Yale University has cultivated and produced many famous and accomplished alumni. Five US presidents graduated from Yale, including William Howard Taft, Gerald Ford, George H.W. Bush, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush. In fact, that total is only surpassed by Harvard's 6. Many famous actors, including Meryl Streep, Edward Norton, Oliver Stone, and Jodie Foster are also Yale alumni. Many influential academics and intellectuals also attended Yale, including philosopher Judith Butler and literary critic Harold Bloom. Yale also has produced 52 Nobel Prize Winners across such varied realms as Economics, Physics, and Chemistry.