Lake Retba
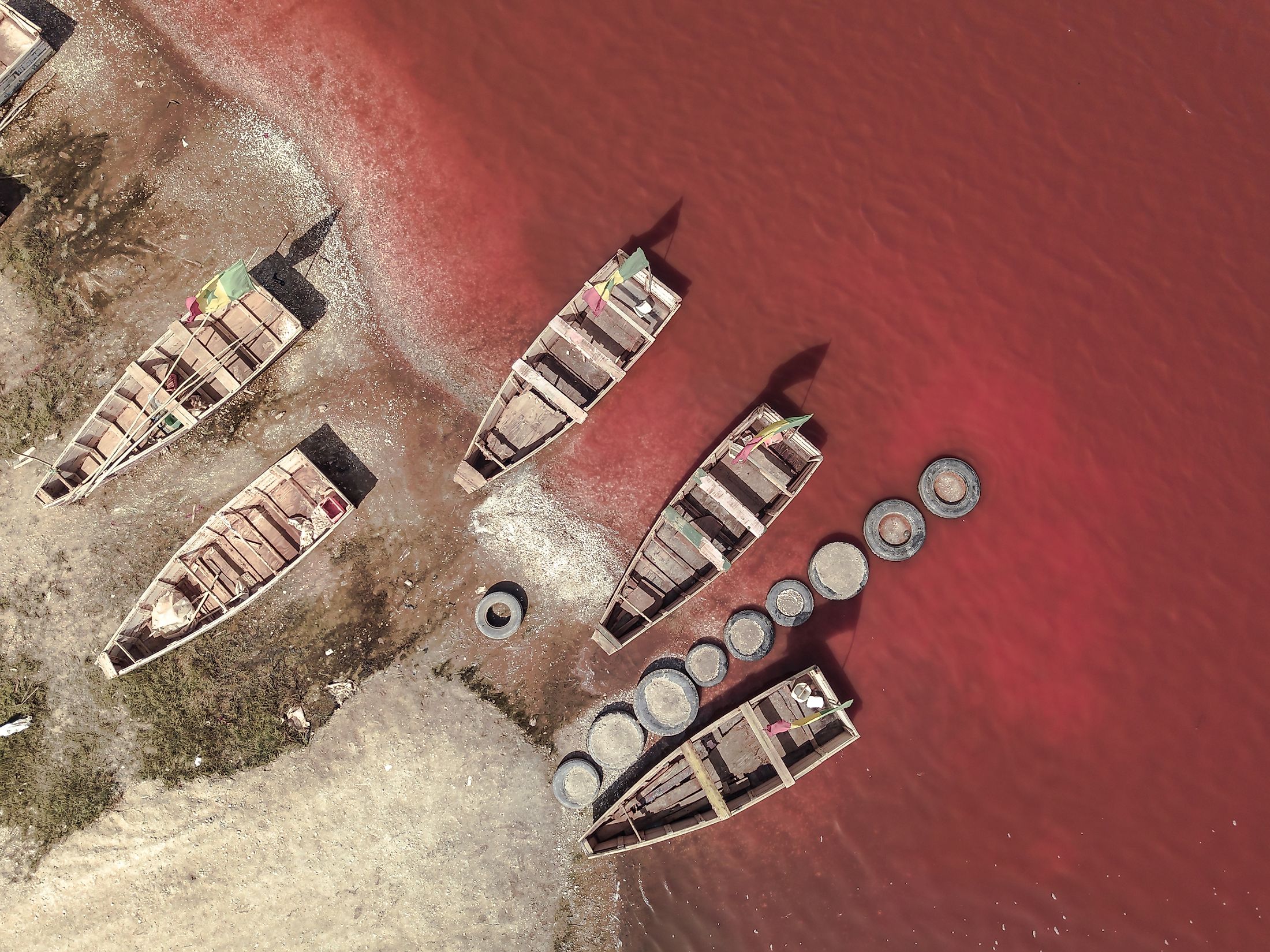
Lake Retba, also known as Lac Rose, is a pink lake in West Africa located on the edge of Cap Vert Peninsula in Senegal and separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a narrow dune. It is one of the world’s saltiest lakes, with a saline level of approximately 40%. The lake’s distinct pink color is caused by an algae known as Dunaliella salina. Very few organisms live in the lake. The water body is used for salt production and as a tourist attraction site. The salt collected from it is used to preserve fish and also exported to neighboring countries.
About Lake Retba
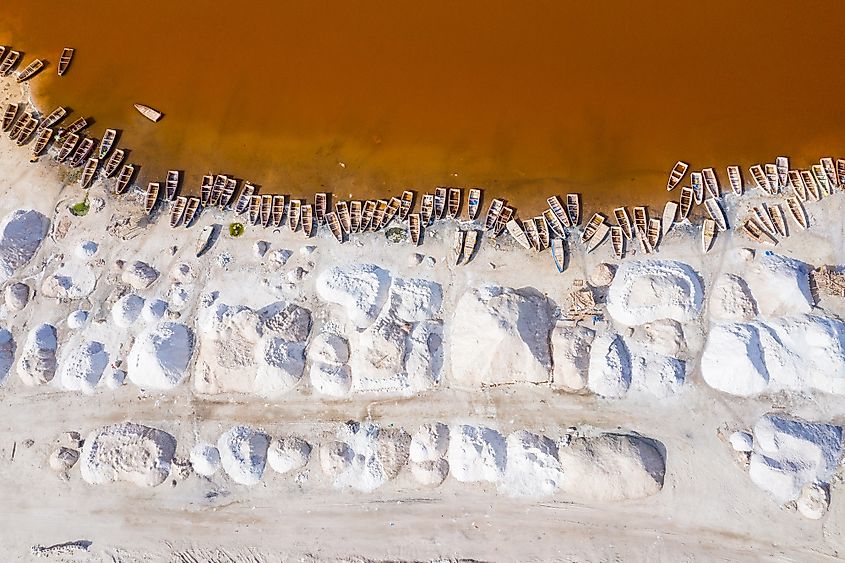

Lake Retba is located in the Dakar Region, Senegal’s most westerly region, in the department of Rufisque. It is the easternmost lake of the three water bodies on the Cap Vert Peninsula. Lake Retba, locally known as Lac Rosa, is a small lake covering only 3 square kilometers. It is also a shallow lake, with a maximum depth of 3 meters. The sandbanks surrounding the lake contain samphire bushes that can tolerate the lake’s high salt content. There are no major towns along the shores of Lake Retba, with Dakar, the country’s capital, located 30 kilometers away.
The Pink Color Of Lake Retba
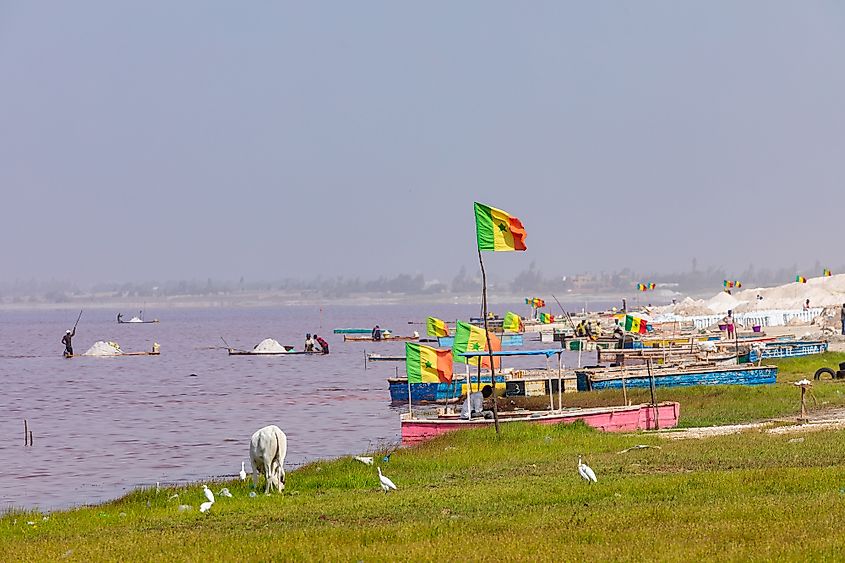

Lac Rosa is famous for its pink appearance, sandy dunes, and white beaches. However, the lake does not retain the pink color throughout the year like Lake Hillier in Australia. The watercolor constantly changes, with the pink color more pronounced during the dry season (between November and June). During the wet season, the rainwater dilutes the lake’s salinity and somehow causes the pink color to fade away but not completely. The pink color is caused by Dunaliella salina algae that can tolerate the high salt content in the lake. The algae produce red pigments that absorb sunlight, giving Retba a striking pink color.
Salinity Of Lake Retba
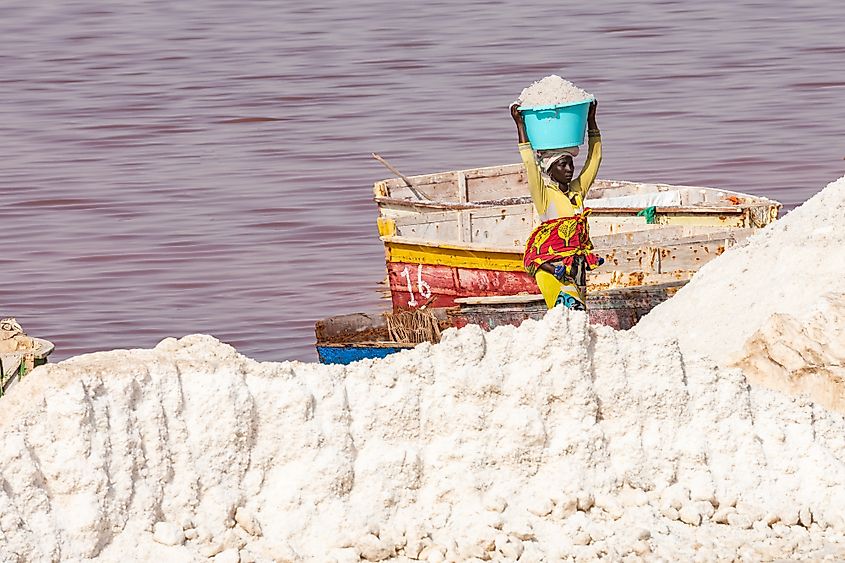

Lake Retba was a freshwater lake until the 1980s when an extended drought period changed the water composition. Today, Lac Rosa is the world’s second saltiest water body after the Gaet’ale Pond in Ethiopia, with its salt content rivaling that of the Dead Sea. The lake’s salt content reaches 40%, making it impossible for most organisms to survive in it. The high salinity is caused by the seawater inflow and the high evaporation rate. Thus, Lake Retba supports the salt industry in the Dakar Region, with some 3,000 people working as salt collectors in the lake. The salt collection is risky and labor-intensive work. The workers cover their bodies with shea butter and dig through the sand with shovels. The lake produces up to 34 million kilograms of salt annually.

Potential World Heritage Site
Lake Retba is one of Senegal’s most popular tourist destinations and was the finish point of the Dakar Rally before it was relocated to South America. The lake was included as one of the candidates for designation as a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its fame and natural significance. However, the lake has been on the waiting list since 2005.